Automatic Scratch Detector for Magnetic Disk
doi: 10.14456/mijet.2021.13
Keywords:
light reflection, scratch detection, magnetic diskAbstract
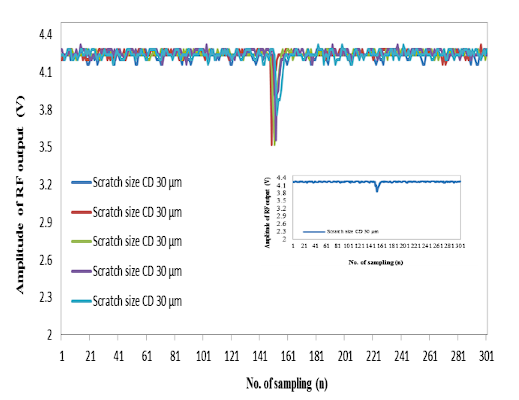
The development of an automatic scratch detector for a magnetic disk aims to detect scratches on magnetic disk surface at the micrometer level. In hard disk manufacturing industry, it is vital to focus on hard disk quality checking. [Every piece is scrutinized, especially a magnetic disk inspected for scratches. They are occurred during industrial manufacturing processes and by read/write head devices. It may affect data storage performance of magnetic disk.] In this study, scratch detector is operated by reflective method, using the principle of laser reflection (Laser). The beam is sent to disk surface and reflected to photo diode, which is a light receiver. It is found that when the intensity of laser beam received by photo diode reflect on scratched and non-scratched area differently. Light intensity is decreased when it reflects on scratched area. The signal amplitude is between 2.1 - 4.3 volts. It is indicated that the magnetic disk surface is scratched. Finally, it revealed that width of scratch magnetic disk measured by Stereo Microscope (SM) was 30 micrometers in a micrometer scale.
References
[2] J. WINDELN, C., BRAM, H. L., ECKES, D., HAMMEL, J., HUTH, J., MARIEN, et al. Applied surface analysis in magnetic storage technology. Applied Surface Science, 2001, vol. 179, p. 167-180.
[3] POLSAWAT, A., TIPCHAROEN, W., SIRITARATIWAT, A. Utilization of CD and DVD Pick-Up Heads for Scratch Inspection of Magnetic Disk in Dynamic State Using Microcontroller. Appl. Sc., 2020, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 1-11.
[4] FURUKAWA, M., XU, J., SHIMIZU, Y., KATO, Y. Scratch-induced demagnetization of perpendicular magnetic disk. IEEE Trans. Magn, 2008, vol. 44, p. 3633–3366.
[5] SAETUNG, S., WARDKEIN, P., KOSEEYAPORN, J. The Media Surface Image Construction with Technique of Reflecting of Laser Beam. In Proceedings of the 26th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC 2011). Gyeongju (South Korea). 2011, (p.1070-1073).
[6] ZAMMANIAN, A., HARDIMAN, C. Electromagnetic Radiation and Human Health: A Review of Sources and Effects. High Frequency Electronics, 2005, vol. 25, p. 16-26.
[7] POLSAWAT, A., KIRAVITTAYA, S., KHUNKITTI, P., SIRITARATIWAT, A. Scratch and Surface Roughness Detection on Magnetic Disk by using Red and Blue Light Reflection Approach. IJERT. 2020, vol. 9, no. 8, p. 567-576.
[8] HWU, E. T., ANJA, B. Hacking CD/DVD/Blu-ray for Biosensing. ACS Sens. 2018, vol. 3, no.7, p. 1222–1232.
[9] ZHU, S., ZHOU, W. and SONG, Y. Detecting oscillation amplitude and defects of hard disk rotating in high speed by laser Doppler technique. Measurement, 2012, vol. 45, no. 1, p. 74-78.
[10] NAGATOMI, K., OGATA, M., ASANO, K., TSUCHIYA, Y., BESSHO, Y. A Smart Model HD DVD/DVD/CD Compatible Pickup Head. IEEE Trans on Consumer Electronics, 2006, vol. 52, no. 1, p. 150-154.
[11] PETER, F., ODGAARD., STOUSTRUP, J., ANDERSEN, P., VIDEL, E. Accommodation of Repetitive Sensor Faults—Applied to Surface Faults on Compact Discs. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2008, vol. 16, no. 2.
[12] SIAUDINYTE, L., JUSKA, V., DUMBRAVA, V., PAGODINAS, D., BRUCAS, D., RYBOKAS, M., THOMAS, K., GRATTAN,V., KRIKSTAPONIS, B. Measurement and determination of encoder disc surface parameters in x-z planes using a conventional optical disc reading head. Measurement. 2019, vol. 152, p. 1–7.
[13] GULARI, M. N., TRIPATHI, A., REZAIE, M.G., CHRONIS, N. An Optofluidic Lens Array Microchip for High Resolution Stereo Microscopy. Micromachines,2014, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 607-621.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Engineering Access

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








