Applications of Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Air Quality Assessment of NOx and SO2 from Waste Incinerator
Main Article Content
Abstract
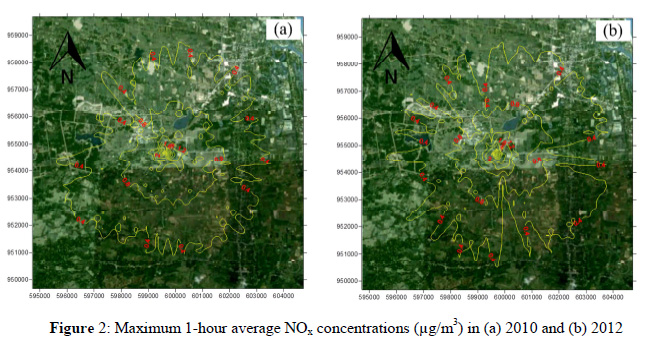
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) are included in the criteria air pollutants and plays the role in the formation of acid rain. Waste incinerator are a major sources of NOx and SO2, particularly on local basic of air pollutions. This study was designed to assess the impact of NOx and SO2 emissions that are emitted from the waste incinerator at Walailak University to the ambient concentrations using an atmospheric dispersion model, AERMOD for the two simulated years of 2010 and 2012. Stack emissions of NOx and SO2 were taken from stack monitoring data of the waste incinerator. Meteorological data were mainly taken from Thai Metrological Department for the study area while terrain data were taken from ASTER GDEM database. Results indicated that maximum NOx concentration were 3.30, 0.30 and 0.13 µg/m3 , respectively for 1-hour, 24-hour and annual average while those for SO2 were 18.68, 1.72 and 0.72 µg/m3 , respectively. Simulated concentrations of NOx and SO2 were well below the values specified in the National Ambient Air Quality Standards of Thailand and World Health Organization Guidelines.
Article Details
How to Cite
Koomsang, R., Chuchue, S., & Kanabkaew, T. (2015). Applications of Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Air Quality Assessment of NOx and SO2 from Waste Incinerator. Environment and Natural Resources Journal, 13(1), 21–27. retrieved from https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ennrj/article/view/70942
Section
Original Research Articles
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.