Paper spray mass spectrometry: A new rapid confirmation method for methamphetamine
Main Article Content
Abstract
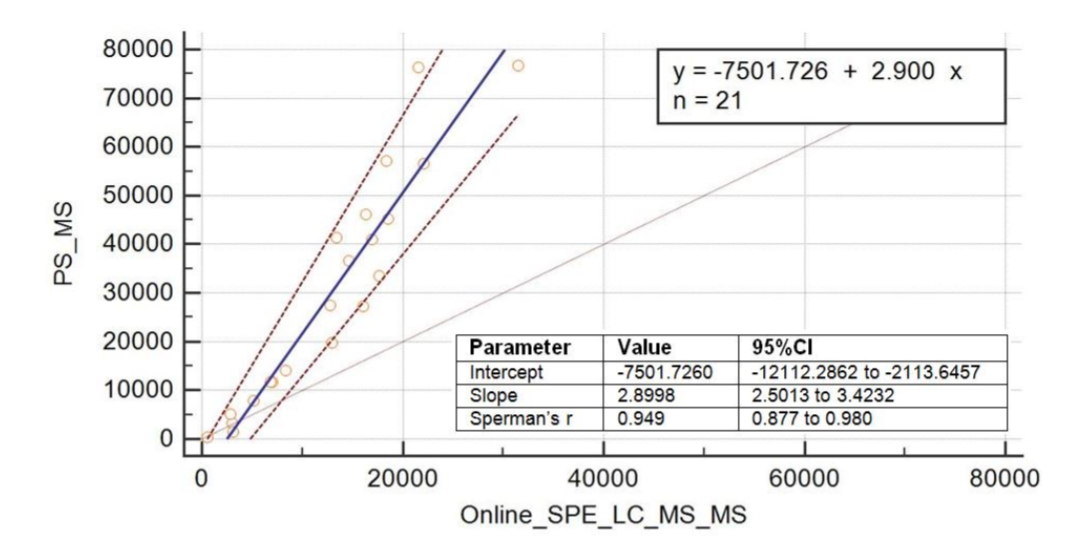
Paper spray mass spectrometry (PS-MS) been shown to be amenable for analysis of drugs and other compounds in biological samples. It has provided a rapid, qualitative and quantitative ambient ionization method for biomolecule analysis, as an alternative to traditional sample preparation and chromatography. The aim of this research is to study the efficiency of postmortem urine methamphetamine (METH) identification using PS-MS (orbitrap) compare with Online-SPE-LC-MS/MS method. Twenty-one of METH positive urine and four of METH negative urine from May 2017-Dec 2019 were randomly sampling and analyzed for METH concentration using both methods, The qualitative results obtained by the PS-MS method founding that twenty-one of METH positive urine cases were passing of three criteria parameters of PS-MS method with the true positive rate equal to 100% and the quantitative results founding that METH concentrations determined by PS-MS method were significantly higher than the results from Online-SPE-LC-MS/MS method (Paired t Test, P value < 0.05). PS-MS method can save time 7.5 fold as compared to the Online-SPE-LC-MS/MS method. In conclusion PS-MS can be used for rapid screening and confirmation of urine METH.
Article Details
References
I. N. Krasnova, J. L. Cadet, Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death, Brain Research Reviews 60(2) (2009) 379 - 407.
C. Chomchai, S. Chomchai, Global patterns of methamphetamine use, Current Opinion in Psychiatry 28(4) (2015) 269 - 274.
UNODC, United Nations Office on Drug and Crime (UNODC) United Nations, World Drug Report, 2020.
H. H. Maurer, Current role of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in clinical and forensic toxicology, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 388(7) (2007) 1315 - 1325.
S. Chiang, W. Zhang, Z. Ouyang, Paper spray ionization mass spectrometry: recent advances and clinical applications, Expert Review of Proteomics 15(10) (2018) 781 - 789.
S. Chiang, W. Zhang, Z. Ouyang, Paper spray ionization mass spectrometry: recent advances and clinical applications, Expert Review of Proteomics 15(10) (2018) 781 - 789.
C. H. Lin, W. C. Liao, H. K. Chen, T. Y. Kuo, Paper spray-MS for bioanalysis, Bioanalysis 6(2) (2014) 199 - 208.
N. E. Manicke, B. J. Bills, C. Zhang, Analysis of biofluids by paper spray MS: advances and challenges, Bioanalysis 8(6) (2016) 589 - 606.
J. Liu, H. Wang, N. E. Manicke, J. M. Lin, R. G. Cooks, Z. Ouyang, Development, characterization, and application of paper spray ionization, Analytical Chemistry 82(6) (2010) 2463 - 2471.
J. McKenna, R. Jett, K. Shanks, N. E. Manicke, Toxicological Drug Screening using Paper Spray High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HR-MS/MS), Journal of Analytical Toxicology 42(5) (2018) 300 - 310.