Mycoremediation Potential of Synthetic Textile Dyes by Aspergillus niger via Biosorption and Enzymatic Degradation 10.32526/ennrj/20/202100171
Main Article Content
Abstract
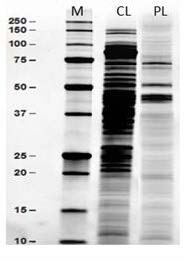
Textile dyes that persist in the environment are highly resistant to the natural degradation processes that occur in the environment. Therefore, the present study isolated, identified, and optimized textile dye decolorization by fungi and elucidated the dye decolorization pathway to develop a low-cost biotechnological approach for decolorization and detoxification of textile dyes. Within 36 hours of incubation at temperatures ranging from 28 to 40°C, pH 7, and shaking at 100 rpm, Aspergillus niger MN990895, which was selected from a total of 77 fungal isolates, completely decolorized the model dye CI Direct Blue 201 (DB 201). A. niger biosorbed 8.4±1.2% of the dye used where live biomass showed complete dye removal. It was found that extracellular crude enzymes were more involved in DB 201 dye decolorization (72.7±3.3%) than intracellular crude enzymes. The enzymatic studies suggested that the primary enzyme involved in DB 201 textile dye decolorization was lacccase, which was further confirmed by the presence of distinct protein bands around 75-100 kDa on the SDS-PAGE. The FTIR spectra and seed germination assays confirmed that A. niger proved successful in DB 201 textile dye degradation and detoxification. The present study suggests that A. niger may have promising implications in the future for the development of an enzyme-based textile wastewater treatment system.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Abdelgalil SA, Attia AM, Reyed RM, Soliman NA, El Enshasy HA. Application of experimental designs for optimization the production of Alcaligenes faecalis Nyso laccase. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research 2018;77(1):713-27.
Ali N, Hameed A, Ahmed S, Khan AG. Decolorization of structurally different textile dyes by Aspergillus niger SA1. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2008;24(7):1067-72.
Almeida EJR, Corso CR. Comparative study of toxicity of azo dye Procion Red MX-5B following biosorption and biodegradation treatments with the fungi Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus terreus. Chemosphere 2014;112:317-22.
Arabaci G, Usluoglu A. The enzymatic decolorization of textile dyes by the immobilized polyphenol oxidase from quince leaves. Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:Article No. 685975.
Asad S, Amoozegar MA, Pourbabaee A, Sarbolouki MN, Dastgheib SMM. Decolorization of textile azo dyes by newly isolated halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. Bioresource technology 2007;98(11):2082-8.
Bagewadi ZK, Mulla SI, Ninnekar HZ. Purification and immobilization of laccase from Trichoderma harzianum strain HZN10 and its application in dye decolorization. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology 2017;15(1):139-50.
Bankole PO, Adekunle AA, Obidi OF, Olukanni OD, Govindwar SP. Degradation of indigo dye by a newly isolated yeast, Diutina rugosa from dye wastewater polluted soil. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2017;5(5):4639-48.
Bankole PO, Adekunle AA, Obidi OF, Chandanshive VV, Govindwar SP. Biodegradation and detoxification of Scarlet RR dye by a newly isolated filamentous fungus, Peyronellaea prosopidis. Sustainable Environment Research 2018;28(5): 214-22.
Bhattacharjee C, Dutta S, Saxena VK. A review on biosorptive removal of dyes and heavy metals from wastewater using watermelon rind as biosorbent. Environmental Advances 2020:2:Article No.100007.
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA. Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2015;166:603-43.
Chemical Book. CI direct blue 201 basic information [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2017 Mar 6]. Available from: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductChemicalPropertiesCB01453522_EN.htm.
Chen H, Hopper SL, Cerniglia CE. Biochemical and molecular characterization of an azoreductase from Staphylococcus aureus, a tetrameric NADPH-dependent flavoprotein. Microbiology 2005;151:1433-41.
