Individual and Combined Effects of Pesticides with Active Ingredients of Mancozeb and Methomyl on the DNA Damage of Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820; Cladocera, Daphniidae) 10.32526/ennrj/21/20230036
Main Article Content
Abstract
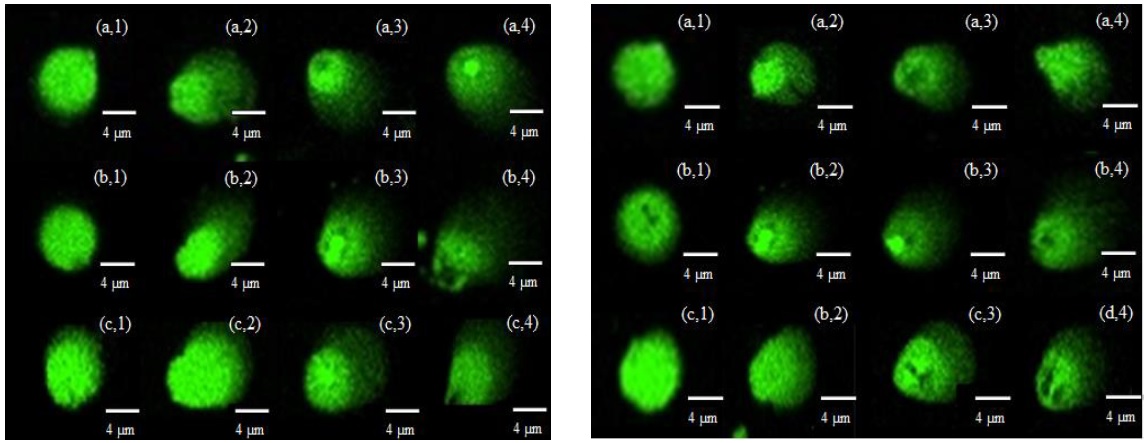
Mancozeb and methomyl are active ingredients commonly contained in pesticides applied in shallot farming. Surface runoff can carry pesticide residues that enter water bodies and affect non-target organisms, such as Daphnia magna. This study evaluated the genotoxicity effects of individual and combined mancozeb and methomyl on the DNA damage of D. magna. Organisms at 24 h old and 48 h old were exposed to individual and combined concentrations of mancozeb and methomyl for 24 h to obtain the LC50-24 h values. These values were used to evaluate DNA damage by calculating the tail intensity (TI) (%), tail moment (TM), and tail factor (TF). Results showed that based on the LC50-24 h values, methomyl has the highest toxicity level, followed by the mancozeb:methomyl combination, and then mancozeb. The combination index of mancozeb:methomyl for both D. magna ages (24 h and 48 h) indicated that the two pesticides antagonistically interact (CI>1). However, based on TI%, TM, and TF values, the level of damage was almost the same between the individual and combined pesticide concentrations, and the DNA damage was more massive with increased pesticide concentration. The DNA damage of 24 h old and 48 h old D. magna did not significantly differ. Increased DNA damage in D. magna indicated that this parameter was sensitive to the presence of pesticides. In application, DNA damage can be used as a biomarker for biomonitoring pesticide pollution in the aquatic ecosystem.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Aktar MW, Sengupta D, Chowdhury A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdisciplinary Toxicology 2009;2(1):1-12.
Alwaini F. Genotoxic Effects of Mancozeb on DNA Damage of Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820; Cladocera, Daphniidae) [dissertation]. Indonesia, Universitas Gadjah Mada; 2021 (in Indonesian)
Antunes SC, Almeida RA, Carvalho T, Lage OM. Feasibility of planctomycetes as a nutritional or supplementary food source for Daphnia spp. International Journal of Limnology 2016; 52:317-25.
Araujo GS, Pinheiro C, Pestana JLT, Soares AMVM, Abessa DMS, Loureiro S. Toxicity of lead and mancozeb differs in two monophyletic Daphnia species. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019;178:230-8.
Ariyanti DP. Genotoxic Effects of Methomyl on DNA Damage of Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820; Cladocera, Daphniidae) [dissertation]. Indonesia, Universitas Gadjah Mada; 2021 (in Indonesian).
Asita OA, Makhalemele R. Genotoxic effects of dithane, malathion, and garden ripcord on onion root tip cells. African Journal of Food Agriculture Nutrition and Development 2009;9(4):1191-209.
