Bacteriological Assessment of Fecal Contamination in the Sediments of the Gulf of Annaba (Southern Mediterranean): A Preliminary Investigation 10.32526/ennrj/21/20230057
Main Article Content
Abstract
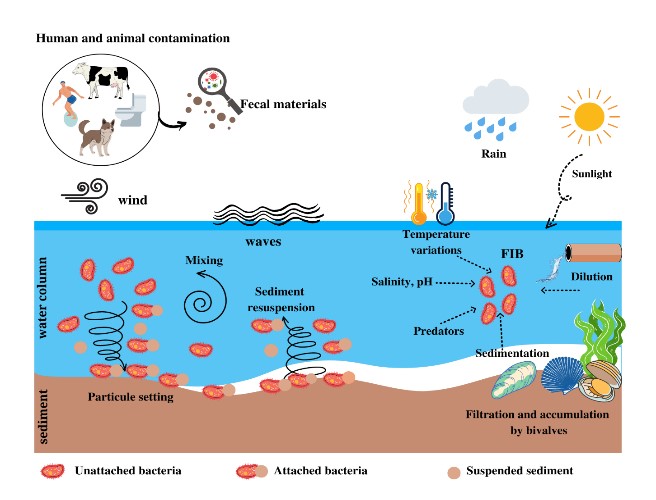
This study investigated the bacteriological and physicochemical quality of seawater and sediment samples collected from four sampling sites in the Gulf of Annaba (Northeastern Algeria) over a one-year period. Culture-based techniques were used to quantify and assess Fecal Indicator Bacteria (FIB) and potentially pathogenic bacteria. Additionally, various physicochemical parameters including temperature, pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and suspended solids were measured. The results revealed seasonal variations in the physicochemical variables, reflecting the influence of environmental conditions in the research area. The highest concentrations of FIB were observed in samples obtained from Sidi Salem and Rezgui Rachid, indicating a possible association with sewage contamination. Furthermore, the sediments collected from all sites exhibited higher levels of FIB and potentially pathogenic bacteria compared to the seawater samples, particularly during the summer and fall seasons.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Abia ALK, Ubomba-Jaswa E, Momba MNB. Competitive survival of Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella typhimurium, and Shigella dysenteriae in riverbed sediments. Microbial Ecology 2016;72:881-9.
Abreu R, Figueira C, Romão D, Brandão J, Freitas MC, Andrade C, et al. Sediment characteristics and microbiological contamination of beach sand: A case-study in the archipelago of Madeira. Science of the Total Environment 2016;573:627-38.
Aminot A, Kérouel R. Hydrology of Marine Ecosystems: Parameters and Analyses. Paris, France: Ifremer; 2004 (in French).
Amri S, Samar MF, Sellem F, Ouali K. Seasonal antioxidant responses in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck 1816) used as a bioindicator of the environmental contamination in the SouthEast Mediterranean. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2017;122:392-402.
Arab S, Nalbone L, Giarratana F, Berbar A. Vibrio spp. in wild and farmed Mytilus galloprovincialis along the Algerian Mediterranean Coast: Evidence of V. cholerae 01 Serotype Ogawa. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology 2021;30:774-83.
Aragonés L, López I, Palazón A, López-Úbeda R, García C. Evaluation of the quality of coastal bathing waters in Spain through fecal bacteria Escherichia coli and Enterococcus. Science of the Total Environment 2016;566:288-97.
Baron S, Larvor E, Chevalier S, Jouy E, Kempf I, Granier SA, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility among urban wastewater and wild shellfish isolates of non-O1/Non-O139 Vibrio cholerae from La Rance Estuary (Brittany, France). Frontiers in Microbiology 2017;8:Article No. 1637.
Barreras H Jr, Kelly EA, Kumar N, Solo-Gabriele HM. Assessment of local and regional strategies to control bacteria levels at beaches with consideration of impacts from climate change. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2019;138:249-59.
Basili M, Campanelli A, Frapiccini E, Luna GM, Quero GM. Occurrence and distribution of microbial pollutants in coastal areas of the Adriatic Sea influenced by river discharge. Environmental Pollution 2021;285:Article No. 117672.
Boufafa M, Kadri S, Redder P, Bensouilah M. Occurrence and distribution of fecal indicators and pathogenic bacteria in seawater and Perna perna mussel in the Gulf of Annaba (Southern Mediterranean). Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021;28:46035-52.