Cui D, Li G, Zhao M, Han S. Decolourization of azo dyes by a newly isolated Klebsiella sp. strain Y3, and effects of various factors on biodegradation. Biotechnology and Biotechnological Equipment 2014;28(3):478-86.
Dhaneshwar A. Decolorisation of Methylene Blue Using Lactuca and Sophora species [dissertation]. New Zealand: University of Canterbury; 2016.
Dhanjal NIK, Mittu B, Chauhan A, Gupta S. Biodegradation of textile dyes using fungal isolates. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2013;6(2):99-105.
Ekanayake EMMS, Manage PM. Decoloriztion of textile dye (CI Direct Blue 201) by selected aquatic plants. Proceedings of the 2nd Environment and Natural Resources International Conference; 2016 Nov 16-17; Bangkok: Thailand; 2016.
Ekanayake EMMS, Manage PM. Decolorization of CI Direct Blue 201 textile dye by native bacteria. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies 2017;4(1):49-58.
Ekanayake EMMS, Manage PM. Decolorization and detoxification of CI Direct Blue 201 textile dye by two fungal strains of genus Aspergillus. Journal of National Science Foundation Sri Lanka 2020a;48(1):69-80.
Ekanayake EMMS, Manage PM. Green approach for decolorization and detoxification of textile dye - CI direct blue 201 using native bacterial strains. Environment and Natural Resource Journal 2020b;18(1):1-8.
El-Rahim WMA, El-Ardy OAM, Mohammad FH. The effect of pH on bioremediation potential for the removal of direct violet textile dye by Aspergillus niger. Desalination 2009; 249(3):1206-11.
Erdem Ö, Cihangir N. Color removal of some textile dyes from aqueous solutions using Trametes versicolor. Hacettepe Journal of Biology and Chemistry 2018;45(4):499-507.
Fernando E, Keshavarz T, Kyazze G. Enhanced bio-decolourisation of acid orange 7 by Shewanella oneidensis through co-metabolism in a microbial fuel cell. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 2012;72:1-9.
Fu Y, Viraraghavan T. Removal of Congo red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Advances in Environmental Research 2002;7(1):239-47.
Gadallah MAA, Sayed SA. Impacts of different water pollution sources on antioxidant defense ability in three aquatic macrophytes in Assiut Province, Egypt. Journal of Stress Physiology and Biochemistry 2014;10(3):47-61.
Goud BS, Cha HL, Koyyada G, Kim JH. Augmented biodegradation of textile azo dye effluents by plant endophytes: A sustainable, eco-friendly alternative. Current Microbiology 2020;77:3240-55.
Gupta N, Kushwaha AK, Chattopadhyaya MC. Application of potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant wastes for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2016;9(1):707-16.
Guruge KS, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Manage PM. Occurrence of perfluorinated acids and fluorotelomers in waters from Sri Lanka. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2007;54(10):1667-72.
Hao OJ, Kim H, Chiang PC. Decolorization of wastewater: Critical reviews. Environmental Science and Technology 2000;30(4):449-505.
Jadhav SB, Yedurkar SM, Phugare SS, Jadhav JP. Biodegradation studies on acid violet 19, a triphenylmethane dye, by Pseudomonas aeruginosa BCH. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water 2012;40(5):551-8.
Kagalkar AN, Jagtap UB, Jadhav JP, Bapat VA, Govindwar SP. Biotechnological strategies for phytoremediation of the sulfonated azo dye Direct Red 5B using Blumea malcolmii Hook. Bioresource Technology 2009;100(18):4104-210.
Kalyani DC, Patil PS, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP. Biodegradation of reactive textile dye Red BLI by an isolated bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SUK1. Bioresource Technology 2008; 99(11):4635-41.
Khalaf MA. Biosorption of reactive dye from textile wastewater by non-viable biomass of Aspergillus niger and Spirogyra sp. Bioresource Technology 2008;99(14):6631-4.
Khan S, Malik A. Environmental and health effects of textile industry wastewater. In: Environmental Deterioration and Human Health. Dordrecht: Springer; 2014. p. 55-71.
