Implementation of a Gamified E-learning Platform Focusing on Traffic Knowledge and Skills among Vietnamese Adolescents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56261/built.v21.248560Keywords:
adolescent riders, e-learning platform, gamification, traffic knowledge , skillsAbstract
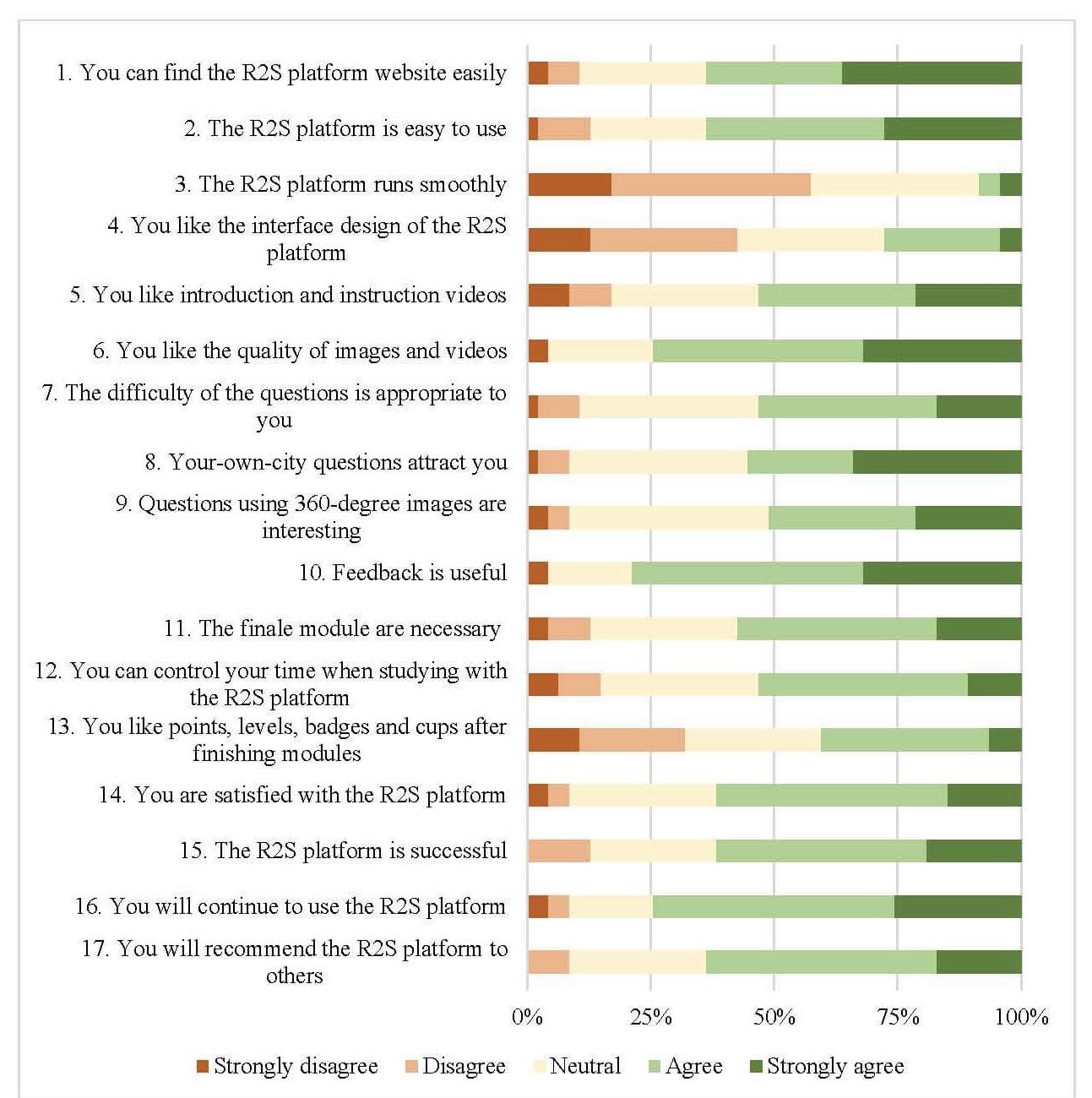
Adolescents are considered as vulnerable road users and education is one way to increase their traffic knowledge and riding skills. In this study, a version of an e-learning platform tailored to the Vietnamese context is used to improve four specific competences, i.e. traffic-related knowledge, situation awareness, risk detection, and risk management. Images and short videos from authentic traffic situations are used as learning stimuli and users have the possibility to self-test their competences via a separate “finale”. Gamification elements (i.e., points, levels, badges and cups) are incorporated into the platform to encourage user engagement. The purpose of this study is to conduct a pilot study using a gamified e-learning platform, and to assess user experience. 47 adolescents (aged 15-16) participated in a single arm (i.e., test group only) within-subject design with baseline and post-measurement. Results indicate that scores on the post-measurement were statistically significantly higher as compared to baseline performance. Scores were better for the risk management module. There were no statistically significantly different in scores between familiar situations (i.e., coming from the city where participants are living) and unfamiliar situations. Males overall performed better than females. Results for user experience are also discussed.
Downloads
References
Akbari, M., Lankarani, K., Heydari, S., Motevalian, A., Tabrizi, R., & Sullman, M. (2021). Is driver education contributing towards road safety? A systematic review of systematic reviews. Journal of Injury & Violence Research, 13. https://doi.org/10.5249/jivr.v13i1.1592 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5249/jivr.v13i1.1592
Akrolu, N., Babyk, B., Gler, M., Atabay, M., & Ylmaz Memi, B. (2017). Gamifying an ICT course. Computers in Human Behavior, 69(C), 98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.018
Allen, T., Newstead, S., Lenné, M. G., McClure, R., Hillard, P., Symmons, M., & Day, L. (2017). Contributing factors to motorcycle injury crashes in Victoria, Australia. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 45, 157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2016.11.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2016.11.003
Al-Mansoori, M., Shaalan, K., & Tawfik, H. (2011). Using E-learning for helping children with diabetes. 2011 International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology, 145–149. https://doi.org/10.1109/INNOVATIONS.2011.5893806 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/INNOVATIONS.2011.5893806
Assailly, J. P. (2017). Road safety education: What works? Patient Education and Counseling, 100, S24–S29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2015.10.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2015.10.017
Ben-Bassat, T., & Avnieli, S. (2016). The effect of a road safety educational program for kindergarten children on their parents’ behavior and knowledge. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 95, 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2016.06.024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2016.06.024
