Evaluation of Antibacterial, Antiinflammatory Activities and GC-MS Profiling of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Leaf and Stem Bark Extracts
Main Article Content
Abstract
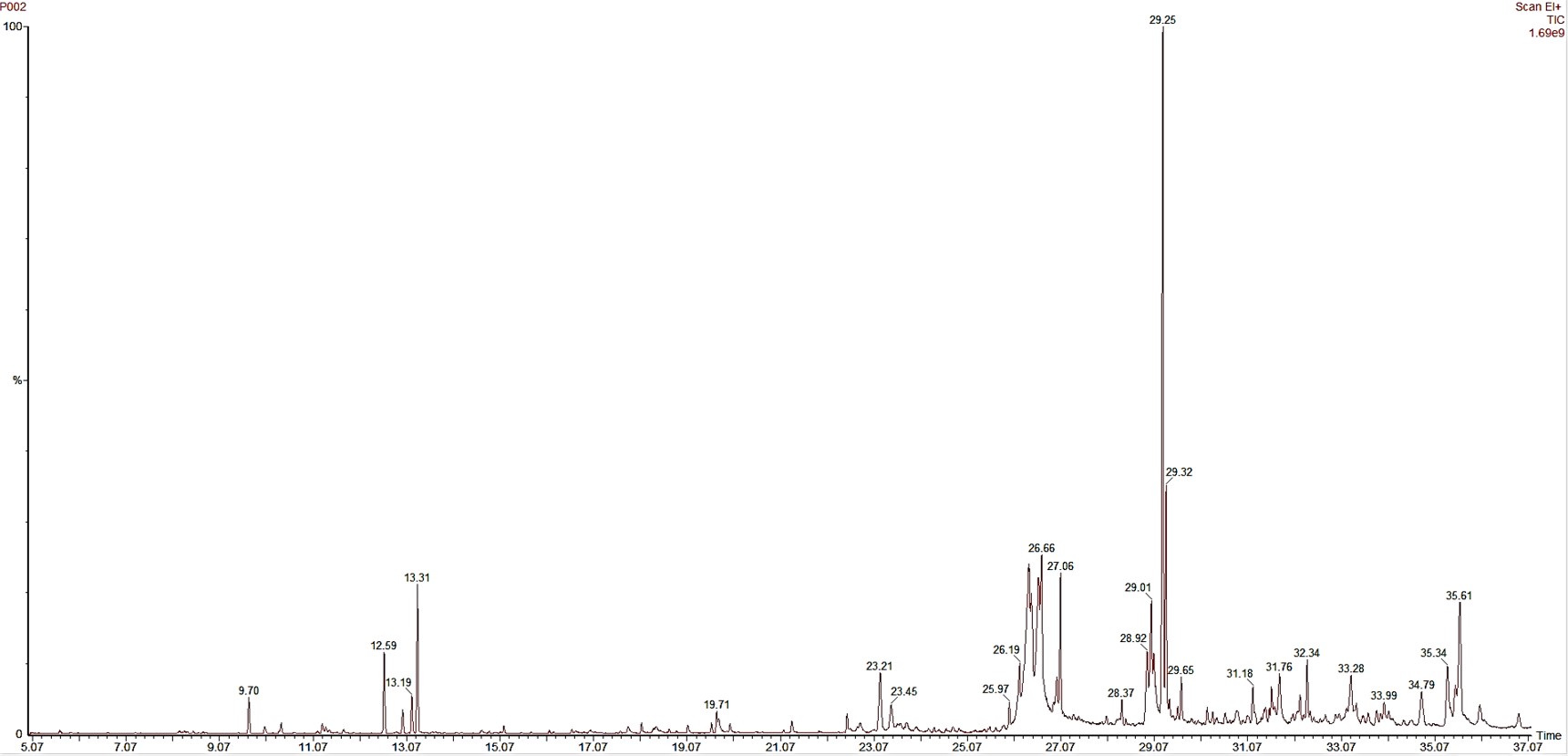
The present study aimed to evaluate the antibacterial and antiinflammatory activity of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. leaf and stem bark extracts and identify the bioactive compounds by GC-MS analysis. This study determined the antibacterial activities using the agar disc diffusion technique. The results revealed the ethanol extract of M. hortensis Linn. stem bark was the highest potential inhibitory against gram-positive bacteria (Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus cereus). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) were performed. The highest inhibitory effect on Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, and Bacillus cereus with MIC and MBC values of 500 mg/ml. This investigation also indicated the M. hortensis Linn. leaf and stem bark extracts had no cytotoxicity against macrophage RAW264.7 cell line and strong antiinflammatory properties. The results of antiinflammatory activity showed that the ethanol extract of M. hortensis Linn. leaf and stem bark extracts were the most effective in inhibiting nitric oxide secretion with IC50 values of 0.25 and 0.41 mg/ml, respectively. GC-MS profiling analyzed the ethanol extract of M. hortensis Linn. stem bark, which had the highest antibacterial and antiinflammatory activity. There were three bioactive substances: 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid, ethyl ester, trans-13-Octadecenoic acid, and oleic acid. The natural functions were antiinflammatory, dermatitigenicity, antioxidants, and antifungal activities. Therefore, the results suggest that the ethanol extract of M. hortensis Linn. stem bark had the highest potential usefulness for treating gram-positive bacteria infection and inflammation-induced ailment. This research will be helpful toward the better acceptability of this extract in therapeutics.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Maher, G.; Enas, A.; Hanee, A.; Maisa, A.; Jafar, E.; Ismael, O. Antimicrobial activity of crude extracts of some plant leaves. Res. J. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1-10.