Mahagamage MGYL, Manage PM. Water quality index (CCME-WQI) based assessment study of water quality in Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. International Journal of Environment and natural resources 2014;1:199-204.
Mishra S, Cheng L, Maiti A. The utilization of agro-biomass/byproducts for effective bio-removal of dyes from dyeing wastewater: A comprehensive review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2021;9(1):Article No. 104901.
Modak JM, Natarajan KA. Biosorption of metals using nonliving biomass: A review. Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration 1995;12(4):189-96.
Módenes AN, Hinterholz CL, Neves CV, Sanderson K, Trigueros DE, Spinoza-Quiñones FR, et al. A new alternative to use soybean hulls on the adsorptive removal of aqueous dyestuff. Bioresource Technology Reports 2019;6:175-82.
Placido J, Chanaga X, Ortiz-Monsalve S, Yepes M, Mora A. Degradation and detoxification of synthetic dyes and textile industry effluents by newly isolated Leptosphaerulina sp. from Colombia. Bioresources and Bioprocessing 2016;3(6):2-14.
Polman K, Breckenridge CR. Biomass-mediated binding and recovery of textile dyes from waste effluents. Textile Chemist and Colorist 1996;28(4):116-21.
Przystas W, Zablocka-Godlewska E, Grabinska-Sota E. Efficacy of fungal decolorization of a mixture of dyes belonging to different classes. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2015;46(2):415-24.
Rani B, Kumar V, Singh J, Bisht S, Teotia P, Sharma S, et al. Bioremediation of dyes by fungi isolated from contaminated dye effluent sites for bio-usability. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2014;45(3):1055-63.
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS, Govindwar SP. Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive dyes and dye wastewater by a developed bacterial consortium. Biodegradation 2010;21(6):999-1015.
Seyis I, Subasioglu T. Comparison of live and dead biomass of fungi on decolorization of methyl orange. African Journal of Biotechnology 2008;7(13):2212-6.
Shah PD, Dave SR, Rao MS. Enzymatic degradation of textile dye Reactive Orange 13 by newly isolated bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis PMS-1. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 2012;69:41-50.
Shah H, Yusof F, Alam MZ. A new technique to estimate percentage decolorization of synthetic dyes on solid media by extracellular laccase from white-rot fungus. Bioremediation Journal 2021:1-9 (In press).
Sumathi S, Phatak V. Fungal treatment of bagasse based pulp and paper mill wastes. Environmental Technology 1999;20(1):93-8.
Telke AA, Kadam AA, Jagtap SS, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP. Biochemical characterization and potential for textile dye degradation of blue laccase from Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 2010;15(4):696-703.
Vairavela P, Murtyb VR. Decolorization of Congo red dye in a continuously operated rotating biological contactor reactor. Desalin Water Treat 2020:196:299-314.
Vasdev K, Kuhad RC, Saxena RK. Decolorization of triphenylmethane dyes by the bird’s nest fungus Cyathus bulleri. Current Microbiology 1995;30(5):269-72.
Watharkar AD, Khandare RV, Kamble AA, Mulla AY, Govindwar SP, Jadhav JP. Phytoremediation potential of Petunia grandiflora Juss., an ornamental plant to degrade a disperse, disulfonated triphenylmethane textile dye Brilliant Blue G. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2013;20(2):939-49.
Wijesekara I, Pangestuti R, Kim SK. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydrate Polymers 2011;84(1):14-21.
Xing Y, Liu D, Zhang LP. Enhanced adsorption of methylene blue by EDTAD-modified sugarcane bagasse and photocatalytic regeneration of the absorbent. Desalination 2010;259:187-91.
Yesilada O, Asma D, Cing S. Decolorization of textile dyes by fungal pellets. Process Biochemistry 2003;38(6):933-8.
Zouari-Mechichi H, Mechichi T, Dhouib A, Sayadi S, Martinez AT, Martinez MJ. Laccase purification and characterization from Trametes trogii isolated in Tunisia: Decolorization of textile dyes by the purified enzyme. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 2006;39(1):141-8.