Box, E., & Dorn, L. (2023). A cluster randomised controlled trial (cRCT) evaluation of a pre-driver education intervention using the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 94, 379–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2023.03.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2023.03.001
Brown, I. D., & Groeger, J. A. (2007). Risk perception and decision taking during the transition between novice and experienced driver status. Ergonomics, 31(4), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140138808966701 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00140138808966701
Casutt, G., Theill, N., Martin, M., Keller, M., & Jäncke, L. (2014). The drive-wise project: Driving simulator training increases real driving performance in healthy older drivers. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00085 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00085
Cuenen, A., Brijs, K., Brijs, T., Van Vlierden, K., Daniels, S., & Wets, G. (2016). Effect evaluation of a road safety education program based on victim testimonials in high schools in Belgium. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 94, 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2016.05.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2016.05.006
da Rocha Seixas, L., Gomes, A. S., & de Melo Filho, I. J. (2016). Effectiveness of gamification in the engagement of students. Computers in Human Behavior, 58, 48–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.021
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., & Nacke, L. (2011). From game design elements to gamefulness: Defining “gamification.” Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1145/2181037.2181040 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2181037.2181040
Ding, L. (2019). Applying gamifications to asynchronous online discussions: A mixed methods study. Computers in Human Behavior, 91, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.09.022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.09.022
Dong, Z. (2018). Gender Difference in Situation Awareness when Receiving Wayfinding Direction by Landmarks and Headings. PhD Dissertations and Master’s Theses. https://commons.erau.edu/edt/382
Floreskul, V., Žardeckaitė-Matulaitienė, K., Endriulaitienė, A., & Šeibokaitė, L. (2016). Effectiveness of pre-driver education programme for high school students: Application of Theory of Planned Behaviour on road risk taking behaviour. Journal of Behavior, Health & Social Issues, 8(1), 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbhsi.2017.08.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbhsi.2017.08.003
Gafni, R., Achituv, D. B., Eidelman, S., & Chatsky, T. (2018). The effects of gamification elements in e-learning platforms. Online Journal of Applied Knowledge Management (OJAKM), 6(2), 37–53. https://doi.org/10.36965/OJAKM.2018.6(2)37-53 DOI: https://doi.org/10.36965/OJAKM.2018.6(2)37-53
Glendon, A. I., McNally, B., Jarvis, A., Chalmers, S. L., & Salisbury, R. L. (2014). Evaluating a novice driver and pre-driver road safety intervention. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 64, 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2013.11.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2013.11.017
GRSP. (2017, October 10). Road safety for school children, a focus for Total Vietnam. Global Road Safety Partnership. https://www.grsproadsafety.org/road-safety-school-children-focus-total-vietnam/
Hamari, J., & Koivisto, J. (2015). Why do people use gamification services? International Journal of Information Management, 35(4), 419–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2015.04.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2015.04.006