Chapman D. Water Quality Assessments: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring. London and New York: Taylor and Francis; 1996.
Chávez-Díaz LV, Gutiérrez-Cacciabue D, Poma HR, Rajal VB. Sediments quality must be considered when evaluating freshwater aquatic environments used for recreational activities. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health 2020;223:159-70.
Crabill C, Donald R, Snelling J, Foust R, Southam G. The impact of sediment fecal coliform reservoirs on seasonal water quality in Oak Creek, Arizona. Water Research 1999;33:2163-71.
Craig DL, Fallowfield HJ, Cromar NJ. Use of microcosms to determine persistence of Escherichia coli in recreational coastal water and sediment and validation with in situ measurements. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2004;96:922-30.
Curran JF, Zaggia L, Quero GM. Metagenomic characterization of microbial pollutants and antibiotic- and metal-resistance genes in sediments from the Canals of Venice. Water 2022; 14:Article No. 1161.
Davies CM, Bavor HJ. The fate of storm water‐associated bacteria in constructed wetland and water pollution control pond systems. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2000;89:349-60.
Debnath A, Mizuno T, Miyoshi SI. Comparative proteomic analysis to characterize temperature-induced viable but non-culturable and resuscitation states in Vibrio cholerae. Microbiology 2019;165:737-46.
Esiobu N, Mohammed R, Echeverry A, Green M, Bonilla T, Hartz A, et al. The application of peptide nucleic acid probes for rapid detection and enumeration of eubacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in recreational beaches of S. Florida. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2004; 57:157-62.
Fang T, Cui Q, Huang Y, Dong P, Wang H, Liu WT, et al. Distribution comparison and risk assessment of free-floating and particle-attached bacterial pathogens in urban recreational water: Implications for water quality management. Science of the Total Environment 2018;613:428-38.
Garrido-Pérez MC, Anfuso E, Acevedo A, Perales-Vargas-Machuca JA. Microbial indicators of faecal contamination in waters and sediments of beach bathing zones. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health 2008;211:510-7.
González-Fernández A, Symonds EM, Gallard-Gongora JF, Mull B, Lukasik JO, Navarro PR et al. Relationships among microbial indicators of fecal pollution, microbial source tracking markers, and pathogens in Costa Rican coastal waters. Water Research 2021;188:Article No. 116507.
Gutiérrez-Cacciabue D, Teich I, Poma HR, Cruz MC, Balzarini M, Rajal VB. Strategies to optimize monitoring schemes of recreational waters from Salta, Argentina: A multivariate approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2014;186:8359-80.
Hébert S, Légaré S. Monitoring the water quality of rivers and small streams [Internet]. 2000 [cited 2017 Nov 13]. Available from: https://belsp.uqtr.ca/id/eprint/1288/ (in French).
Hespanha AC, Minto BW, Cardozo MV, Menezes MP, Tasso JB, Moraes PC. Contamination by antimicrobial-resistant enterobacteria isolated from cell phones and hands in a veterinary hospital. Acta Veterinaria Hungarica 2021;69:216-22.
Hidouci S, Djebar AB, Amara R, Sahraoui EH. Bacterial quality of coastal waters of Annaba (East Algeria). European Journal of Scientific Research 2014;120:488-93.
Official Journal of the Algerian Republic (OJAR). OJAR Guidelines for Bathing Water Quality Requirements: Volume 46. Algeria: OJAR; 1993 (in French).
Kadri S, Dahel A, Djebbari N, Barour C, Bensouilah M. Environmental parameters influence on the bacteriological water quality of the Algerian North East coast. International Journal of Biosciences 2015;11:151-65.
Kadri S, Belhaoues S, Touati H, Boufafa M, Djebbari N, Bensouilah M. Environmental parameters and bacteriological quality of the Perna perna mussel (North East Algerian coast). International Journal of Biosciences 2017;11:151-65.
Karbasdehi VN, Dobaradaran S, Nabipour I, Ostovar A, Arfaeinia H, Vazirizadeh A, et al. Indicator bacteria community in seawater and coastal sediment: The Persian Gulf as a case. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering 2017;15:1-15.