Ekta, M. Search for Antimicrobial Efficacy of Certain Indian Medicinal Plants. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharmacological Res. 2012, 4, 187-193.
Maher, G.; Enas, A.; Hanee, A.; Maisa, A.; Jafar, E.; Ismael, O. Antimicrobial activity of crude extracts of some plant leaf. Res. J. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1-10.
Bunyapraphatsara, N.; Blasko, G.; Cordell, G.A. Hortensin, an usual flavones from Millingtonia hortensis. Phytochem. 1989, 28, 1555-1556.
Surendra, K.M.; Ravichandran, N. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial studies of stem bark of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2011, 3, 247-249.
Prakash, L.; Garg, G. Chemical constituents of the roots of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. and Acacia nilotica (Linn.). J. Indian Chem. Soc. 1981, 58, 96-97.
Chaiyasit, S. Antimicrobial activities of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. flower essential oil. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 4, 41-44.
Nagaraja, M.S.; Padmaa, M.P. In vitro anthelmintic activity of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2011, 2, 15-19.
Chumbhale, D.S.; Chaudhari1, S.R.; Upasani, C.D. Preliminary phytochemical analysis and in vitro anthelmintic activity of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Int. j. pharm. chem. sci. 2016, 6, 304-308.
Kaushik, R.; Saini, P. Larvicidal activity of leaf extract of Millingtonia hortensis (Family: Bignoniaceae) against Anopheles stephensi, Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2008, 45, 66-69.
Sharma, M.; Puri, S.; Sharma, P.D. Antifungal activity of Millingtonia hortensis. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 69, 599-601.
Anish, K.; Kshitija, I.; Shanthi, V.; Ramanathan, K. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Millingtonia hortensis for the treatment of dapsone resistance in leprosy. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2014, DOI: 10.4172/1948-5948.R1-006.
Lee, H.S.; Chon, S.H.; Kim, M.A.; Park, J.E.; Lim, Y.M.; Kim, E.J.; Son, E.K.; Kim, S.J.; So, J.H. Fermentation enhances the antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects of Bat Faeces (Ye Ming Sha) via the ERK, p38 MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2009, 62, 57-66.
Surendra, K.M.; Suresh, K.S.; Astalakshmi, N.; Babu, G. Antiinflammatory effect of aqueous extract of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. F. stem bark on rats. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2013, 4(4), 104-105.
Jetty, A.; Iyengar, D.S. Antimicrobial activity of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Pharm. Biol. 2000, 38, 157 -160.
Nagaraja, M.S.; Padmaa, M.P. Antibacterial activity of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Pharmacologyonline. 2011, 2, 841-844.
Kiran, B.; Lalitha, V.; Raveesha, K.A. Investigation of antifungal potentiality of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. leaf against Aspergillus and Fusarium species of Maize. Int. j. inst. pharm. life sci. 2012, 2, 1-6.
Tansuwanwong, S.; Hiroyuki, Y.; Kohzoh, I.; Viniketkumnen, U. Antiproliferation and apoptosis on RKO colon cancer by Millingtonia hortensis. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2009, 64(1), 11-17.
Pichaya, J.; