Association between Noise Exposure and Quality of Life among People Living Near Stone-Mortar Factories, Phayao Province, Northern Thailand 10.32526/ennrj/19/2020050
Main Article Content
Abstract
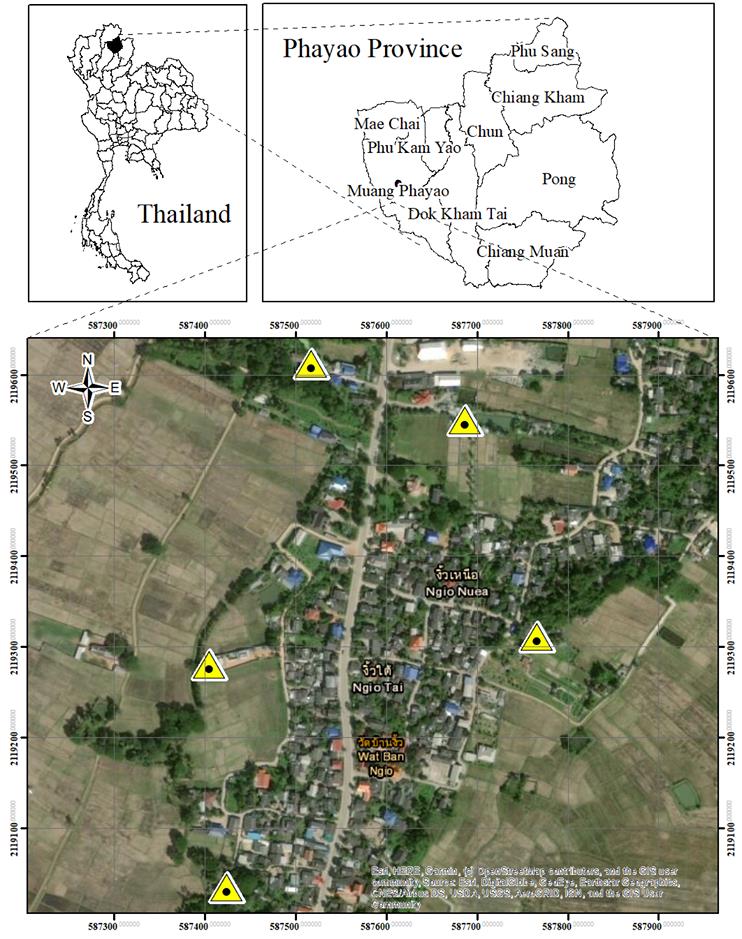
Noise may have adverse effects on health and quality of life (QoL). This study assessed the association between noise exposure and QoL among people living near stone-mortar factories. A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted using 269 subjects. The data was collected using questionnaires, sound level meter, and a geographic information system technique. The statistical analysis was carried out using independent t-test, ANOVA, Pearson’s correlation coefficient test and multiple binary logistic regression analysis. The average noise in factory no. 2, 4, and 5 was found to be higher than the standard level of NIOSH at 85 dB(A) and OSHA at 90 dB(A) for an 8-hour TWA. The multiple binary logistic regression analysis showed that an increasing residential distance was associated with high noise exposure after adjusting for age, education, income, length of stay in community, and overall QoL. The local policy makers should be required to emphasize on the reduction of noise pollution in stone-mortar factories and health surveillance of the residential neighborhood.
Article Details
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Ali A, Hussain RM, Dom NC, Rashid RI. A profile of noise sensitivity on the health-related quality of life among young motorcyclists. Noise and Health 2018;20(93):53-9.
Alshehri KA, Alqulayti WM, Yaghmoor BE, Alem H. Public awareness of ear health and hearing loss in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. South African Journal of Communication Disorders 2019;66(1):1-6.
Basner M, Babisch W, Davis A, Brink M, Clark C, Janssen S, et al. Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014;383(9925):1325-32.
Boyle MD, Soneja S, Quirós-Alcalá L, Dalemarre L, Sapkota AR, Sangaramoorthy T, et al. A pilot study to assess residential noise exposure near natural gas compressor stations. PloS One. 2017;12(4):e0174310.
Chen GD, Decker B, Muthaiah VP, Sheppard A, Salvi R. Prolonged noise exposure-induced auditory threshold shifts in rats. Hearing Research 2014;317:1-8.
Chepesiuk R. Decibel hell: The effects of living in a noisy world. Environmental Health Perspectives 2005;113(1):34-41.
Correia AW, Peters JL, Levy JI, Melly S, Dominici F. Residential exposure to aircraft noise and hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases: Multi-airport retrospective study. British Medical Journal 2013;347:f5561.
D'Souza MS, Karkada SN, Somayaji G. Factors associated with health-related quality of life among Indian women in mining and agriculture. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2013;11:9.
