Adsorptive Removal of Chromium (VI) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Banana Pseudo Stem Adsorbent 10.32526/ennrj/21/20230166
Main Article Content
Abstract
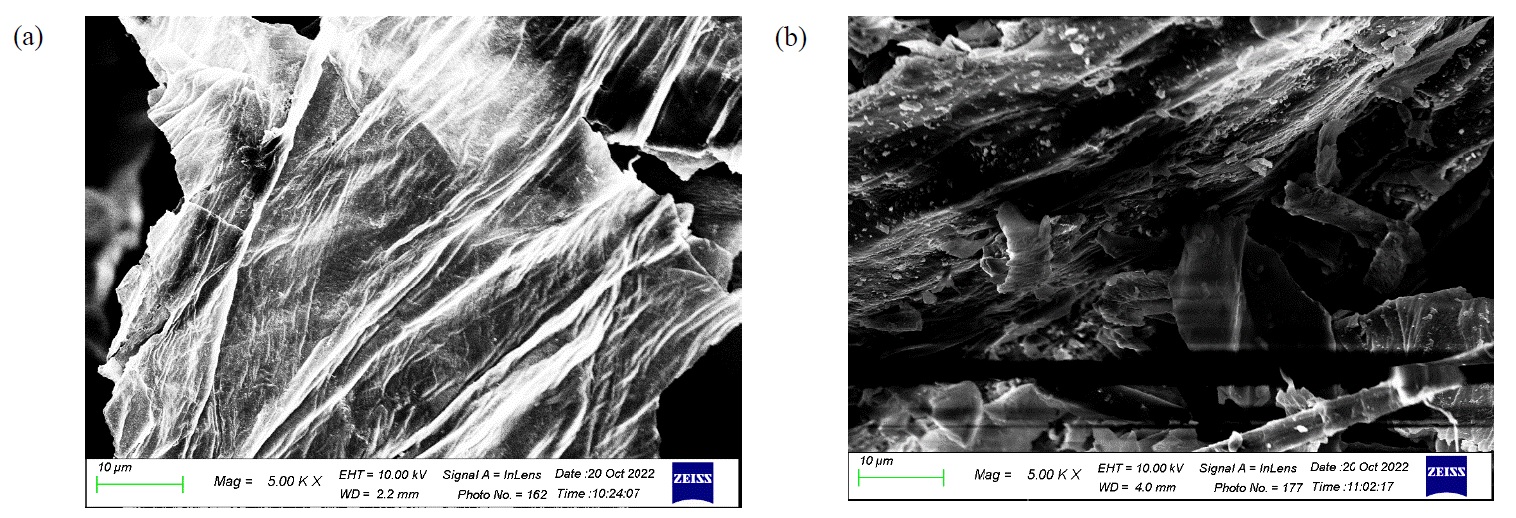
The presence of Cr ions in wastewater must be treated before being released into the environment due to its detrimental impact on both the environment and human health. In this study, the removal of Cr (VI) ions from an aqueous solution was investigated by adsorption using an adsorbent derived from agriculture wastes, banana pseudo stem. The adsorbent was prepared by oven-drying the banana stem waste at 105°C for 24 h. The surface structure of the adsorbent was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Batch adsorption experiments were carried out to determine the removal efficiency of Cr (VI) ions based on four adsorption operation parameters: pH of the solution, adsorbent dosage, contact time and initial concentration of ion solution. At room temperature, the highest Cr (VI) ions removal of 88.2% was achieved using 0.5 g banana pseudo stem adsorbent, with an initial concentration of chromium solution of 500 ppm at pH 2 and after 90 min of contact time. For the equilibrium study, the experimental data were better fitted by the Langmuir isotherm model with a maximum adsorption capacity of 33.33 mg/g. Meanwhile, the kinetic isotherm was best fitted by the pseudo-second-order model. Therefore, the banana pseudo stem showed great potential as an efficient, low-cost and natural green adsorbent for Cr (VI) ions removal from an aqueous solution via adsorption.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Abilio TE, Soares BC, José JC, Milani PA, Labuto G, Carrilho ENVM. Hexavalent chromium removal from water: Adsorption properties of in natura and magnetic nanomodified sugarcane bagasse. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021;28:24816-29.
Abubeah R, Altaher H, Khalil TE. Removal of hexavalent chromium using two innovative adsorbents. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal 2018;17(7):1621-34.
Aharchaou I, Py JS, Cambier S, Loizeau JL, Cornelis G, Rousselle P, et al. Chromium hazard and risk assessment: New insights from a detailed speciation study in a standard test medium. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2018;37(4):983-92.
Badessa TS, Wakuma E, Yimer AM. Bio-sorption for effective removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater using Moringa stenopetala seed powder (MSSP) and banana peel powder (BPP). BMC Chemistry 2020;14:Article No. 71.
Baharim NH, Sjahrir F, Taib RM, Idris N, Daud TAT. Methylene blue adsorption by acid post-treated low temperature biochar derived from banana (Musa Acuminata) pseudo stem. Sains Malaysiana 2023;52(2):547-61.