Azqueta A, Collins AR. The essential comet assay: A comprehensive guide to measuring DNA damage and repair. Archives of Toxicology 2013;87(6):949-68.
Castro M, Sobek A, Yuan B, Breitholtz M. Bioaccumulation potential of CPs in aquatic organisms: Uptake and depuration in Daphnia magna. Environmental Science and Technology 2019;53(16):9533-41.
Christin F, Elystia S, Yenie E. Acute toxicity test of tofu liquid waste against Daphnia magna with the renewal test method. Jurnal Teknik 2015;2(2):1-9 (in Indonesian).
European Commission (EC). Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market. Ispra, Italy: European Commission Joint Research Centre; 2003.
Darlina, Rahardjo T, Syaifudin M. Evaluation of the relationship of radiation dose to DNA damage of lymphocyte cells by using the comet test. Jurnal Sains dan Teknologi Nuklir Indonesia 2018;19(1):13-20 (in Indonesia).
Focke F, Schuermann D, Kuster N, Schar P. DNA fragmentation in human fibroblast under extremely low electromagnetic field exposure. Mutation Research 2010;683:74-83.
Hart RW, Hall KY, Daniel FB. DNA repair and mutagenesis in mammalian cells. Photochemistry and Photobiology 1978; 28:131-55.
Hertika AMS, Baghaz R. Ecotoxicology for Aquatic Environments. Malang, Indonesia: UB Press; 2019 (in Indonesian).
Izdihar RNT. Genotoxic Effects of Methomyl and Mancozeb on DNA Damage of Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820; Cladocera, Daphniidae) [dissertation]. Indonesia, Universitas Gadjah Mada; 2021 (in Indonesian).
Jha AN. Ecotoxicological applications and significance of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 2008;23:207-21.
Kaur K, Kaur R. Occupational pesticide exposure, impaired DNA repair, and disease. Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2018;22(2):74-81.
Klüttgen B, Dülmer U, Engels M, Ratte HT. ADaM, an artificial freshwater for the culture of zooplankton. Water Research 1994;28:743-6.
Knapik LFO, Ramsdorf W. Ecotoxicity of malathion pesticide and its genotoxic effects over the biomarker comet assay in Daphnia magna. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2020;192(264):1-9.
Kretschmann A, Ashauer R, Preuss TG, Spaak P, Escher BI, Hollender J. Toxicokinetic model describing bioconcentration and biotransformation of diazinon in Daphnia magna. Environmental Science and Technology 2011;45:4995-5002.
Liang CA, Chang SS, Chen HY, Tsai KF, Lee WC, Wang IK, et al. Human poisoning with methomyl and cypermethrin pesticide mixture. Toxics 2023;11(372):1-10.
Li X, Naseem S, Hussain R, Ghaffar A, Li K, Khan A. Evaluation of DNA damage, biomarkers of oxidative stress, and status of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater fish (Labeo rohita) exposed to pyriproxyfen. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2022;2022:Article No. 5859266.
Liyan Z, Ying H, Guangxing L. Using DNA damage to monitor water environment. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 2005;23:340-8.
Lorenzo Y, Costa S, Collins AR, Azqueta A. The comet assay, DNA damage, DNA repair, and cytotoxicity: Hedgehogs are not always dead. Mutagenesis 2013;28(4):427-32.
Lushchak VI, Matviishyn TM, Husak VV, Storey JM, Storey KB. Pesticide toxicity: Mechanistic approach. EXCLI Journal 2018;17:1101-36.
Mahmood I, Imadi SR, Shazadi K, Gul KA. Effects of pesticides on environment. In: Hakeem K, Akhtar M, Abdullah S, editors. Plant, Soil and Microbes. Switzerland: Springer, Cham; 2015. p. 260.
Markovsky E, Baabur-Cohen H, Satchi-Fainaro R. Anticancer polymeric nanomedicine bearing synergistic drug combination is superior to a mixture of individually-conjugated drugs. Journal of Controlled Release 2014;187:145-57.
Mayer FR, Ellersieck MR. Manual of Acute Toxicity: Interpretation and Data Base for 410 Chemicals and 66 Species of Freshwater Animals. Columbia, USA: U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service; 1986.
