Effect of chemical fertilizer on leaf nutrient concentration and fruit quality in rose apple (Syzygium jambos L.) cv. Tabtimjan
Main Article Content
Abstract
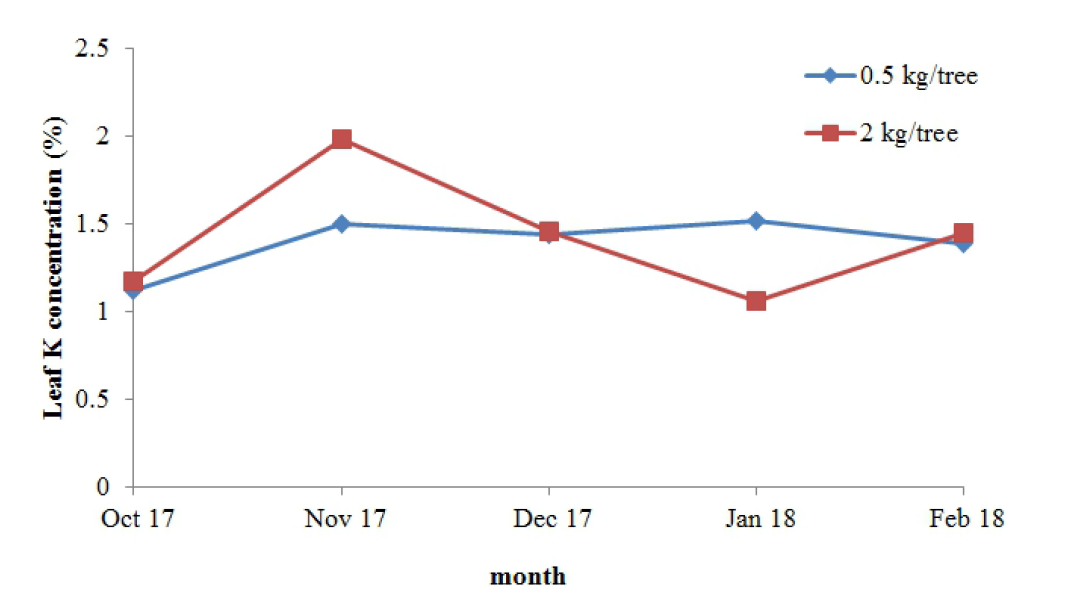
The effect of chemical fertilizer on leaf nutrient concentration and fruit quality in rose apple (Syzygium jambos L.) cv. Tabtimjan was studied in Ratchaburi province, Thailand. The different chemical fertilizer doses applied to the rose apple tree by soil application was used as treatment, 2 kg/tree and 0.5 kg/tree of 17-17-17 chemical fertilizer formula. Both of chemical fertilizer doses were based on the farmer used in on and off season. The results showed that the different chemical fertilizer doses did not statistically affect (t > 0.05) to leaf nutrient concentration in rose apple. The leaf nitrogen (N) concentration was 1.51-1.79 % and 1.47- 1.77 % for 2 kg/tree and 0.5 kg/tree, respectively. The leaf phosphorus (P) concentration was 0.11-0.17 % and 0.13-0.17 % for 2 kg/tree and 0.5 kg/tree, respectively. The leaf potassium (K) concentration was 1.06-1.98 % and 1.04-1.52 % for 2 kg/tree and 0.5 kg/tree, respectively. While, there was significant difference in soil N, P and K concentration in some period of the study which 2 kg/tree gave the higher soil N, P and K concentration than those in 0.5 kg/tree (t < 0.05). For fruit quality, there was no significant difference in fruit quality but using 2 kg/tree gave the lower TSS:TA in December and February than those in 0.5 kg/tree (t < 0.05). From the results, it was concluded that the higher chemical fertilizer dose (2 kg/tree) applied to the rose apple trees did not necessary increase the leaf nutrient concentration as the optimum leaf nutrient concentration had met by the low chemical fertilizer dose (0.5 kg/tree) applied to the rose apple tree. Therefore, the 0.5 kg/tree chemical fertilizer dose should be optimum for the rose apple production.
Article Details
References
M.S. Coyne, Soil microbiology: An Exploratory Approach - Laboratory Workbook, Delmar Publishers Inc. Albany, NY, 1999.
M. A. Sheikh, P. Dwivedi, H. S. Dwivedi, Impact of Chemical Fertilizer and Organic Manure on the Germination and Growth of Soybean (Glycine max L.), Advances in Life Science and Technology 31 (2015) 73 – 77.
P. Nartvaranant, Determination suitable sample method of rose apple (Syzygium jambos L.) for evaluation of plant nutrient status, Journal of Plant Nutrition 41(20) (2018) 2741 – 2748.
M. Peech, Hydrogen-Ion Activity. In: Black CA, editor, Methods of soil analysis part 2, USA: American society of Agronomy, Inc., Publisher, 1965.
R. Beck, Soil analysis handbook of reference methods, USA: Soil and Plant Analysis Council,Inc., CRC Press, 1999.
R. H. Bray II, L. T. Kurtz, Determination of total, organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils, Soil Science 59 (1945) 39 – 45.
Y. Osotsapha, A. Wongmaneeroj, C. L. Hongprayoon, Fertilizer for sustainable agriculture. Bangkok, Thailand: Kasetsart University Press, 2008.
S. H. Hana, J. Y. Anb, J. Hwangc, S. B. Kima, B. B. Park, The effects of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on the growth and nutrient concentrations of yellow poplar (textit{Liriodendron tulipifera} Lin.) in a nursery system, Forest Science and Technology 12(3) (2016) 137 - 143.
T. Milosevic, N. Milosevic, The effect of zeolite, organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil chemical properties, growth and biomass yield of apple trees, Plant soil and environment 55(12) (2009) 528 - 535.
M. S. Ullah, M. S. Islam, M. A. Islam, T. Haque, Effects of organic manures and chemical fertilizers on the yield of brinjal and soil properties, Journal of Bangladesh Agricultural University 6(2) (2008) 271 - 276.
P. I. Glisic, M. T. Milosevic, S. I. Glisic, T. N. Milosevic, The effect of natural zeolites and organic fertilizers on the characteristics of degraded soils and yield of crops grown in Western Serbia, Land Degradation and Development 20(2009) 33 - 40.