Lamine I, Alla AA, Bourouache M, Moukrim A. Monitoring of physicochemical and microbiological quality of Taghazout Seawater (Southwest of Morocco): Impact of the new tourist resort “Taghazout Bay”. Journal of Ecological Engineering 2019;20(7):79-89.
Luna GM, Dell’Anno A, Pietrangeli B, Danovaro R. A new molecular approach based on qPCR for the quantification of fecal bacteria in contaminated marine sediments. Journal of Biotechnology 2012;157:446-53.
Luna GM, Quero GM, Perini L. Next generation sequencing reveals distinct fecal pollution signatures in aquatic sediments across gradients of anthropogenic influence. Advances in Oceanography and Limnology 2016;7:115-24.
Malham SK, Rajko-Nenow P, Howlett E, Tuson KE, Perkins TL, Pallett DW, et al. The interaction of human microbial pathogens, particulate material and nutrients in estuarine environments and their impacts on recreational and shellfish waters. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts 2014;16:2145-55.
Mihanović H, Vilibić I, Šepić J, Matić F, Ljubešić Z, Mauri E, et al. Observation, preconditioning and recurrence of exceptionally high salinities in the Adriatic Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 2021;8:Article No. 834.
Mohammed RL, Echeverry A, Stinson CM, Green M, Bonilla TD, Hartz A, et al. Survival trends of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Clostridium perfringens in a sandy South Florida beach. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2012;64:1201-9.
Mote BL, Turner JW, Lipp EK. Persistence and growth of the fecal indicator bacteria enterococci in detritus and natural estuarine plankton communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2012;78:2569-77.
O'Mullan GD, Juhl AR, Reichert R, Schneider E, Martinez N. Patterns of sediment-associated fecal indicator bacteria in an urban estuary: Benthic-pelagic coupling and implications for shoreline water quality. Science of the Total Environment 2019;656:1168-77.
Perkins TL, Clements K, Baas JH, Jago CF, Jones DL, Malham SK, et al. Sediment composition influences spatial variation in the abundance of human pathogen indicator bacteria within an estuarine environment. PLoS ONE 2014;9:e112951.
Rincé A, Balière C, Hervio-Heath D, Cozien J, Lozach S, Parnaudeau S, et al. Occurrence of bacterial pathogens and human noroviruses in shellfish-harvesting areas and their catchments in France. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018; 9:Article No. 2443.
Rozen Y, Belkin S. Survival of enteric bacteria in seawater. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2001;25:513-29.
Rodier J, Legube B, Merlet N, Brunet R. Water Analysis: Natural Waters, Wastewater, Seawater. Paris, France: Dunod; 2009.
Shah AH, Abdelzaher AM, Phillips M, Hernandez R, Solo‐Gabriele HM, Kish J, et al. Indicator microbes correlate with pathogenic bacteria, yeasts and helminthes in sand at a subtropical recreational beach site. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2011;110:1571-83.
Soumastre M, Piccini J, Rodríguez-Gallego L, González L, Rodríguez-Graña L, Calliari D, et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics and potential pathogenicity of fecal coliforms in coastal shallow groundwater wells. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2022;194:1-17.
Valério E, Santos ML, Teixeira P, Matias R, Mendonça J, Ahmed W, et al. Microbial source tracking as a method of determination of beach sand contamination. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022; 19:Article No. 7934.
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y. Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: Analysis, assessment, and management. Exposure and Health 2020;12:307-22.
Whitman RL, Harwood VJ, Edge TA, Nevers MB, Byappanahalli M, Vijayavel K, et al. Microbes in beach sands: Integrating environment, ecology and public health. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 2014;13:329-68.
Zhang Q, He X, Yan T. Differential decay of wastewater bacteria and change of microbial communities in beach sand and seawater microcosms. Environmental Science and Technology 2015;49:8531-40.
Zhang SY, Tsementzi D, Hatt JK, Bivins A, Khelurkar N, Brown J, et al. Intensive allochthonous inputs along the Ganges River and their effect on microbial community composition and dynamics. Environmental Microbiology 2019;21:182-96.
Zimmer-Faust AG, Thulsiraj V, Marambio-Jones C, Cao Y, Griffith JF, Holden PA, et al. Effect of freshwater sediment characteristics on the persistence of fecal indicator bacteria and genetic markers within a Southern California watershed. Water Research 2017;119:1-11.