Formulation of Novel Microbial Consortia for Rapid Composting of Biodegradable Municipal Solid Waste: An Approach in the Circular Economy 10.32526/ennrj/22/20230270
Main Article Content
Abstract
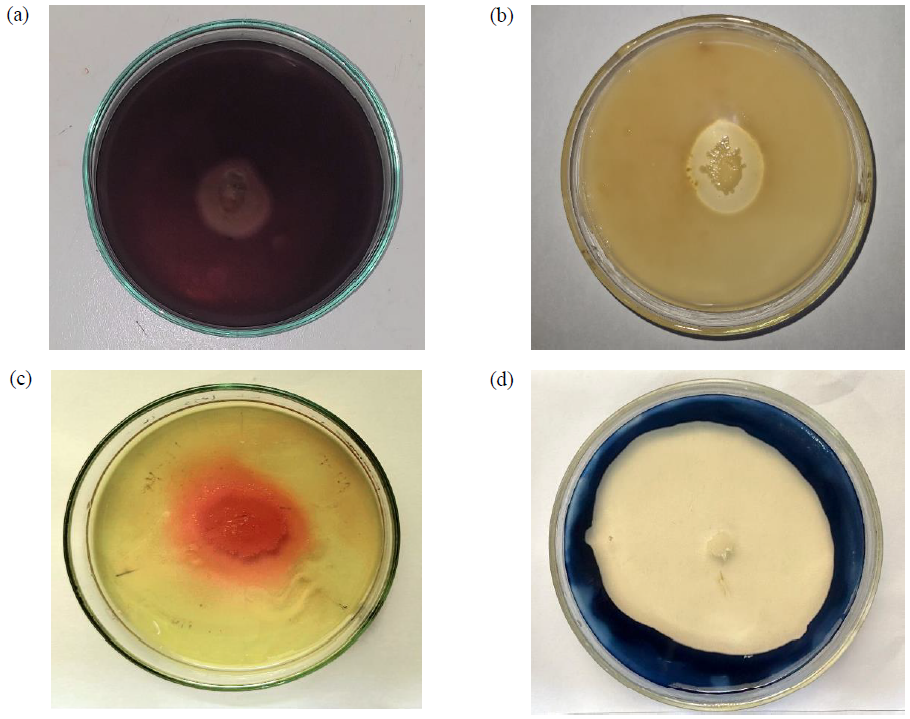
Urbanization and rapid industrialization have led to the escalation of municipal solid waste generation and accumulation. Composting is widely recognized as a sustainable solution for solid waste management. However, its long-term investment is considered a disadvantage. The present research study discusses the rapid biotransformation of solid waste into valorized compost. Bacteria were isolated from soil, solid waste, and leachate samples from open dump sites. From the 18 different bacterial consortia created using potential isolates, the five most promising consortia were selected based on concurrent different enzyme production. These selected consortia were incorporated into typical compost bins with Municipal Solid Waste (MSW). Daily monitoring of enzymatic activity, pH, conductivity, bulk density, moisture, and temperature, along with other composting parameters, was conducted. The study’s results demonstrated that consortium No. 5, comprising Bacillus haynesii, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and Bacillus safensis, exhibited significant (p<0.05) enzyme activity of cellulase, amylase, lipase and proteinase enzymes during composting compared to the control and other treatment setups. Consortium No. 5 also facilitated rapid and successful composting, as evidenced by significant alterations of composting parameters by exhibiting a shorter average composting time, reducing it from 110±10 days to 20±3 days, showcasing the potential applicability of formulated bacterial consortium as a sustainable and greener approach to the global solid waste problem. The novelty of this study lies in the isolation of local bacterial strains from open dump sites soil, MSW, and MSW leachate samples, which were then utilized in the composting organic fraction of MSW, enhancing the potential for effective waste management.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Al-Dhabi NA, Esmail GA, Mohammed Ghilan AK, Valan Arasu M. Composting of vegetable waste using microbial consortium and biocontrol efficacy of Streptomyces sp. Al-Dhabi 30 is isolated from the Saudi Arabian environment for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2019;11(23):Article No. 6845.
Andlar M, Rezic T, Mardetko N, Kracher D, Ludwig R, Santek B. Lignocellulose degradation: An overview of fungi and fungal enzymes involved in lignocellulose degradation. Engineering in Life Sciences 2018;18(11):768-78.
Awasthi MK, Wang Q, Wang M, Chen H, Ren X, Zhao J, et al. In-vessel co-composting of food waste employing enriched bacterial consortium. Food Technology and Biotechnology 2018;56(1):83-9.
Blair EM, Dickson KL, O’Malley MA. Microbial communities and their enzymes facilitate degradation of recalcitrant polymers in anaerobic digestion. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2021;64:100-8.
