Treating Tapioca Starch Industrial Wastewater Using Two-Phase Multi-Staged Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (MS-UASB) 10.32526/ennrj/21/202200210
Main Article Content
Abstract
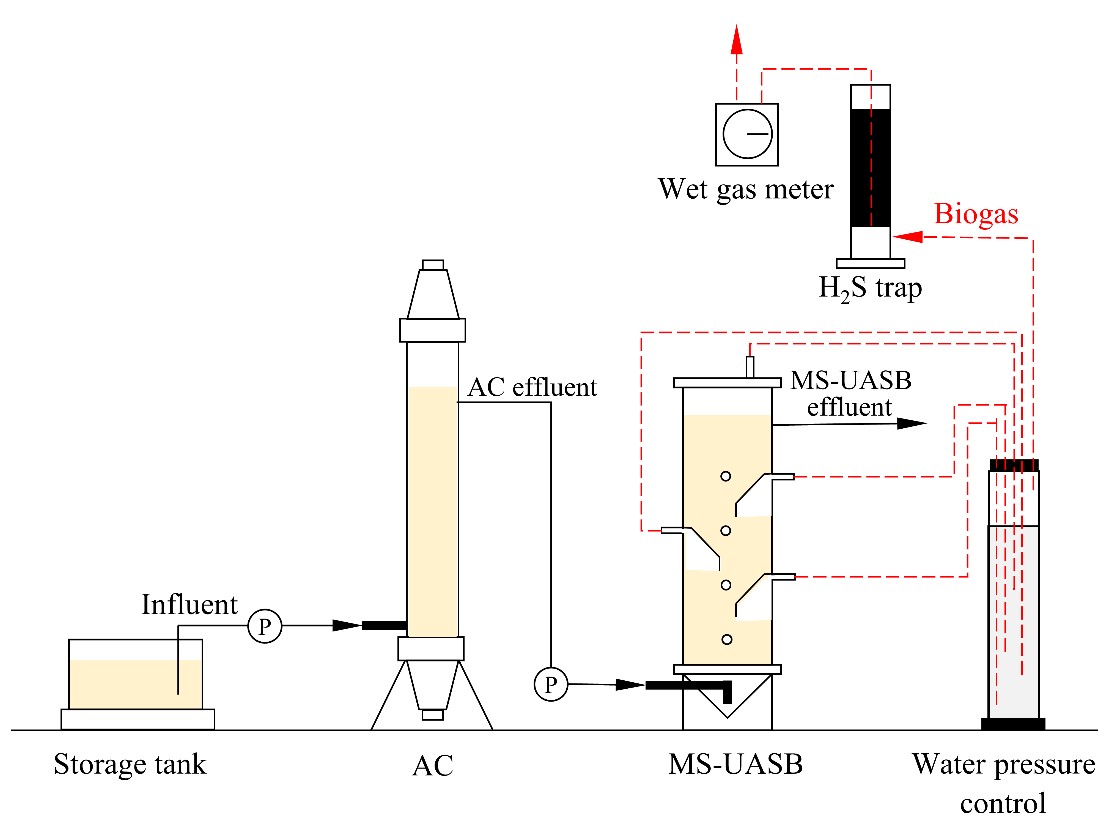
A laboratory-scale, two-phase multi-staged up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (MS-UASB) treatment system was monitored over time in order to evaluate its treatment efficiency and performance when treating non-diluted industrial tapioca starch wastewater under ambient temperature in Thailand. The system consisted of an acidification (AC) reactor and MS-UASB reactor and was operated for 280 days. The two-phase MS-UASB achieved a maximum organic loading rate (OLR) of 8 kg-COD/m3/day for the overall system and reached 80.5% of chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency. Based on the inlet wastewater of each reactor, the AC reactor removed 61.85% of suspended solids and achieved acidification of the wastewater to produce volatile fatty acids at over 50%. Meanwhile, the MS-UASB reactor achieved 74.5% COD removal efficiency. Further analysis found that the increase in soluble extracellular polymeric substances per bound extracellular polymeric substances (S-EPS/B-EPS) was related to the floating sludge phenomenon, which occurred under excess OLR condition.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Akunna JC. Anaerobic Waste-Wastewater Treatment and Biogas Plants: A Practical Handbook. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press; 2018.
Angelidaki I, Sanders W. Assessment of the anaerobic biodegradability of macropollutants. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 2004;3(2):117-29.
Annachhatre AP, Amatya PL. UASB treatment of tapioca starch wastewater. Journal of Environmental Engineering 2000;126(12):1149-52.
Baird RB, Eaton AD, Rice EW. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), and Water Environment Federation (WEF); 2017.
Breuninger WF, Piyachomkwan K, Sriroth K. Tapioca/cassava starch: Production and use: In: Starch. USA: Academmic Press; 2009. p. 541-68.
Cervantes FJ, Pavlostathis SG, van Haandel A. Advanced Biological Treatment Processes for Industrial Wastewaters. London, UK: IWA Publishing; 2006.
Chabalina LD, Rodriguez M, Prats D. Study of the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in different types of membrane bioreactor (MBR) effluents. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment 2008;111:491-500.
Chavalparit O, Ongwandee M. Clean technology for the tapioca starch industry in Thailand. Journal of Cleaner Production 2009;17(2):105-10.
Choeisai P, Jitkam N, Silapanoraset K, Yubolsai C, Yoochatchaval W, Yamaguchi T, et al. Sugarcane molasses-based bio-ethanol wastewater treatment by two-phase multi-staged up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) combination with up-flow UASB and down-flow hanging sponge. Water Science and Technology 2014;69(6):1174-80.
