In silico screening of potential inhibitor from Andrographis paniculata constituents against three targets of SARS-CoV-2: Main protease, Spike protein, and Nsp15
Main Article Content
Abstract
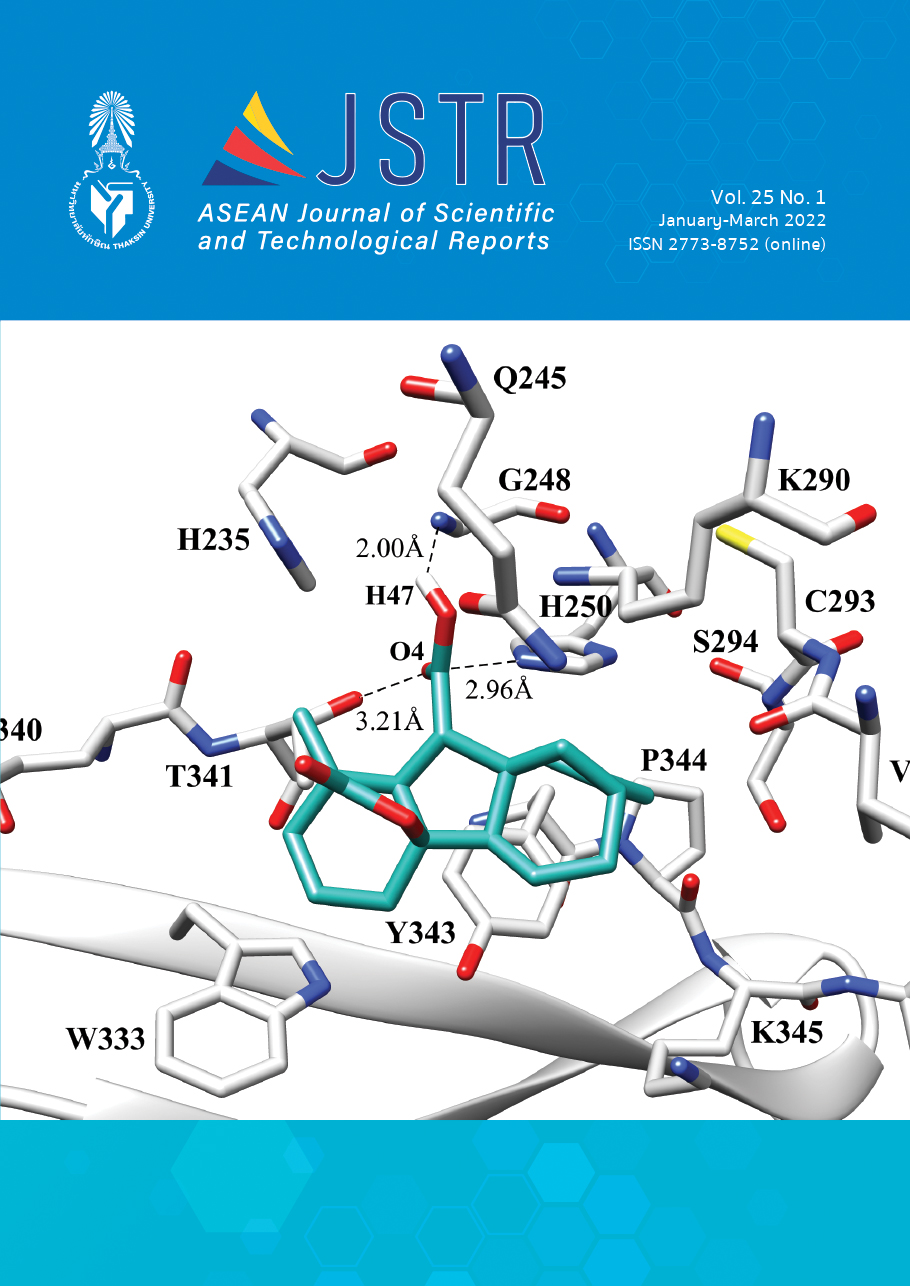
The current pandemic of COVID-19 is caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which has increased the morbidity and mortality rate throughout the world. World Health Organization has declared this COVID-19 outbreak as a health emergency throughout the world. At this time, there are very few drugs against SARS-CoV-2. So, this study aimed to screen 91 Andrographis paniculata against three targets of SARS-CoV-2: main protease, spike protein, and Nsp15 by molecular docking. The calculation result revealed that mostly bioactive compounds from Andrographis paniculata are a good binding affinity with the main protease than that of Nsp15 and spike protein. The top six compounds and their interactions with the active site were visualized. Among them, 7,8-dimethoxy flavone-5-b-D-glucopyranosyloxy flavone and Stigmasterol compounds from Andrographis paniculata had a superior binding affinity of -11.65 and -11.33 kcal/mol toward the main protease. A detailed understanding of ligand-protein interaction could be helpful in further drug design and development for COVID-19 treatment.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Pulakuntla, S.; Lokhande, K.B.; Padmavathi, P.; Pal, M.; Swamy, K.V.; Sadasivam, J.; Singh, S.A.; Aramgam, S.L.; Reddy, V.D. Mutational analysis in international isolates and drug repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: molecular docking and simulation approach. Virusdisease. 2021, 32, 1-13.
