Improve Quality of Discharge Water from Ratchaburi Electric Power Plant by Plants
Main Article Content
Abstract
Some plants were studied to improve the quality of discharge water from Ratchaburi
Electric Power Plant, which had high conductivity. Experiments were divided into 2 groups.
Each group had 4 treatments and 3 replicates. The pond sizes were 1 X 10 X 1 m3. Group 1 was
anthropogenic soil ponds: sedge, cattail, canna and control (no plant). Group 2 was concrete
ponds: water hyacinth, sacred lotus, water lettuce and control (no plant). The experiment was
performed for 3 separate 3 - monthly periods during November 2008-January 2009, March-May
2009 and July-September 2009.
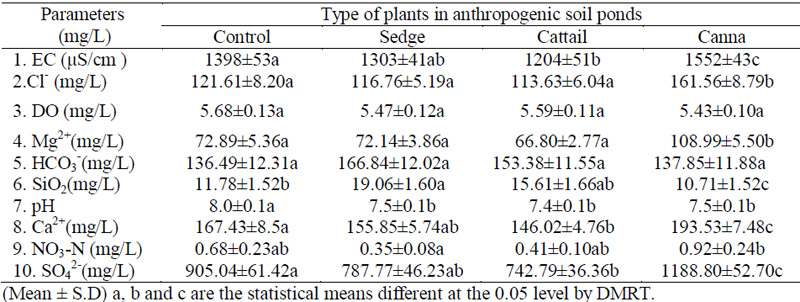
The results in group 1 showed that levels of conductivity, pH, calcium ion, magnesium
ion, chloride ion and sulfate ion in cattail ponds were less than those in the others. The levels of
conductivity, calcium ion, magnesium ion and chloride ion in the canna ponds were higher than
those in the control ponds. Almost all water quality parameters of the sedge and cattail ponds
were not significantly different from the control samples. However, water quality means of the
cattail ponds were lower than the control ponds in most parameters. Therefore, cattail might be
the most efficient plant for treating wastewater from Ratchaburi Power Plant.
The results in group 2 showed that levels of pH, and chloride ion in the water hyacinth
ponds and the levels of conductivity, dissolved oxygen, nitrate – nitrogen, calcium ion and
magnesium ion in the water lettuce ponds were less than those in the others. Almost all water
quality parameters of the sacred lotus ponds were higher than those in control ponds except for
silicate and pH. Almost all the parameters of the water hyacinth and water lettuce ponds were
not significantly different from the control ponds (p>0.05) except for bicarbonate ion but the
water hyacinth means were lower than the control ponds in most parameters except for
bicarbonate ion. Therefore, the water hyacinth might be the most efficient plant for treating
wastewater from Ratchaburi Power Plant.
Article Details
Published articles are under the copyright of the Environment and Natural Resources Journal effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Environment and Natural Resources Journal all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.