Cremonez PA, Teleken JG, Meier TR, Alves HJ. Two-Stage anaerobic digestion in agroindustrial waste treatment: A review. Journal of Environmental Management 2021;281: Article No. 111854.
Devereux S, Shuttleworth PS, Macquarrie DJ, Paradisi F. Isolation and characterization of recovered starch from industrial wastewater. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 2011;19(4):971-9.
Dilallo R, Albertson OE. Volatile acids by direct titration. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation 1961:33(4);356-65.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Food Outlook - Biannual Report on Global Food Markets, November 2018. Rome, Italy: Trade and Markets Division of FAO; 2018.
Harada H, Uemura S, Momonoi K. Interaction between sulfate-reducing bacteria and methane-producing bacteria in UASB reactors fed with low strength wastes containing different levels of sulfate. Water Research 1994;28(2):355-67.
Intanoo P, Rangsanvigit P, Malakul P, Chavadej S. Optimization of separate hydrogen and methane production from cassava wastewater using two-stage upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (UASB) system under thermophilic operation. Bioresource Technology 2014;173:256-65.
Jiraprasertwong A, Maitriwong K, Chavadej S. Production of biogas from cassava wastewater using a three-stage upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Renewable Energy 2019;130:191-205.
Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI). Tapioca: Planting area in Thailand [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2021 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www3.rdi.ku.ac.th/?p=18045.
Khanal SK. Anaerobic Biotechnology for Bioenergy Production: Principles and Applications. New Jersey, USA: John Wiley and Sons; 2011.
Li S, Cui Y, Zhou Y, Luo Z, Liu J, Zhao M. The industrial applications of cassava: Current status, opportunities and prospects. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2017;97(8):2280-90.
Liu H, Fang HH. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. Journal of Biotechnology 2002;95(3):249-56.
Liu XM, Sheng GP, Luo HW, Zhang F, Yuan SJ, Xu J, et al. Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the sludge aggregation. Environmental Science and Technology 2010;44(11):4355-60.
Lowry OH. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1951;193:265-75.
Lu X, Zhen G, Estrada AL, Chen M, Ni J, Hojo T, et al. Operation performance and granule characterization of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating wastewater with starch as the sole carbon source. Bioresource Technology 2015; 180:264-73.
Lu X, Ni J, Zhen G, Kubota K, Li YY. Response of morphology and microbial community structure of granules to influent COD/SO42- ratios in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating starch wastewater. Bioresource Technology 2018;256:456-65.
Miron Y, Zeeman G, Van Lier JB, Lettinga G. The role of sludge retention time in the hydrolysis and acidification of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins during digestion of primary sludge in CSTR systems. Water Research 2000;34(5):1705-13.
Nielsen SS. Food Analysis Laboratory Manual. Switzerland: Springer Cham; 2017. p. 137-41.
Onodera T, Sase S, Choeisai P, Yoochatchaval W, Sumino H, Yamaguchi T, et al. High-rate treatment of molasses wastewater by combination of an acidification reactor and a USSB reactor. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A 2011;46(14):1721-31.
Rajbhandari BK, Annachhatre AP. Anaerobic ponds treatment of starch wastewater: Case study in Thailand. Bioresource Technology 2004;95(2):135-43.
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnology Advances 2010;28(6):882-94.
Sowcharoensuk C. Industry Outlook 2020-2022: Cassava Industry [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2022 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.krungsri.com/en/research/industry/industry-outlook/agriculture/cassava/IO/io-cassava-20.
Stronach SM, Rudd T, Lester JN. Anaerobic Digestion Processes in Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2012.
Syutsubo K, Harada H, Ohashi A. Granulation and sludge retainment during start-up of a thermophilic UASB reactor. Water Science and Technology 1998;38(8-9):349-57.
Syutsubo K, Sinthurat N, Ohashi A, Harada H. Population dynamics of anaerobic microbial consortia in thermophilic granular sludge in response to feed composition change. Water Science and Technology 2001;43(1):59-66.
Tagawa T, Takahashi H, Sekiguchi Y, Ohashi A, Harada H. Pilot-plant study on anaerobic treatment of a lipid-and protein-rich food industrial wastewater by a thermophilic multi-staged UASB reactor. Water Science and Technology 2002;45(10): 225-30.
Thai Tapioca Development Institute (TTDI). Tapioca starch [Internet]. 2000 [cited 2021 Aug 31]. Available from: https://tapiocathai.org/English/E4_e.html.
Thai Tapioca Starch Association (TTSA). Export tapioca products [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www.thaitapiocastarch.org/en/information/statistics/export_tapioca_products.
Thepubon T, Choeisai P, Mungkarndee P, Choeisai K, Syutsubo K. Effect of suspended solids removal methods on methane production from tapioca starch wastewater. Engineering and Applied Science Research 2020;47(1):87-92.
Van Lier JB, Van der Zee FP, Frijters CT, Ersahin ME. Celebrating 40 years anaerobic sludge bed reactors for industrial wastewater treatment. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 2015;14(4):681-702.
Wang B, Wu D, Zhang X, Mackey HR, Chen GH. Sludge flotation, its causes and control in granular sludge upflow reactors. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2018; 102(15):6383-92.
Wu J, Jiang B, Feng B, Li L, Moideen SN, Chen H, et al. Pre-acidification greatly improved granules physicochemical properties and operational stability of upflow anaerobic sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor treating low-strength starch wastewater. Bioresource Technology 2020;302:Article No. 122810.