Water Quality Degradation and Management Strategies for Swine and Rice Farming Wastewater in the Tha Chin River Basin
Main Article Content
Abstract
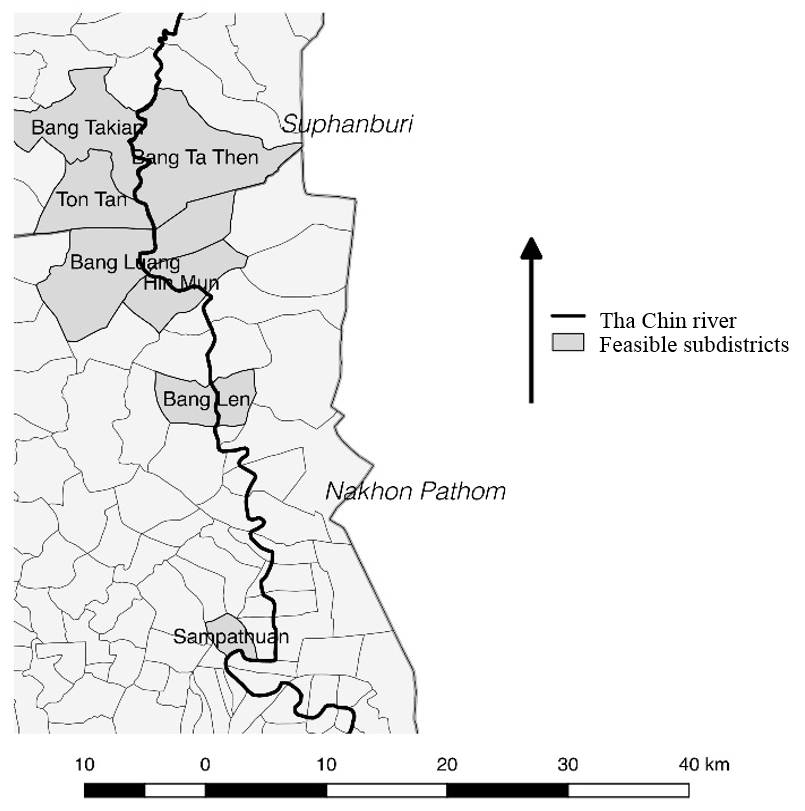
Water quality in the Tha Chin River regularly exceeds biological oxygen demand (BOD) standards of Thailand’s Enhancement and Conservation of National Environmental Quality Act. This study quantified the BOD loading from rice cultivation and swine farming to the Tha Chin River using effluent data and procedures from the Pollution Control Department (PCD), geospatial land-use maps from the Land Development Department, and water quality data from the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment. It was determined that the BOD loading was 12 tons/day from swine farming in 2015 and 52 tons/day, on average, from rice farming between 2002 and 2011. Technology-specific, community-scale wastewater management strategies were recommended for both industries: feasibility studies revealed 66 potential sites for constructed wetland implementation and 7 subdistricts suitable for biogas network pipelines. It was determined that if these projects are implemented in conjunction, the BOD would be reduced by 6% (0.3 mg/L) in the entire river or 11% (0.5 mg/L) at the three water quality monitoring stations proximate to swine farms. These reductions would have a substantial effect on the water quality of the Tha Chin River, and governmental agencies such as the PCD should strongly consider subsidization and implementation of these projects.
Article Details
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.