Bayuo J, Pelig-Ba KB, Abukari MA. Adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution unto groundnut shell. Applied Water Science 2019;9:Article No. 107.
Birhanu Y, Leta S, Adam G. Removal of chromium from synthetic wastewater by adsorption onto Ethiopian low-cost Odaracha adsorbent. Applied Water Science 2020;10:Article No. 227.
Garg R, Garg R, Sillanpää M, Alimuddin, Khan MA, Mubarak NM, et al. Rapid adsorptive removal of chromium from wastewater using walnut-derived biosorbents. Scientific Report 2023;13:Article No. 6859.
Guo X, Hu W, Gu Z, Li J, Xie Z, Fang C, et al. Enhanced removal of aqueous chromium (VI) by KOH-activated soybean straw-based carbon. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 2021;232:Article No. 484.
Gupta GK, Ram M, Bala R, Kapur M, Mondal MK. Pyrolysis of chemically treated corncob for biochar production and its application in Cr(VI) removal. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy 2018;37:1606-17.
Hanafiah SFM, Salleh NFM, Ghafar NA, Shukri NM, Kamarudin NHN, Hanapi M, et al. Efficiency of coconut husk as an agricultural adsorbent in removal of chromium and nickel ions from aqueous solution. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2020;596:Article No. 012048.
Jock AA, Oboh IO, Inyang UE, Ganchok LP, Adeku O. Chromium and nickel metal ions removal from contaminated water using Nigerian bentonite clay. Water Practice and Technology 2021;16(3):825-36.
Kokate S, Parasuraman K, Prakash H. Adsorptive removal of lead ion from water using banana stem scutcher generated in fiber extraction process. Results in Engineering 2022;15:Article No. 100439.
Li A, Deng H, Jiang Y, Ye C. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by Mg-loaded biochars: Adsorption process and removal mechanism. Materials (Basel) 2020;13(4):Article No. 947.
Liu X, Li G, Chen C, Zhang X, Zhou K, Long X. Banana stem and leaf biochar as an effective adsorbent for cadmium and lead in aqueous solution. Scientific Reports 2022;12:Article No. 1588.
Martín RD, Mouhaffel AG, Lisperguer RC, Rio CD. Kinetic study of absorption of chromium (VI) using canary bananas peels in contaminated water. International Journal of Innovation and Scientific Research 2016;22:139-45.
Melese T, Chala K, Ayele Y, Abdisa M. Preparation, characterization of raw corncob adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using batch method. Africa Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry 2020;4(4):81-90.
Parlayici Ş, Pehlivan E. Comparative study of Cr (VI) removal by bio-waste adsorbents: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology 2019;10:Article No. 15.
Payel S, Hashem MA, Sarker M, Nur-A-Tomal AS. Chromium adsorption on banana adsorbent from tannery wastewater: Optimization, isotherm, kinetics and desorption studies. Textile and Leather Review 2020;3(3):118-34.
Qasem NAA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021;4:Article No. 36.
Qi J, Li B, Zhou P, Su X, Yang D, Wu J, et al. Study on adsorption of hexavalent chromium by composite material prepared from iron-based solid wastes. Scientific Report 2023;13:Article No. 135.
Rigueto CVT, Alessandretti I, da Silva DH, Rosseto M, Loss RA, Geraldi CAQ. Agroindustrial wastes of banana pseudo-stem as adsorbent of textile dye: Characterization, kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chemistry Africa 2021;4(2):1069-78.
Selimin MA, Latif AFA, Er YC, Muhamad MS, Basri H, Lee TC. Adsorption efficiency of banana blossom peels (Musa acuminata Colla) adsorbent for chromium (VI) removal. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022;57(3):1262-8.
Song D, Pan K, Tariq A, Azizullah A, Sun F, Li Z, et al. Adsorptive removal of toxic chromium from waste-water using wheat straw and Eupatorium adenophorum. PLoS ONE 2021;11(12):e0167037.
Speer RM, Wise SS, Croom-Perez TJ, Aboueissa AEM, Martin-Bras M, Barandiaran M, et al. A comparison of particulate hexavalent chromium cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in human and leatherback sea turtle lung cells from a one environmental health perspective. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2019;376:70-81.
Stambulska UY, Bayliak MM, Lushchak VI. Chromium (VI) toxicity in legume plants: Modulation effects of rhizobial symbiosis. Biomed Research International 2018;2018:Article No. 8031213.
Sukmana H, Bellahsen N, Pantoja F, Hodur C. Adsorption and coagulation in wastewater treatment: Review. Progress in Agricultural Engineering Sciences 2021;17(1):49-68.
Taib RM. Pyrolysis of Banana Pseudo-Stem and Leaf through Fast and Slow Processes [dissertation]. Penang, Universiti Sains Malaysia; 2019.
Xu S, Yu W, Liu S, Xu C, Li J, Zhang Y. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium using banana pseudostem biochar and its mechanism. Sustainability 2018;10:Article No. 4250.
Yang YM, Chen N, Feng C, Li M, Gao Y. Chromium removal using a magnetic corncob biochar/polypyrrole composite by adsorption combined with reduction: Reaction pathway and contribution degree. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2018;556:201-9.