Menconi M, Beckman J. Hazard Assessment of the Insecticide Methomyl to Aquatic Organism in the San Joaquin River System. California, USA: State of California the Resources Agency Department of Fish and Game; 1996.
Mitchelmore CL, Birmelin C, Livingstone DR, Chipman JK. Detection of DNA strand breaks in isolated mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) digestive gland cells using the “comet” assay. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 1998;41(1):51-8.
Nebeker AV, Ciarns MA, Onjukka ST, Titus RH. Effect of age on sensitivity of D. magna to cadmium, copper and cyanazine. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 1986;55:527-30.
Nunes B, Leal C, Rodrigues S, Antunes SC. Assessment of ecotoxicological effects of ciprofloxacin in Daphnia magna: Life-history traits, biochemical and genotoxic effects. Water Science and Technology 2018;2017(3):835-44.
Pellacani C, Buschin A, Furlini M, Poli P, Rossi C. A battery of in vivo and in vitro tests useful for genotoxic pollutant detection in surface waters. Aquatic Toxicology 2006;77:1-10.
Pellegri V, Gorbi G, Buschini A. Comet assay on D. magna in eco-genotoxicity testing. Aquatic Toxicology 2014;155:261-8.
Pellegri V, Gorbi G, Buschini A. DNA damage detection by comet assay on Daphnia magna: Application in freshwater bio-monitoring. Science of the Total Environment 2020;705:1-11.
Pereira JL, Goncalves D. Effects of food availability on the acute and chronic toxicity of the insecticide methomyl on Daphnia spp. Science of the Total Environment 2007;386(1-3):9-20.
Phromchaloem C, Nakphlaiphan A, Piriyamasakul S, Pruksarojanakul W, Pewnim T. Single cell gel electrophoresis of microcrustaceans Moina macrocopa exposed to cadmium. Veridian E-Journal Science and Technology Silpakorn University 2018;5(1):36-45.
Prasath A, Panneerselvan L, Provatas A, Naidu R, Megharaj M. Genotoxicity assessment of acute exposure of 2, 4-dinitroanisole, its metabolites and 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene to Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicology 2016;25:1873-9.
Rajini A, Revathy K, Chitrikha T. Toxicity and reproductive effect of combination pesticide to Daphnia magna. Indian Journal of Science and Technology 2016;9(3):1-5.
Ren Q, Zhao R, Wang C, Li S, Zhang T, Ren Z, et al. The role of AChE in swimming behavior of Daphnia magna: Correlation analysis of both parameters affected by deltamethrin and methomyl exposure. Journal of Toxicology 2017;2017: Article No. 3265727.
Shaposhnikov SA, Salenko VB, Brunborg G, Nygren J, Collins AR. Single-cell gel electrophoresis (the comet assay): Loops or fragments. Electrophoresis 2008;29:3005-12.
Silva ARR, Cardoso DN, Cruz A, Mendo S, Soares AMVM. Long-term exposure of Daphnia magna to carbendazim: How it affects toxicity to another chemical or mixture. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2019;26: 16289-302.
Srivastava A, Singh D. Assessment of malathion toxicity on cytophysiological activity, DNA damage and antioxidant enzymes in root of Allium cepa model. Scientific Reports 2020;10:Article No. 886.
Surtikanti HK, Juansah R, Frisda D. Optimization of Daphnia cultures as test animals in ecotoxicology. Jurnal Biodjati 2017:2(2):83-8.
Seleem AA. Teratogenicity and neurotoxicity effects induced by methomyl insecticide on the developmental stage of Bufo arabicus. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 2019;72:1-9.
Traudt EM, Ranville JF, Meyer JS. Effect of age on acute toxicity of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in individual-metal exposure to Daphnia magna neonates. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry 2017;36(1):113-9.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Registration Eligibility Decision for Mancozeb. Washington, USA: USEPA; 2005.
Vasiljević T, Grujić S, Radišić M, Dujaković N, Laušević M. Pesticide residues in surface water and groundwater. In: Rathore HS, Nollet LML, editors. Pesticides: Evaluation of Environmental Pollution. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press; 2012. p. 259-98.
Yahia D, El-Amir YO, Rushdi M. Mancozeb fungicide-induced genotoxic effects, metabolic alterations, and histological changes in the colon and liver of Sprague Dawley rats. Toxicology and Industrial Health 2019;35(4):265-76.