A Study of Disruptive Technology Impacts on Industrial Engineering Professionals under the Context of Thailand 4.0
Main Article Content
Abstract
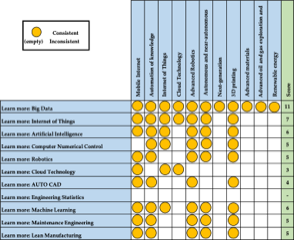
The purpose of this study is to examine the impact of disruptive technologies on the industrial engineering profession and learn how to deal with such disruptions. The study uses questionnaires to collect data from 8,149 individuals practicing industrial engineering at the Associate Engineering level and Senior Professional Engineering levels. After that, the sample is calculated using the Taro Yamane method with a confidence level of 95 percent. Then, the main reasons for the impact of disruptive technology on industrial engineers were analyzed using the Affinity Diagram, and the problem structure was clarified using the Relations Diagram. The main cause was analyzed to find a solution with the help of a Tree Diagram. Finally, the matrix diagram was used to find the correlation of solutions by comparing 11 technologies that will affect global change, according to research by McKinsey Global Institute. The result of this research shows that disruptive technology directly impacts the work of the sample, affecting Decision Making and investment in industry and technology rather than replacing people. Therefore, industrial engineers should further explore technology and engineering such as Big Data, the Internet of Things (IoT), and maintenance engineering. This also includes improving one's language skills and ability to collaborate with others.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Pornsing, C. Industrial work study. Silpakorn University, 2019. (in Thai).
Blair, R. N; Whiston, C. W. Elements of industrial systems engineering. 1st ed. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1971.
Malisuwan, S. The End of Nokia, Lessons leaders need to learn. (in Thai), 2016. Available online https://www.it24HRS.COM/2016/Nokia-case-study/ (accessed on 27 March 2020)
Martinez-Vergara, S. J.; Valls-Pasola, J. Clarifying the disruptive innovation puzzle: a critical review. European Journal of Education and Management. 2021, 24(3), 893-918.
Ministry of Industry. Industrial Development Strategy of Thailand 4.0 for 20 years (2017 – 2036). (in Thai), Available online https://waa.inter.nstda.or.th/stks/pub/2017/20171114-oie.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2020)
Nascimento, D. L.M.; Alencastro, V.; Quelhas, O. L. G.; Caiado, R. G. G.; Garza-Reyes, J. A.; Rocha-Lona, L.; Tortorella, G. Exploring Industry 4.0 technologies to enable circular economy practices in a manufacturing context A business model proposal, Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management. 2018, 30(3), 607-627.
Yothongyot, M.; Sawasdisan. Determination of sample size for research. (in Thai). Institute for the Promotion of Research and Development Innovation, Available online http://www.fsh.mi.th/km/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/resch.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2020)
Pongpornsub, W. Let's get to know 7 New QC Tools. (in Thai). Technology Promotion Association (Thailand-Japan). Available online http://www.tpa.or.th/publisher/pdfFileDownloadS/QM206_P24-25.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2020)
McKinsey & Company. Disruptive technologies: Advances that will transform life. business, and the global economy. Available online https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey (accessed on 16 March 2020)
Manarangsan, S.; Apiwanworarat, T. ‘PIM’ continues to build on "Ready to Work". (in Thai). Available online https://www.techtalkthai.com/pim-through-disruptive-technology-trend/ (accessed on 29 February 2020)