Chen L, Li W, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Zhang S, Meng L. Effects of compound bacterial agent on gaseous emissions and compost maturity during sewage sludge composting. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022;366:Article No. 133015.
Chen Z, Li Y, Peng Y, Ye C, Zhang S. Effects of antibiotics on hydrolase activity and structure of microbial community during aerobic co-composting of food waste with sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology 2021;321:Article No. 124506.
Chukwuma OB, Rafatullah M, Kapoor RT, Tajarudin HA, Ismail N, Siddiqui MR, et al. Isolation and characterization of Lignocellulolytic bacteria from municipal solid waste landfill for identification of potential hydrolytic enzyme. Fermentation 2023;9(3):Article No. 298.
Dantroliya S, Joshi C, Mohapatra A, Shah D, Bhargava P, Bhanushali S, et al. Creating wealth from waste: An approach for converting organic waste into value-added products using microbial consortia. Environmental Technology and Innovation 2022;25:Article No. 102092.
Dhiman VK, Chauhan V, Kanwar SS, Singh D, Pandey H. Purification and characterization of actinidin from Actinidia deliciosa and its utilization in inactivation of α-Amylase. Bulletin of the National Research Centre 2021; 45:Article No. 213.
Finore I, Feola A, Russo L, Cattaneo A, Donato PD, Nicolaus B, et al. Thermophilic bacteria and their thermozymes in composting processes: A review. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture 2023;10(1):Article No. 7.
Goushterova A, Nacheva L, Dinev N, Kabaivanova L. Addition of microbial inoculum as a way for compost improvement by enhancing the activities of hydrolytic enzymes. Baltica 2020;33(9):16-35.
Gunaratne KBB, Wijerathna PAKC, Manage PM. Identification of Salmonella sp., Shigella sp., and Pathogenic E. coli in dug wells water around Karadiyana, Meethotamulla, and Kerawalapitiya open dump sites. Proceedings of International Forestry and Environment Symposium; 2024 Jan 5-6, (Vol. 28); Nugegoda, Sri Lanka: University of Sri Jayewardenepura; 2024.
Harindintwali JD, Zhou J, Yu X. Lignocellulosic crop residue composting by cellulolytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria: A novel tool for environmental sustainability. Science of the Total Environment 2020;715:Article No. 136912.
Ince O, Ozbayram EG, Akyol C, Erdem EI, Gunel G, Ince B. Bacterial succession in the thermophilic phase of composting of anaerobic digesters. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020;11:841-9.
Koyama M, Kakiuchi A, Syukri F, Toda T, Tran QNM, Nakasaki K. Inoculation of Neurospora sp. for improving ammonia production during thermophilic composting of organic sludge. Science of the Total Environment 2022;802:Article No. 149961.
Kumar R, Kim TH, Basak B, Patil SM, Kim HH, Ahn Y, et al. Emerging approaches in lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment and anaerobic bioprocesses for sustainable biofuel production. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022;333:Article No. 130180.
Lin H, Cheng Q, Sun W, Yang F, Ding Y, Ma J. Copper exposure effects on antibiotic degradation in swine manure vary between mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Science of the Total Environment 2022;841:Article No. 156759.
Ma Y, Liu Y. Turning food waste to energy and resources towards a great environmental and economic sustainability: An innovative integrated biological approach. Biotechnology Advances 2019;37(7):Article No. 107414.
Mahapatra S, Ali MH, Samal K. Assessment of compost maturity-stability indices and recent development of composting bin. Energy Nexus 2022;6:Article No. 100062.
Malik WA, Javed S. Biochemical characterization of Cellulase from Bacillus subtilis strain and its effect on digestibility and structural modifications of lignocellulose rich biomass. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 2021;9:Article No. 800265.
Meena MD, Dotaniya ML, Meena MK, Meena BL, Meena KN, Doutaniya RK, et al. Maturity indices as an index to evaluate the quality of sulphur-enriched municipal solid waste compost using a variable byproduct of sulphur. Waste Management 2021;126:180-90.
Mei J, Shen X, Gang L, Xu H, Wu F, Sheng L. A novel lignin degradation bacteria-Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SL-7 used to degrade straw lignin efficiently. Bioresource Technology 2020;310:Article No. 123445.
Ng SM, Tey LH, Leong SY, Ng SA. Isolation, screening and characterization of the potential microbes to enhance the conversion of food wastes to bio-fertilizer. Proceedings of AIP Conference; 2019 Sep (Vol. 2157, No. 1); United States of America: American Institute of Physics (AIP); 2019.
