Antimicrobial Activity of Extremely Halophilic Archaea Isolated from Southern Thai Salt-Fermented Products and Solar Saltern of Pattani, Thailand
Main Article Content
Abstract
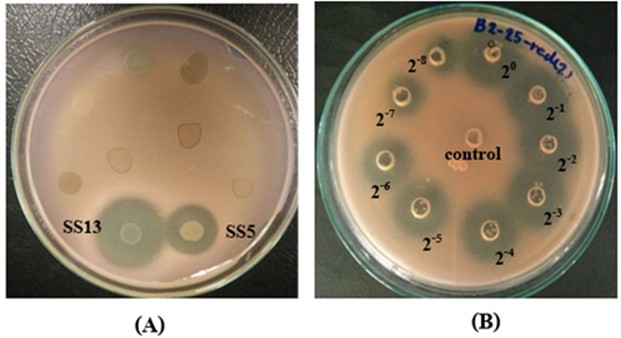
This research aimed to study the diversity and antimicrobial activity of culturable haloarchaea in soil samples of solar saltern in Pattani Province, Thailand and Southern Thai salt-fermented food. Seventy-seven extremely haloarchaea were isolated on Halophilic medium agar containing 25% NaCl at 37°C for 7-21 days. They were grouped by Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis (ARDRA) with two restriction enzymes, RsaI and HindIII. The ARDRA patterns illustrated 6 different Operation Taxonomic Units (OTUs). Partial 16S rRNA gene sequences (938 bp) of the representative of each OTUs were aligned with the GenBank database. The results showed that the representatives of OTU1, OTU2, OTU3, OTU4, OTU5, and OTU6 had 99-100% similarity to Halobacterium salinarum, 99-100% similarity to Halostagnicola larsenii, 99% similarity to Natronococcus sp., 99-100% similarity to Haloferax alexandrinus, 99-100% similarity to Natrialba sp. and 97% similarity to Halococcus sp., respectively. The antimicrobial activity testing of the 17 isolated haloarchaeal strains from solar saltern was performed against 5 tested strains of Hbt. salinarum and 1 strain of Natrialba sp. were isolated from fermented food. Seven (41.2%) were candidate halocin-producing strains. In addition, no phage activity was observed. The 14-day fermentation broth of Natronococcus sp. SS13 showed the highest antimicrobial activity against Hbt. salinarum PK08, BD07 and BD09 (>5,120 AU/ml).
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Williams, T.J.; Allen, M.A.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Tringe, S.G.; Woyke, T.; Cavicchioli, R. Microbial ecology of an Antarctic hypersaline lake: Genomic assessment of ecophysiology among dominant haloarchaea. ISME J 2014, 8, 1645-1658.
Parte, A.C.; SardàCarbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Goker, M. List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2020, 70, 5607-5612.
Oren, A. Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes. Front Microbiol 2013, 4, 315. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00315
Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitas, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2018, 42, 353-375.
Ghanmi, F.; Carré-Mlouka, A.; Vandervennet, M.; Boujelben, I.; Frikha, D.; Ayadi, H.; Peduzzi, J.; Rebuffat, S.; Maalej, S. Antagonistic interactions and production of halocin antimicrobial peptides among extremely halophilic prokaryotes isolated from the solar saltern of Sfax, Tunisia. Extremophiles 2016, 20, 363-374.
Najjari, A.; Stathopoulou, P.; Elmnasri, K.; Hasnaoui, F.; Zidi, I.; Sghaier, H.; Ouzari, H.I.; Cherif, A.; Tsiamis, G. Assessment of 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic diversity of archaeal communities in halite-crystal salts processed from natural Saharan saline systems of Southern Tunisia. Biology 2021, 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050397
Besse, A.; Peduzzi, J.; Rebuffat, S.; Carre-Mlouka, A. Antmicrobial peptides and proteins in the face of extremes: lessons from archaeocins. Biochimie 2015, 118, 344-355.
O’Connor, E.M.; Shand, R.F. Halocins and sulfolobicins: the emerging story of archaeal protein and peptide antibiotics. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2002, 28(1), 23-31.
Quadri, I.; Hassani, I.I.; Haridon, S.; Chalopin, M.; Hacene, H.; Jebbar, M. Characterization and antimicrobial potential of extremely halophilic archaea isolated from hypersaline environments of the Algerian Sahara. Microbiol Res 2016, 186-187, 119-131.
Mazguene, S.; Rossi, M.; Gogliettino, M.; Palmieri, G.; Cocca, E.; Mirino, S.; Imadalou-Idres, N.; Benallaoua, S. Isolation and characterization from solar salterns of North Algeria of a haloarchaeon producing a new halocin. Extremophiles 2018, 22, 259-270.
Besse, A.; Vandervennet, M.; Goulard, C.; Peduzzi, J.; Isaac, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Carré-Mlouka, A. Halocin C8: an antimicrobial peptide distributed among four halophilic archaeal genera: Natrinema, Haloterrigena, Haloferax and Halobacterium. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 623-638.
Oren, A. Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms. Environ Technol 2010, 31, 825-834.
Ispirli, N.H.; Gulluce, M.; Karadayi, M.; Demir, A.Y. Culturable bacteriorhodopsin-producing haloarchaea of Tuz Lake (Turkey). Geomicrobiol J 2019, 36, 831-836.