Hamari, J., Koivisto, J., & Sarsa, H. (2014). Does Gamification Work? – A Literature Review of Empirical Studies on Gamification. 2014 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 3025–3034. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2014.377 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2014.377
Haworth, N. L., & Mulvihill, C. (2006). A comparison of hazard perception and responding in car drivers and motorcyclists. Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Qld (CARRS-Q); Faculty of Health; Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation. 2006 International Motorcycle Safety Conference: The Human Element, Long Beach, California. https://eprints.qut.edu.au/7139/
Henderson, J., & Alexander, S. (2012). E-Learning – The future of child and adolescent obesity! Obesity Research & Clinical Practice, Supplement 1(6), 75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2012.08.153 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2012.08.153
Ker, K., Roberts, I., Collier, T., Beyer, F., Bunn, F., & Frost, C. (2005). Post-licence driver education for the prevention of road traffic crashes: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Accident; Analysis and Prevention, 37, 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2004.09.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2004.09.004
Khuat, H., & Huyen, T. (2011). Education influence in traffic safety: A case study in Vietnam. Lancet, 34, 87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iatssr.2011.01.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iatssr.2011.01.004
Krause, U.-M., Stark, R., & Mandl, H. (2009). The effects of cooperative learning and feedback on e-learning in statistics. Learning and Instruction, 19(2), 158–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.03.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.03.003
Liaw, S.-S., & Huang, H.-M. (2013). Perceived satisfaction, perceived usefulness and interactive learning environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-learning environments. Computers & Education, 60(1), 14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.07.015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.07.015
Liu, C. C., Hosking, S. G., & Lenné, M. G. (2009). Hazard perception abilities of experienced and novice motorcyclists: An interactive simulator experiment. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 12(4), 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2009.04.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2009.04.003
Lopez, C. E., & Tucker, C. S. (2019). The effects of player type on performance: A gamification case study. Computers in Human Behavior, 91, 333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.10.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.10.005
Lund, I. O., & Rundmo, T. (2009). Cross-cultural comparisons of traffic safety, risk perception, attitudes and behaviour. Safety Science, 47(4), 547–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2008.07.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2008.07.008
Markl, M. (2016). Effectiveness of Road Safety Educational Program for Pre-drivers about DUI: Practical Implication of the TPB in Developing New Preventive Program in Slovenia. Transportation Research Procedia, 14, 3829–3838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2016.05.468 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2016.05.468
Mayhew, D., Marcoux, K., Wood, K., Simpson, H., Vanlaar, W., Lonero, L., & Clinton, K. (2014). Evaluation of Beginner Driver Education Programs: Studies in Manitoba and Oregon. https://trid.trb.org/view/1324346
