Factors influencing adoption of vertical forced-air sulfur dioxide fumigation technology of fresh longan exporters in Thailand
Main Article Content
Abstract
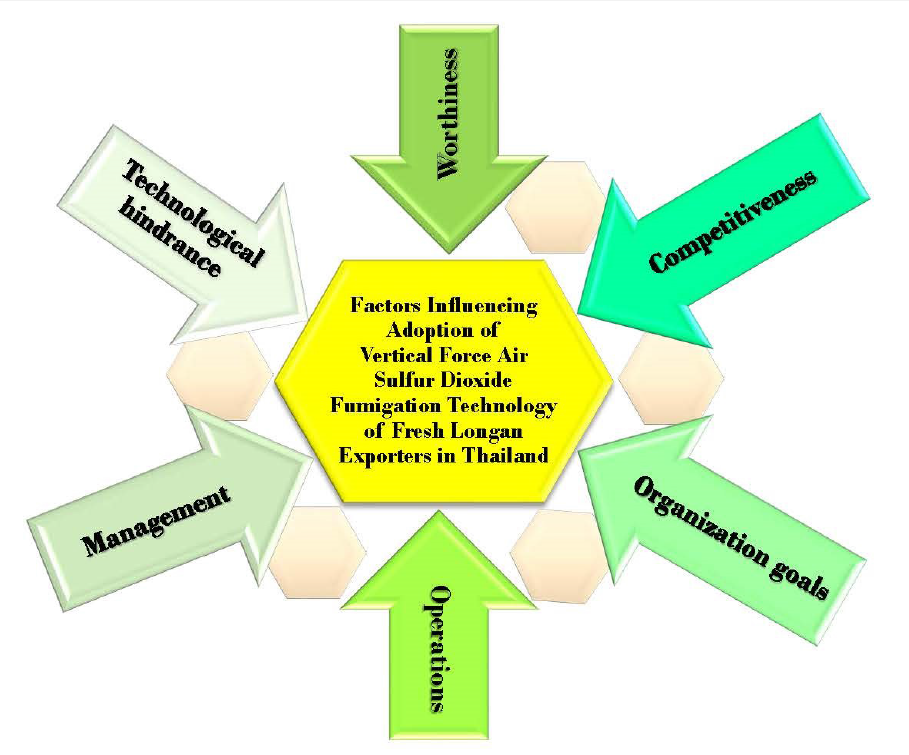
The research aimed to study the factors influencing an adoption of vertical forced-air SO2 fumigation technology of longan exporters of Thailand. A questionnaire was applied as a tool of data collection, from 101 representative samples in the northern and eastern regions of Thailand which are two main plantation areas of fresh longan. Statistical analysis was applied by factor analysis from the in-depth interviews with 36 variables. The result indicates that there were 28 factors in 6 components which influenced the exporters’ decision in adopting the technology with the sum of variance of 53.958%. These components were worthiness, competitiveness, organization goals, operations, management, and technological hindrance. Our findings are useful for further development of the strategic plan and policy, especially for the fresh longan exporters of Thailand, to enhance an adoption of SO2 fumigation with vertical forced-air technology for safer operation and better food safety.
Article Details
References
Office of Agricultural Economics, Situation and trend of agricultural commodities in 2020, http://www.oae.go.th/ assets/portals/1/files/trend2563-Final-Download.pdf.
Regional Commerial Affairs Division, Longan commodities the 3rd week of September 2019 (16 - 20 September 2019), http://kbp.ops.moc.go.th/ewt dl link.php?nid=2343.
J. Phimphimol, Postharvest management of commercial fresh longan 2012, Chiang Mai, Thailand: Chiang Mai Documentary Design, 174.
Y. Jiang, et al., Review: Postharvest biology and handling of longan fruit (Dimocarpus longan Lour.), Postharvest Biology and Technology 26 (2002) 241-252.
L. Hetong, et al., Technologies of post-harvest handling and storage for longan fruits, in 2011 International Conference on New Technology of Agricultural Engineering (ICAE 2011), pp. 758-763.
J. Varith, S. Jaturonglumlert, C. Nitatwichit, P. Supapunt, T. Awirothananon, R. Kongtanajaruanun, P. Intanoo, P. Klinkajorn, Policy proposals to push the Vertical Force-air fumigation technology to perform commercial and enhance the export of fresh longan fruits vol. 1, Chiang Mai, Thailand: Wanida printing.
National Bureau of Agricultural Commodity and Food Standards, Code of practice for sulphur dioxide fumigation of fresh fruits, Government gazette, Announcement and general editions, 2015.
J. Pimpimol, et al., Improved Sulfur Dioxide Fumigation of Fresh Longan Using a Vertical Forced-Air Technique, Acta horticulturae 880 (2010) 415-422.
Department of Agriculture, List of the firms to be recognized, 2016.
Department of Trade Negotiations. Barriers to export longan fruit to China, http://www.thaifta.com/thaifta/portals/0/logancnsep57.pdf
The Oce Agricultural A airs, P.R.C. Thailand fruit market situation in China in 2018 and trends, https://www.opsmoac.go.th/guangzhou-news-files-412991791854
A. L. Asnawi, A. M. Gravell, G. B. Wills, Factor analysis: Investigating important aspects for agile adoption in Malaysia, in 2012 Agile India.
Office of Agricultural Economics, Annual report in 2018.
J. Y. L. Thong, C. S. Yap, CEO characteristics, organizational characteristics and information technology adoption in small businesses, Omega 23(4) (1995) 429-442.