Photocatalytic Degradation of Synthetic Dye Wastewater Using Photocatalysts Modified with Coffee Ground-Derived Carbon
doi: 10.14456/mijet.2022.21
Keywords:
coffee ground, zinc oxide, hydrothermal process, photocatalytic process, visible lightAbstract
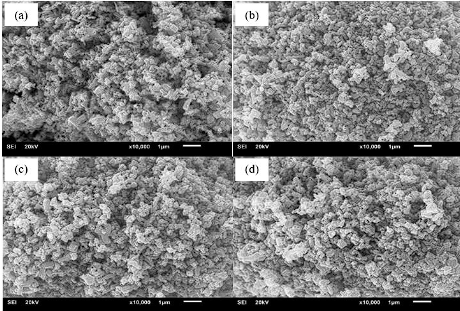
Textile industries discharge large amounts of colored wastewater which is one of the main environmental problems. It affects aquatic ecosystems and the vision of public water resources. Various processes have been developed for the degradation of dye wastewater, one of the most attractive and promising alternative technologies is semiconductor photocatalysis because the reactions can occur at room temperature and pressure. Several studies on photocatalysts, zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles are promising photocatalysts with high photocatalytic activity, biocompatibility, and nontoxicity to human cells. One of the techniques used to enhance the properties of ZnO is doping, especially with carbon (C). Doping the crystal lattice of ZnO with C allows a shift of the bandgap from the UV to the visible light. C can be synthesized from various kinds of waste. Coffee ground waste is one of the interesting C sources. Therefore, it is a good solution to convert coffee ground waste to a C source. In this research, C-doped ZnO was synthesized by a hydrothermal process for the degradation of synthetic dye wastewater (methylene blue). ZnO was modified with C solution (i.e. 10 mL, 20 mL, and 30 mL). The result indicated that the photocatalytic effect of the composites showed a phenomenon of first strengthening and then weakening. The highest photocatalytic degradation was obtained on the C-doped ZnO with an initial C solution of 20 mL. The removal efficiency of color was 91% under visible light.
References
P. Kemacheevakul and S. Chuangchote, "Photocatalytic Remediation of Organic Pollutants in Water. In: Inamuddin, Ahamed M.I., Lichtfouse E. (eds) Water Pollution and Remediation: Photocatalysis," Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World, Springer, Cham, vol. 57. 2021.
T. A. Saleh and V. K. Gupta, "Photo-catalyzed degradation of hazardous dye methyl orange by use of a composite catalyst consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and titanium dioxide," Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, vol. 371, no. 1, pp. 101–106, 2012.
R. Muangmora, P. Kemacheevakul and S. Chuangchote, "Titanium Dioxide and its Modified Forms as Photocatalysts for Air Treatment," Current Analytical Chemistry, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 185-201, 2021.
S. Cho, J. W. Jang, J. S. Lee and K. H. Lee, "Carbon-doped ZnO nanostructures synthesized using vitamin C for visible light photocatalysis," CrystEngComm, vol. 12, pp. 3929-3935, 2010.
P. Surendran, A. Lakshmanan, S. Priya, K. Balakrishnan, P. Rameshkumar, K. Kannan, P. Geetha, T. Hegde and G. Vinitha, "Bioinspired fluorescence carbon quantum dots extracted from natural Honey, Efficient material for photonic and antibacterial applications," Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, vol. 24, pp. 1-10, 2020.
S. Ray, A. Saha, N. R. Jana and R. Sarkar, "Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Bioimaging Application," The Journal of Physics Chemistry C., vol. 113, no. 43, pp. 18546-18551, 2009.
J. Zhou, C. Booker, R. Li, X. Zhou, T. K. Sham, X. Sun and X. Ding, "An Electrochemical Avenue to Blue Luminescent Nanocrystals from Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)," Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 129, no. 4, pp. 744-745, 2007.
J. Deng, Q. Lu, N. Mi, H. Li, M. Liu, M. Xu, L. Tan, Q. Xie, Y. Zhang and S. Yao, "Synthesis of graphene-transition metal oxide hybrid nanoparticles and their application in various fields," Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, vol. 8, pp. 688-714, 2017.
S. L. Hu, K. Y. Niu, J. Sun, J. Yang, N. Q. Zhao and X. W. Du, "One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation," Journal of Materials Chemistry, 19: 484-488, 2009.
H. Li, X. He, Z. Kang, H. Huang, Y. Liu, J. Liu, S. Lian, C. H. A. Tsang, X. Yang and S. T. Lee, "Review on Carbon Dots and Their Applications," Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 139-150, 2010.
L. Cao, X. Wang, M. J. Meziani, F. Lu, H. Wang, P. G. Luo, Y. Lin, B. A. Harruff, L. M. Veca, D. Murray and J. Am., "Carbon Dots for Multiphoton Bioimaging," Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 129, no. 37, pp. 11318-11319, 2007.
X. Zhai, P. Zhang, C. Liu, T. Bai, W. Li, L. Dai and W. Liu, "Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis," Chemical Communications, vol. 48, no. 64, pp. 7955-7970, 2012.
Y. Yang, J. Cui, M. Zheng, C. Hu, S. Tan, Y. Xiao, Q. Yang and Y. Liu, "One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan," Chemical Communications, vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 380-382, 2012.
J. Wang, Q. Li, J. Zhou, T. Wang, L. Yu, H. Peng and J. Zhu, "Synthesis, characterization, and cells and tissues imaging of carbon quantum dots," Optical Materials, vol. 72, pp. 15-19, 2017.
A. Moezzi, A. M. McDonagh and M. B. Cortie, "Zinc oxide particles: Synthesis, properties and applications," Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 185, pp. 1-22, 2012.
N. Suriyachai, S. Chuangchote, N. Laosiripojana, V. Champreda and T. Sagawa, "Synergistic Effects of Co-Doping on Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide on Glucose Conversion to Value-Added Chemicals," ACS Omega, vol. 5, no. 32, pp. 20373-20381, 2020.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