Mayhew, D. R. (2007). Driver education and graduated licensing in North America: Past, present, and future. Journal of Safety Research, 38(2), 229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsr.2007.03.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsr.2007.03.001
Mayhew, D., Simpson, H., Williams, A., & Ferguson, S. (1998). Effectiveness and Role of Driver Education and Training in a Graduated Licensing System. Journal of Public Health Policy, 19, 51–67. https://doi.org/10.2307/3343089 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/3343089
McDonald, C. C., Curry, A. E., Kandadai, V., Sommers, M. S., & Winston, F. K. (2014). Comparison of teen and adult driver crash scenarios in a nationally representative sample of serious crashes. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 72, 302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2014.07.016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2014.07.016
Meyer, S., Sagberg, F., & Torquato, R. (2014). Traffic hazard perception among children. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 26, 190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2014.07.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trf.2014.07.007
Ministry of Transport of Vietnam. (2010). Master plan on road traffic safety in Vietnam up to 2020. https://mt.gov.vn/vn/tin-tuc/8080/bo-gtvt-cung-cap-tai-lieu-quy-hoach-tong-the-ve-an-toan-giao-thong-duong-bo-viet-nam-den-nam-2020.aspx
Nistor, G. C., & Iacob, A. (2018). The Advantages of Gamification and Game-Based Learning and their Benefits in the Development of Education. The International Scientific Conference ELearning and Software for Education, 1, 308–312. http://dx.doi.org/10.12753/2066-026X-18-042 DOI: https://doi.org/10.12753/2066-026X-18-042
O’Neill, B. (2020). Driver education: How effective? International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion, 27(1), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/17457300.2019.1694042 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17457300.2019.1694042
Ong, C.-S., & Lai, J.-Y. (2006). Gender differences in perceptions and relationships among dominants of e-learning acceptance. Computers in Human Behavior, 22(5), 816–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2004.03.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2004.03.006
Petzoldt, T., Weiß, T., Franke, T., Krems, J. F., & Bannert, M. (2013). Can driver education be improved by computer based training of cognitive skills? Accident Analysis & Prevention, 50, 1185–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2012.09.016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2012.09.016
Pham, N. H. (2019). An Application of the gamified e-learning platform to improve road safety education in Vietnam [UHasselt]. https://documentserver.uhasselt.be//handle/1942/29518
Putri, Z. H. (2020). An Application of the Gamified E-Learning Platform to Improve Road Safety Education in Indonesia: Case Study Jakarta [UHasselt]. https://documentserver.uhasselt.be//handle/1942/32389
Rakoczi, G., Duchowski, A., Casas-Tost, H., & Pohl, M. (2013). Visual perception of international traffic signs: Influence of e-learning and culture on eye movements. Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Eye Tracking South Africa, 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1145/2509315.2509317 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2509315.2509317
Ramayah, T., & Lee, J. W. C. (2012). System Characteristics, Satisfaction and E-Learning Usage: A Structural Equation Model (SEM). Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology - TOJET, 11(2), 196–206.
