Factors Affecting Traffic Noise and Annoyance from Different Types of Roads: A Case Study in Nakorn Pathom Province, Thailand 10.32526/ennrj/21/20230006
Main Article Content
Abstract
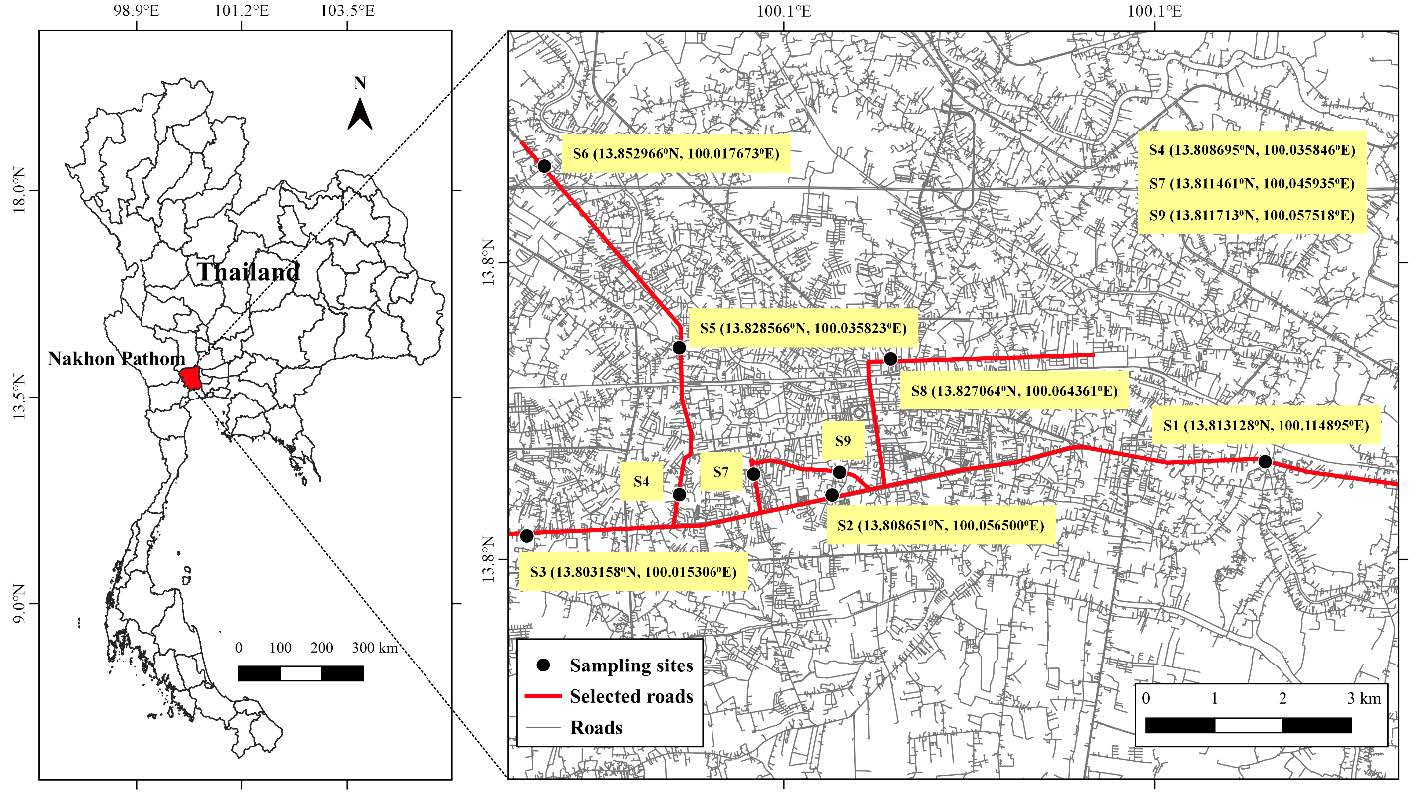
This study investigated factors associated with road traffic noise and residents’ annoyance from three distinct types of roads (major arterial, minor arterial, and collector roads). Nine sampling locations in Thailand’s Nakorn Pathom Province were chosen for the measurement of noise levels and three contributing characteristics: traffic volume, vehicle speed, and the proportion of heavy to total vehicles. Along with a housing survey, face to face interviews with a total of 387 roadside dwellers recorded their sociodemographic data, activity-based locations, and noise impacts experienced. A statistical analysis based on Spearman correlation revealed a positive relationship between traffic volume and traffic noise level on major arterial (r=0.607) and collector roads (r=0.885). Residents around collector roads were more sensitive than those along the main arterial road, in spite of having lower noise levels and less intense traffic patterns. Longer housing setbacks appeared to be a key factor in reducing noise annoyance from all road types, according to an exact logistic regression analysis (OR=0.11, 95% CI: 0.003, 0.73 for the major arterial road; OR=0.29, 95% CI: 0.10, 0.78 for the minor arterial road; and OR=0.32, 95% CI: 0.12, 0.84 for collector roads). However, performing activities in closed areas (OR=0.05, 95% CI: 0.01, 0.17 for the minor arterial road; OR=0.22, 95% CI: 0.54, 0.90 for collector roads) and living in soundproof structures (OR=0.05, 95% CI: 0.001, 0.31 for collector roads) played additional roles to reduce the annoyance of residents along the roads with shorter setback lines.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Abdur-Rouf K, Shaaban K. Measuring, mapping, and evaluating daytime traffic noise levels at urban road intersections in Doha, Qatar. Future Transportation 2022;2:625-43.
Ahmad SA, Sarkar PK. Traffic noise studies on arterial and collector road in Delhi, India. International Journal of Structural and Civil Engineering Research 2014;3:138-50.
Anachkova M, Domazetovska S, Nikolovski F, Gavriloski V. Statistical analysis of urban noise measurement data: Case study for the city of Skopje. Proceedings of the Bi-annual Baltic Nordic-Acoustic Meetings; 2022 May 9-11; Aalborg: Denmark; 2022.