Don, T.M.; Chen, C.W.; Chan, T.H. Preparation and characterization of poly (hydroxyalkanoate) from the fermentation of Haloferax mediterranei. J Biomater Sci Polym Edn 2006, 17, 1425-1438.
Martínez-Espinosa, R.M.; Zafrilla, B.; Camacho, M.; Bonete, M.J. Nitrate and nitrite removal from salted water by Haloferax mediterranei. Biocatal Biotransform 2007, 25, 295-300.
Akolkar, A.V.; Durai, D.; Desai, A.J. Halobacterium sp. SP1 as a starter culture for accelerating fish sauce fermentation. J Appl Microbiol 2010, 109, 44-53.
Rodrigo-Baños, M.; Garbayo, I.; Vílchez, C.; Bonete, M.J.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M. Carotenoids from haloarchaea and their potential in biotechnology. Mar Drugs 2015, 13(9), 5508-5532.
Yachai, M.; Tanasupawat, S.; Itoh, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Valyasevi, R. Halobacterium piscisalsi sp. nov., from fermented fish (pla-ra) in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2008, 58, 2136-2140.
Tapingkae, W.; Tanasupawat, S.; Itoh, T.; Parkin, K.L., Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Valyasevi, R. Natrinema gari sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from fish sauce in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2008, 58, 2378-2383.
Namwong, S.; Tanasupawat, S.; Kudo, T.; Itoh, T. Haloarcula salaria sp. nov. and Haloarcula tradensis sp. nov., isolated from salt in Thai fish sauce. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2011, 61, 231-236.
Namwong, S.; Tanasupawat, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kudo, T.; Itoh, T. Halococcus thailandensis sp. nov., from fish sauce in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2007, 57, 2199-2203.
Delong, E.F. Archaea in coastal marine environments. PNAS 1992; 89, 5685-5689.
Karthikeyan, P.; Bhat, S.G.; Chandrasekaran, M. Halocin SH10 production by an extreme haloarchaeon Natrinema sp. BTSH10 isolated from salt pans of South India. Saudi J Biol Sci 2013, 20(2), 205-212.
Boujelben, I.; Martínez-García, M.; van Pelt, J.; Maalej, S. Diversity of cultivable halophilic archaea and bacteria from superficial hypersaline sediments of Tunisian solar salterns. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 675-692.
Ahmad, N.; Johri, S.; Sultan, P.; Abdin, M.Z.; Qazi, G.N. Phylogenetic characterization of archaea in saltpan sediments. Indian J Microbiol 2011, 51(2), 132-137.
Roh, S.; Kim, K.H.; Nam, Y.D.; Chang, H.W.; Park, E.J.; Bae, J.W. Investigation of archaeal and bacterial diversity in fermented seafood using barcoded pyrosequencing. ISME J 2010, 4, 1-16.
Birbir, M.; Calli, B.; Mertoglu, B.; Bardavid, R.E.; Oren, A.; Ogmen, M.N.; Ogan, A. Extremely halophilic Archaea from Tuz Lake, Turkey, and the adjacent Kaldirim and Kayacik salterns. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2007, 23, 309-316.
Atanasova, N.S.; Roine, E.; Oren, A.; Bamford, D.H.; Oksanen, H.M. Global network of specific virus-host interactions in hypersaline environments. Environ Microbiol 2012, 14(2), 426-440.
Atanasova, N.S.; Pietila, M.K.; Oksanen, H.M. Diverse antimicrobial interactions of halophilic archaea and bacteria extend over geographical distances and cross the domain barrier. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2(5), 811-825.
Rodríguez-Valera, F.; Juez, G.; Kushner, D.J. Halocins: salt-dependent bacteriocins produced by extremely halophilic rods. Can J Microbiol 1982, 28:151-154.
Li, Y.; Xiang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Tan, H. Purification and biological characterization of halocin C8, a novel peptide antibiotic from Halobacterium strain AS7092. Extremophiles 2003, 7(5), 401-407.
Torreblanca, M.; Meseguer, I.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. Halocin H6, a Bacteriocin from Haloferax gibbonsii. J Gen Microbiol 1989, 135, 2655-2661.
Pasic, L.; Velikonja, B.H.; Ulrih, N.P. Optimization of the culture conditions for the production of a bacteriocin from halophilic archaeon Sech7a. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 2008, 38(3), 229-45.
Kumar, V.; Tiwari, S.K. Halocin HA1: An archaeocin produced by the haloarchaeon Haloferax larsenii HA1. Process Biochem 2017, 61, 202-208.
Mazguene, S.; Rossi, M.; Gogliettino, M.; Palmieri, G.; Cocca, E.; Mirino, S.; Imadalou-Idres, N.; Benallaoua, S. Isolation and characterization from solar salterns of North Algeria of a haloarchaeon producing a new halocin. Extremophiles 2018, 22(2), 259-270.
Meseguer, I.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Production and purification of halocin H4. FEMS Microbio Lett 1985; 28(2), 177-182.
Cheung, J.; Danna, K.J.; O'Connor, E.M.; Price, L.B.; Shand, R.F. Isolation, sequence, and expression of the gene encoding halocin H4, a bacteriocin from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei R4. J Bacteriol 1997, 179(2), 548-551.
Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Mei, S.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, H. A single gene directs both production and immunity of halocin C8 in a haloarchaeal strain AS7092. Mol Microbiol 2005, 57(2), 537-549.