Riaz, M. S., Cuenen, A., Janssens, D., Brijs, K., & Wets, G. (2019). Evaluation of a gamified e-learning platform to improve traffic safety among elementary school pupils in Belgium. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 23(5), 931–941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-019-01221-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-019-01221-4
Robson, K., Plangger, K., Kietzmann, J. H., McCarthy, I., & Pitt, L. (2015). Is it all a game? Understanding the principles of gamification. Business Horizons, 58(4), 411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2015.03.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2015.03.006
Rosenbloom, T., Mandel, R., Rosner, Y., & Eldror, E. (2015). Hazard perception test for pedestrians. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 79, 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2015.03.019 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2015.03.019
Sagberg, F., & Bjørnskau, T. (2006). Hazard perception and driving experience among novice drivers. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 38(2), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2005.10.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2005.10.014
Sailer, M., Hense, J. U., Mayr, S. K., & Mandl, H. (2017). How gamification motivates: An experimental study of the effects of specific game design elements on psychological need satisfaction. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.033 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.033
Salmon, P. M., Young, K. L., & Cornelissen, M. (2013). Compatible cognition amongst road users: The compatibility of driver, motorcyclist, and cyclist situation awareness. Safety Science, 56, 6–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2012.02.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2012.02.008
Schwebel, D. C., Davis, A. L., & O’Neal, E. E. (2012). Child Pedestrian Injury: A Review of Behavioral Risks and Preventive Strategies. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 6(4), 292–302. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066611404876 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066611404876
Shell, D. F., Newman, I. M., Córdova-Cazar, A. L., & Heese, J. M. (2015). Driver education and teen crashes and traffic violations in the first two years of driving in a graduated licensing system. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 82, 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2015.05.011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2015.05.011
Sitohang, I. F. (2022). Understanding the support of route2school (R2S) education implementation in Indonesia [UHasselt]. https://documentserver.uhasselt.be//handle/1942/38611
Stubbé, H., Badri, A., Telford, R., van der Hulst, A., & van Joolingen, W. (2016). E-Learning Sudan, Formal Learning for Out-of-School Children. Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 14(2), 136–149.
Twisk, D. A. M., Vlakveld, W. P., Commandeur, J. J. F., Shope, J. T., & Kok, G. (2014). Five road safety education programmes for young adolescent pedestrians and cyclists: A multi-programme evaluation in a field setting. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 66, 55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2014.01.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2014.01.002
United Nations. (2018). Road Safety Performance Review. 121.
Useche, S. A., Alonso, F., Montoro, L., & Esteban, C. (2019). Explaining self-reported traffic crashes of cyclists: An empirical study based on age and road risky behaviors. Safety Science, 113, 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2018.11.021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2018.11.021
Vasilyeva, E., Pechenizkiy, M., & De Bra, P. (2008). Adaptation of Elaborated Feedback in e-Learning. In W. Nejdl, J. Kay, P. Pu, & E. Herder (Eds.), Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-Based Systems (pp. 235–244). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70987-9_26 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70987-9_26
Vidotto, G., Bastianelli, A., Spoto, A., & Sergeys, F. (2011). Enhancing hazard avoidance in teen-novice riders. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 43(1), 247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2010.08.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2010.08.017
Vu, A. T., & Nguyen, D. V. M. (2017). Analysis of Children Road Traffic Accidents and Proposed Measures for Children Safety Improvement in Ho Chi Minh City. 7.
World Health Organization. (2015). Global status report on road safety 2015. WHO. http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/road_safety_status/2015/en/
Wright, M. C., Taekman, J. M., & Endsley, M. R. (2004). Objective measures of situation awareness in a simulated medical environment. BMJ Quality & Safety, 13(suppl 1), i65–i71. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2004.009951 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2004.009951
Yeh, T.-H., Chang, H.-L., & Chang, H.-W. (2008). Initial age of unlicensed motorcycling experience for a cohort of high school students. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 40(2), 511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2007.08.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2007.08.005
Zainuddin, Z., Shujahat, M., Haruna, H., & Chu, S. K. W. (2020). The role of gamified e-quizzes on student learning and engagement: An interactive gamification solution for a formative assessment system. Computers & Education, 145, 103729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103729 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103729
Zeedyk, M. S., & Wallace, L. (2003). Tackling children’s road safety through edutainment: An evaluation of effectiveness. Health Education Research, 18(4), 493–505. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/cyf033 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/her/cyf033
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 International Journal of Building, Urban, Interior and Landscape Technology (BUILT)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.