Azodo A, Onwubalili C, Mezue T. Assessment of observed building structure setback of shops along an arterial road and noise intrusion level. Journal of Engineering 2019;25:62-71.
Bouzid I, Derbel A, Elleuch B. Factors responsible for road traffic noise annoyance in the city of Sfax, Tunisia. Applied Acoustics 2020;168:Article No. 107412.
Bunnakrid K, Sihabut T, Patthanaissaranukool W. The relationship between road traffic noise and annoyance levels in Phuket Province, Thailand. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology 2017;22:1-9.
Brink M, Giorgis-Allemand L, Schreckenberg D, Evrard AS. Pooling and comparing noise annoyance scores and “High Annoyance” (HA) responses on the 5-point and 11-point scales: Principles and practical advice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021;18:Article No. 7339.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). What noises cause hearing loss? [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2022 Jun 1]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/hearing_loss/ what_noises_cause_hearing_loss.html.
Cochran WG. The estimation of sample size. In: Cochran WG, editor. Sampling Techniques. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1977. p. 72-85.
Danish Road Directorate (DRD). Noise Annoyance from Urban Roads and Motorways. Copenhagen, Denmark: Vejdirek-toratet; 2016.
Dratva J, Zemp E, Dietrich DF, Bridevaux P, Rochat T, Schindler C, et al. Impact of road traffic noise annoyance on health-related quality of life: Results from a population-based study. Quality of Life Research 2010;19:37-46.
Erkan İ. Horn sounds in transportation systems and a cognitive perspective on the instant mood-condition disorder. Procedia Engineering 2017;187:357-94.
European Environment Agency (EEA). Health risk caused by environmental noise in Europe [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2022 Aug 1]. Available from: https://www.eea.europa.eu/ publications/health-risks-caused-by-environmental.
Fields JM, De Jong RG, Gjestland T, Flindell IH, Job RFS, Kurra S, et al. Standardized general-purpose noise reaction questions for community noise surveys: Research and a recom-mendation. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2001;242:641-79.
González DM, Morillas JMB, Rey-Gozalo G. Effects of noise on pedestrians in urban environments where road traffic is the main source of sound. Science of the Total Environment 2023;857:Article No.159406.
Grubeša S, Suhanek M. Traffic noise. In: Siano D, González E, editors. Noise and Environment. London, UK: IntechOpen; 2021. p. 1-21.
