Characterization and Visible Light-driven Photocatalytic Activity of SnS2/BiVO4 Nanocomposites Prepared by Sonochemical-based Process
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48048/siam.2024.67001Abstract
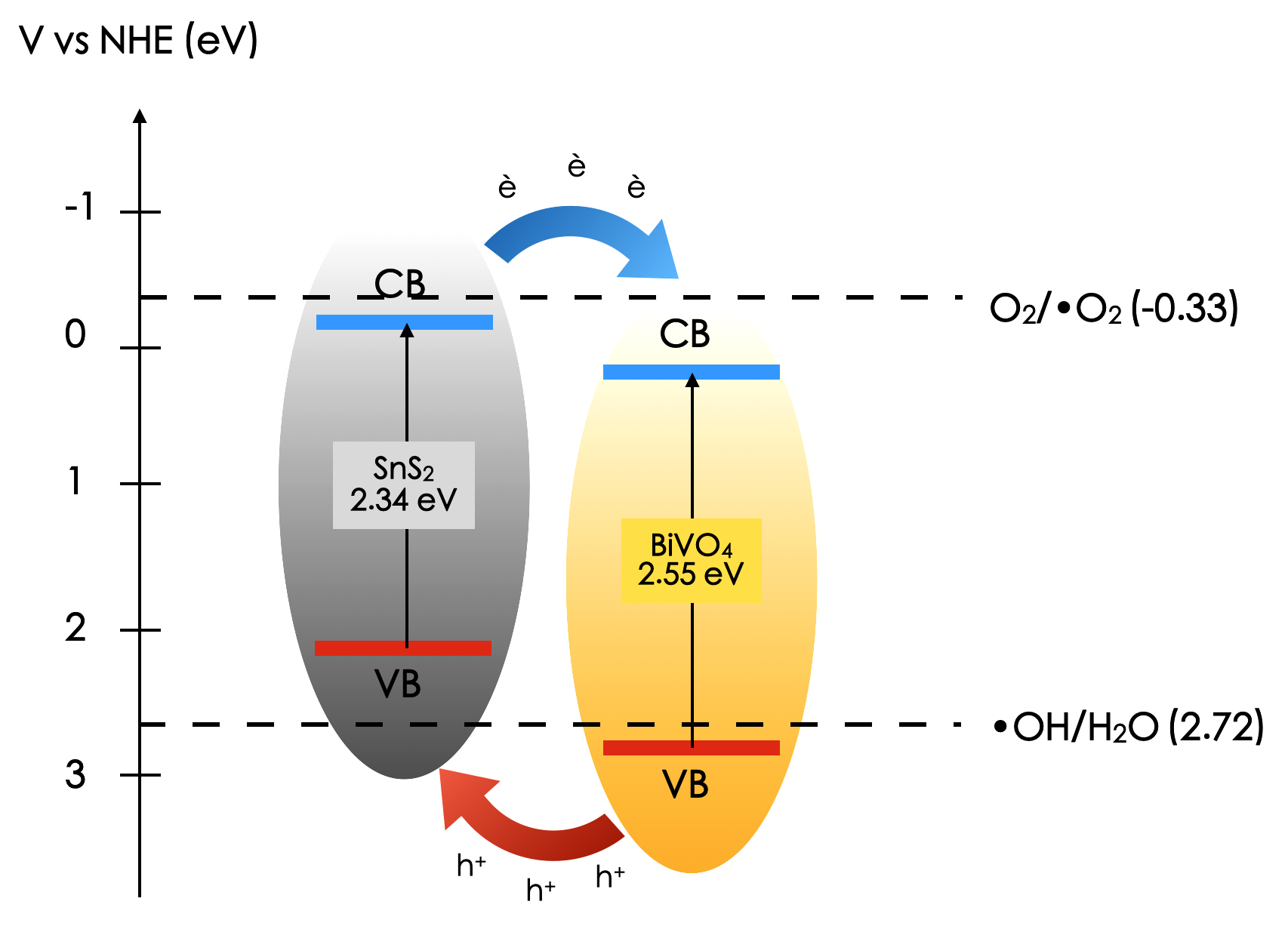
Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is a good candidate photocatalyst material with good activity under visible light exposure. The photodecomposition performance of BiVO4 could be enhanced by combining it with compatible tin sulfide (SnS2). In this work, the synthesis of SnS2/BiVO4 nanocomposite was carried out by sonochemical process at room temperature with varying concentration ratios of SnS2:BiVO4 (0.05:1, 0.10:1, 0.15:1, 0.50:1 and 1:1). The crystallinity and morphological features of as-synthesized powders demonstrate the majority of BiVO4 monoclinic phase accompanying minority of SnS2 rhombohedral phase. FE-SEM micrograph shows the irregular shape with various particle sizes. The optical band gap of the composite inquired by Kubellka-Munk calculation is about 2.6 eV. The photocatalytic performance of as-synthesized nanocomposite was evaluated by means of decomposition of organic dye under visible light irradiation. The 0.05:1 ratio of the SnS2/BiVO4 sample exhibits superior photocatalytic activity with 60% decomposition of Rhodamine-B organic dye within 120 minutes.
Keywords: Bismuth vanadate, Tin sulfide, Nanocomposite, Photocatalyst material