Fonseca VR, Marques J, Panegalli F, Gonçalves CGO, Souza W. Prevention of the evolution of workers' hearing loss from noise-induced hearing loss in noisy environments through a hearing conservation program. International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology 2016;20(1):43-7.
Fuente A, Hickson L. Noise-induced hearing loss in Asia. International Journal of Audiology 2011;50(sup1):3-10.
Han L, Li Y, Yan W, Xie L, Wang S, Wu Q, et al. Quality of life and influencing factors of coal miners in Xuzhou, China. Journal of Thoracic Disease 2018;10(2):835-44.
Han ZX, Lei ZH, Zhang CL, Xiong W, Gan ZL, Hu P, et al. Noise monitoring and adverse health effects in residents in different functional areas of Luzhou, China. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health 2015;27(sup2):93-9.
Huang FJ, Hsieh CJ, Young CH, Chung SH, Tseng CC, Yiin LM. The assessment of exposure to occupational noise and hearing loss for stoneworkers in Taiwan. Noise and Health 2018;20(95):146-51.
Jirarattanaphochai K, Jung S, Sumananont C, Saengnipanthkul S. Reliability of the medical outcomes study short-form survey version 2.0 (Thai version) for the evaluation of low back pain patients. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2005;88(10):1355-61.
Kitcher ED, Ocansey G, Tumpi DA. Early occupational hearing loss of workers in a stone crushing industry: our experience in a developing country. Noise and Health 2012;14(57):68-71.
Landen D, Wilkins S, Stephenson M, McWilliams L. Noise exposure and hearing loss among sand and gravel miners. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene 2004;1(8):532-41.
Lim LL, Seubsman SA, Sleigh A. Thai SF-36 health survey: Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, reliability and validity in healthy men and women. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2008;6(1):52.
McKnight PE, Kashdan TB. The importance of functional impairment to mental health outcomes: A case for reassessing our goals in depression treatment research. Clinical Psychology Review 2009;29(3):243-59.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Noise and hearing loss prevention guidance and regulations [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2020 Feb 20]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/noise/reducenoiseexposure/regsguidance.html.
Nelson DI, Nelson RY, Concha-Barrientos M, Fingerhut M. The global burden of occupational noise‐induced hearing loss. American Journal of Industrial Medicine 2005;48(6):446-58.
Nitschke M, Tucker G, Simon DL, Hansen AL, Pisaniello DL. The link between noise perception and quality of life in South Australia. Noise and Health 2014;16(70):137-42.
Padungtod C, Ekpanyaskul C, Nuchpongsai P, Laemun N, Matsui T, Hiramatsu K. Aircraft noise exposure and its effects on quality of life and cognitive function among thai residents. Epidemiology 2011;22(1):259.
Seidman MD, Standring RT. Noise and quality of life. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2010;7(10):3730-8.
Sordello R, De Lachapelle FF, Livoreil B, Vanpeene S. Evidence of the environmental impact of noise pollution on biodiversity: A systematic map protocol. Environmental Evidence 2019;8(1):8.
Tenailleau QM, Bernard N, Pujol S, Houot H, Joly D, Mauny F. Assessing residential exposure to urban noise using environmental models: Does the size of the local living neighborhood matter?. Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology 2015;25(1):89-96.
Thongtip S, Sangkham S, Sukpromson R. Factors associated with occupational hearing loss among stone-mortar workers in Phayao Province, Northern Thailand. Journal of Health Science and Medical Research 2020a;38(3):213-9.
Thongtip S, Siviroj P, Prapamontol T, Deesomchok A, Wisetborisut A, Nangola S, et al. A suitable biomarker of effect, club cell protein 16, from crystalline silica exposure among Thai stone-carving workers. Toxicology and Industrial Health 2020b;36(4):287-96.
Wang R, Wu C, Zhao Y, Yan X, Ma X, Wu M, et al. Health related quality of life measured by SF-36: A population-based study in Shanghai, China. BMC Public Health 2008;8(1):292.
Ware Jr JE, Gandek B. The SF-36 health survey: Development and use in mental health research and the IQOLA Project. International Journal of Mental Health 1994;23(2):49-73.
Ware Jr JE, Gandek B. Overview of the SF-36 health survey and the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) Project. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1998;51(11):903-12.
Welch D, Dirks KN, Shepherd D, McBride D. Health-related quality of life is impacted by proximity to an airport in noise-sensitive people. Noise and Health 2018;20(96):171-7.
World Health Organization (WHO). Occupational exposure to noise: Evaluation, prevention and control [Internet]. 2001 [cited 2020 Feb 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/ occupational_health/publications/occup noise/en/.
World Health Organization (WHO). Burden of disease from environmental noise [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2020 Feb 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/quantifying_ehimpacts /publications/e94888/en/.
World Health Organization (WHO). Addressing the rising prevalence of hearing loss [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2020 Feb 20]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/260336.