Halim H, Hamid NFN, Yusob MFM, Nor NAM, Hilmi NHFM, Sukor NSA, et al. Road traffic noise levels at different types of residential areas in Nibong Tebal, Penang. International Journal of Integrated Engineering 2019;11:101-12.
Jeon JY, Lee PJ, You J. Perceptual assessment of quality of urban soundscapes with combined noise source and water sound. Journal of Acoustic Society of America 2010;127:1357-66.
Lechner C, Schnaiter D, Siebert U, Böse-ÓReilly S. Effects of motorcycle noise on annoyance-a cross-sectional study in the Alps. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020;17:Article No. 1580.
Ministry of Interior. Ministerial Regulations Issued under the Road Traffic Act, Royal Thai Government Gazette Volume 96, Part 95, Dated 14th Jun B.E. 2522. Bangkok, Thailand: Office of the Council of State; 1979.
Ministry of Interior. Ministerial Regulations Issued under the Road Traffic Act, Royal Thai Government Gazette Volume 98, Part 8, Dated 20th Jan B.E. 2524. Bangkok, Thailand: Office of the Council of State; 1981.
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. Notifications of National Environment Board RE: Prescribing Standard on Environmental Noise, Royal Thai Government Gazette Volume 114, Part 27d, Dated 3rd Apr B.E. 2540. Bangkok, Thailand: Office of the Council of State; 1997.
Miškinytė A, Dėdelė A. Evaluation and analysis of traffic noise level in Kaunas city. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Engineering; 2014 May 22-23; Vilnius: Lithuania; 2014.
Moshtaghie M, Kaboli M, Malekpouri P. Relationship between road vehicle traffic and noise pollution of Khojir National Park in the viewpoint of feasibility of fencing and soundproofing. International Journal of Environmental Health Engineering 2012;1:33-8.
Office of National and Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). Gross Regional and Provincial Product: Chain Volume Measures 2020 Edition. Bangkok, Thailand: Office of National and Economic and Social Development Council; 2022.
Paiva KM, Cardoso MRA, Paulo PHT. Exposure to road traffic noise: Annoyance, perception and associated factors among Brazil’s adult population. Science of the Total Environment 2019;650(Part 1):978-86.
Phan HAT, Yano T, Phan HYT, Nishimura T, Sato T, Hashimoto Y. Annoyance caused by road traffic noise with and without horn sounds. Acoustic Science and Technology 2009;30:327-37.
Peeters B, Blokland GV. The Noise Emission Model for European Road Traffic. Vught, Netherland: M+P-Consulting Engineers; 2007.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2020 Nov 19]. Available from: https://www.R-project.org/.
Sieber C, Ragettli MS, Brink M, Olaniyan T, Baatjies R, Saucy A, et al. Comparison of sensitivity and annoyance to road traffic and community noise between a South African and a Swiss population sample. Environmental Pollution 2018;241:1056-62.
Singhal V, Jain S, Parida M. Train sound level detection system at unmanned railway level crossings. European Transport/ Trasporti Europei 2018;68:1-18.
Sung JH, Lee J, Park SJ, Sim CS. Relationship of transportation noise and annoyance for two metropolitan cities in Korea: Population based study. PLoS ONE 2016;11:1-10.
Thareejit M, Sihabut T, Patthanaissaranukool W. The association between road traffic noise and annoyance levels in residential and sensitive areas of Ayutthaya, Thailand. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology 2020;25:1-13.
Tripura DD, Sarkar PP. Traffic noise prediction model in Agartala City, India. International Review of Applied Engineering Research 2011;1:93-8.
World Health Organization (WHO). Environmental noise guidelines for the European region [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2022 Jun 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/europe/ publications/i/item/9789289053563.
Zamorano-González B, Pena-Cardenas F, Velázquez-Narváez Y, Parra-Siera V, Vargas-Martinez JI, Monreal-Aranda O, et al. Traffic noise annoyance in the population of North Mexico: Case study on the daytime period in the city of Matamoros. Frontiers in Psychology 2021;12:Article No. 657428.
Zamar D, McNeney B, Graham J. Elrm: Software implementing exact-like inference for logistic regression models. Journal of Statistical Software 2007;21:1-18.