Ion Balance Measuring and Recording System for Air Ionizers
doi: 10.14456/mijet.2021.6
Keywords:
Electrostatic Sensor, Ion Balance, Charged Plate MonitorAbstract
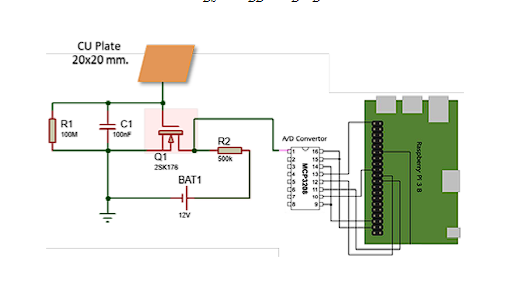
Most electronic manufacturing processes require the control of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) for preventing products from damages. Air ionizers are one of the most popular devices used for controlling ESD due to their considerable cost and ease in using. However, all recent air ionizers could not measure ESD by real-time, as well as, could not automatically send measured values to the database wirelessly. Most industrial factories therefore utilize human to measure the ESD regularly as specified. This would not only lead to the lake of continuously control of ESD, but also disturb the manufacturing process and risk for high error measurement. This research presents an automatic, balanced ionizing measurement system for an air ionizer with wireless data sensing. The system consists of an analog ESD sensor, a microcontroller and a charge discharging sensor, that converts analog ESD signals into balanced ionizing values with sensor values with the decision coefficient (R2) equal to 0.944 The experimental results showed that the measured balanced ionizing values obtained from the proposed system provided low error in value between 3.067 volts - 6.957 volts in compared to the ion balance at 0 volts. The measured values could be converted into voltage in the range between -35 and +35 volts.
References
[2] Kittikhun Thongpull, “Development of a wireless electrostatic discharge (ESD) events locator system for hard disk assembly line,” Prince of Songkla University, 2010.
[3] Albert Z. H. Wang, 0n-chip ESD protection for integrated circuits. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002.
[4] N. M. Takahiro Yoshida, “A Study on Discharge Current and Radiation Noise of ESD from Charged Metal and Charged Human Body,” IEEE Ind. Appl. Soc. Annu. Meet., 2008.
[5] K. Yan, R. Gaertner, and S. Lim, “An Effective ESD Protection System in the Back End ( BE ) Semiconductor Manufacturing Facility,” New York. 2001.
[6] Pijag_Permprasert, “Study of methods for controlling Electrostatic discharge in industry,” Khon Kaen University, 2011.
[7] Sayan Plong-ngooluam, “A Development of Partial Surfaces Ion Balance Analyzer,” Prince of Songkla University, 2017.
[8] S. Yoshioka, T. Terashige, T. Ikehata, and K. Okano, “Comparison of ion balance sensors for static control systems of air ionizer,” IEEJ Trans. Sensors Micromachines, vol. 135, no. 3, pp. 108–111, 2015.
[9] I. EOS/ESD Association, “ESD Association.” [Online].Available: https://www.esda.org/standards/.
[10] E. Association, ANSI ESD STM 3.1-2015: EOS/ESD Association Standard for Protection of Electronic Discharge, Susceptible Items-Ionization. 7900 Turin Road, Bldg. 3, Rome, NY, 2015.
[11] I. E. Commission, IEC 61340-4-7: ELECTROSTATICS Part 4-7: Standard test methods for specific applications–Ionization. 2010
[12]Panich Intra, “Aerosol Charging Technology by Electric Field Theory and Innovation”. Rajamangala University of Technology Lanna , 2017.
[13] A. Ohsawa, “Computer Simulations of Insulator Charge Neutralisations with a Corona Ioniser-Influence of Initial Surface Charge Distribution,” J. Electrost., vol. 71, pp. 287–293, 2013.
[14] A. Ohsawa, “Efficient Charge Neutralization with an AC Corona Ionizer,” J. Electrost., vol. 66, pp. 598–606, 2007.
[15] A. Ohsawa, “Modeling of Charge Neutralization by Ionizer,” J. Electrost., vol. 63, pp. 767–773, 2005.
[16] M. Sakuyama, M. Takeuchi, T. Terashige, S. Yoshioka, and K. Okano, “Development of ion balance sensor by using MOSFET,” Electr. Overstress/Electrostatic Disch. Symp. Proc., no. I, pp. 235–239, 2006.
[17] M. N. O. Alexander, C. K., & Sadiku, Fundamentals of electric circuits (2nd ed.). Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2004.
[18] Nakhon Pathom Rajabhat University, “MOSFET,” 2012. [Online]. Available: http://pws.npru.ac.th/thawatchait. [Accessed: 09-Nov-2019].
[19] D. A. Neamen, Semiconductor Physics and Devices Basic Principles. Elizabeth A. Jones, 2003.
[20] S. Yoshioka, T. Terashige, T. Ikehata, and K. Okano, “Comparison of ion balance sensors for static control systems of air ionizer,” IEEJ Trans. Sensors Micromachines, vol. 135, no. 3, pp. 108–111, 2015.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.