Pal DB, Tiwari AK. Sustainable Valorization of Agriculture and Food Waste Biomass: Application in Bioenergy and Useful Chemicals. Springer Nature; 2023.
Pan I. Exploration for thermostable β-Amylaseof a Bacillus sp. isolated from compost soil to degrade bacterial biofilm. Microbiology Spectrum 2021;9(2):e0064721.
Parameswaran R, Liyanage GY, Wijerathna PAKC, Manage PM. Characterization of compost and screening of antibiotic residues, antibiotic-resistant bacteria in commercially available compost in Sri Lanka. Proceedings of International Forestry and Environment Symposium; 2024 Jan 5-6, (Vol. 28); Nugegoda, Sri Lanka: University of Sri Jayewardenepura; 2024.
Patel AR, Mokashe NU, Chaudhari DS, Jadhav AG, Patil UK. Production optimisation and characterisation of extracellular protease secreted by newly isolated Bacillus subtilis AU-2 strain obtained from Tribolium castaneum gut. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2019;19:Article No. 101122.
Rashwan MA, Alkoaik FN, Saleh HAR, Fulleros RB, Ibrahim MN. Maturity and stability assessment of composted tomato residues and chicken manure using a rotary drum bioreactor. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association 2021;71(5):529-39.
Rich N, Bharti A, Kumar S. Effect of bulking agents and cow dung as inoculant on vegetable waste compost quality. Bioresource Technology 2018;252:83-90.
Sahu PK, Singh S, Gupta AR, Gupta A, Singh UB, Manzar N, et al. Endophytic bacilli from medicinal-aromatic perennial Holy basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum L.) modulate plant growth promotion and induced systemic resistance against Rhizoctonia solani in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biological Control 2020;150:Article No. 104353.
Sarkar P, Chourasia R. Bioconversion of organic solid wastes into bio fortified compost using a microbial consortium. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture 2017;6:321-34.
Shah R, Nair SS, Shah MD, Patil SA. Development of augmented microbial consortium for kitchen waste composting. Research Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2022;13(2):365-70.
Sun L, Long M, Li J, Wu R, Ma L, Tang D, et al. Different effects of thermophilic microbiological inoculation with and without biochar on physicochemical characteristics and bacterial communities in pig manure composting. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021;12:Article No. 746718.
Sun Q, Chen J, Wei Y, Zhao Y, Wei Z, Zhang H, et al. Effect of semi-continuous replacements of compost materials after inoculation on the performance of heat preservation of low-temperature composting. Bioresource Technology 2019; 279:50-6.
Wan L, Wang X, Cong C, Li J, Xu Y, Li X, et al. Effect of inoculating microorganisms in chicken manure composting with maize straw. Bioresource Technology 2020;301:Article No. 122730.
Wang L, Wang T, Xing Z, Zhang Q, Niu X, Yu Y, et al. Enhanced lignocellulose degradation and composts fertility of cattle manure and wheat straw composting by Bacillus inoculation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2023;11(3):Article No. 109940.
Wijerathna PAKC, Udayagee KPP, Idroos FS, Manage PM. Waste biomass valorization and its application in the environment. In: Pal DB, Tiwari AK, editors. Sustainable Valorization of Agriculture and Food Waste Biomass: Application in Bioenergy and Useful Chemicals. Singapore: Springer Nature; 2023. p. 1-28.
Wijerathna PAKC, Udayagee KPP, Idroos FS, Manage PM. Novel bacterial consortium for the reduction of composting odor emission and enhancing compost maturation rate in municipal solid waste. Proceedings of 11th Ruhuna International Science and Technology Conference; 2024 Jan 24; Matara, Sri Lanka: University of Ruhuna; 2024.
Zaccardelli M, Sorrentino R, Caputo M, Scotti R, De Falco E, Pane C. Stepwise-selected Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and B. subtilis strains from composted aromatic plant waste able to control soil-borne diseases. Agriculture 2020;10(2):Article No. 30.
Zainudin MHM, Singam JT, Sazili AQ, Shirai Y, Hassan MA. Indigenous cellulolytic aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacterial communities enhanced the composting of rice straw and chicken manure with biochar addition. Scientific Reports 2022;12(1):Article No. 5930.
Zhang Z, Shah AM, Mohamed H, Tsiklauri N, Song Y. Isolation and screening of microorganisms for the effective pretreatment of lignocellulosic agricultural wastes. BioMed Research International 2021;2021:Article No. 5514745.
Zhimo VY, Biasi A, Kumar A, Feygenberg O, Salim S, Vero S, et al. Yeasts and bacterial consortia from kefir grains are effective biocontrol agents of postharvest diseases of fruits. Microorganisms 2020;8(3):Article No. 428.