Luo, L.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, F.; Liu, K.; Lan, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; Luo, H.. Drug repurposing against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A review. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2021, 11, 683-90.
Hasan, M.; Parvez, M.S.A.; Azim, K.F.; Imran, M.A.S.; Raihan, T.; Gulshan, A.; Muhit, S.; Akhand, R.N.; Ahmed, S.S.U.; Uddin M.B.. Main protease inhibitors and drug surface hotspots for the treatment of COVID-19: A drug repurposing and molecular docking approach. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherap. 2021, 140, 111742.
Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; Mclellan, J.S.. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science Advances. 2020, 367, 1260-3.
Kim, Y.; Wower, J.; Maltseva, N.; Chang, C.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Wilamowski, M.; Kang, S.; Nicolaescu, V.; Randall, G.; Michalska, K.; Joachimiak, A..Tipiracil binds to uridine site and inhibits Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2. Communications Biology 2021, 4:193, 1-11.
Murugesan, S.; Kottekad, S.; Crasta, I.; Sreevathsan, S.; Usharani, D.; Perumal, M.K.; Mudliar, S.N.. Targeting COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease through active phytocompounds of ayurvedic medicinal plants – Emblica officinalis (Amla), Phyllanthus niruri Linn. (Bhumi Amla) and Tinospora cordifolia (Giloy) – A molecular docking and simulation study. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2021, 136, 104683.
Murugan, N.A.; Pandian, C.J.; Jeyakanthan, J. Computational investigation on Andrographis paniculata phytochemicals to evaluate their potency against SARS-CoV-2 in comparison to known antiviral compounds in drug trials. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics. 2021, 39, 4415-26.
Sukardiman, Ervina, M., Fadhil Pratama, M.R., Poerwono, H., Siswodihardjo, S. The coronavirus disease 2019 main protease inhibitor from Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f) Ness. Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology and research. 2020, 11, 157-62.
Rajagopal, K.; Varakumar, P.; Baliwada, A.; Byran, G. Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020, 6, 104.
Verma, D.; Mitra, D.; Paul, M.; Chaudhary, P.; Kamboj, A.; Thatoi, H.; Janmeda, P.; Jain, D.; Panneerselvam, P.; Shrivastav, R.; Pant, K.; Das Mohapatra, P. K. Potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) proteases PLpro and Mpro/ 3CLpro: molecular docking and simulation studies of three pertinent medicinal plant natural components. Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery. 2021, 2, 100038.
Xu, J.; Gao, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, S.-d. In silico screening of potential anti–COVID-19 bioactive natural constituents from food sources by molecular docking. Nutrition. 2021, 82, 111049.
Alghamdi, H. A.; Attique, S. A.; Yan, W.; Arooj, A.; Albulym, O.; Zhu, D.; Bilal, M.; Nawaz, M. Z. Repurposing the inhibitors of COVID-19 key proteins through molecular docking approach. Process Biochemistry. 2021, 110, 216-222.
Dennington, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J. GaussView, Version 5. Semichem Inc., Shawnee Mission KS. 2009.
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A. V.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B. G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H. P.; Ortiz, J. V.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Williams; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery Jr., J. A.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M. J.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E. N.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T. A.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A. P.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 16 Revision a. 03. Wallingford CT, 2016, 2,
Bernstein, F.C.; Koetzle, T.F.; Williams, G.J.; Meyer, E.F.; Brice, Jr.; M.D.; Rodgers, J.R.; Kennard, O.; Shimanouchi, T.; Tasumi, M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. Journal of Molecular Bioogyl. 1977, 112, 535-42.
Sacco, M.D.; Ma, C.; Lagarias, P.; Gao, A.; Townsend, J.A.; Meng, X.; Dube, P.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Kitamura, N.; Hurst, B.; Tarbet, B.; Marty, T.M.; Kolocouris, A., Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.. Structure and inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease reveal strategy for developing dual inhibitors against M(pro) and cathepsin L. Science Advances. 2020, 6, eabe0751.
Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, C.; Peng, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Bi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, H.; Fan, Z.; Tan, S.; Wu, G.; Tan, W.; Lu, X.; Fan, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qi, J.; Gao, G. F.; Gao, F.; Liu, L. Science. 2020, 368 (6496), 1274-1278.
Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Arthur, O. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and empirical binding free energy function. Journal of Computational Chemistry. 1998, 19, 1639-62.
Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity-a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron. 1980, 36, 3219-28.
Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Arthur, O. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. Journal of Computational Chemistry. 2009, 30, 2785-91.
Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsel, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. Journal of Computational Chemistry. 2007, 28, 1145–52.
Ermakova, E. Structural insight into the glucokinase-ligands interactions. Molecular docking study. Computational Biology Chemistry. 2016, 64, 281-96.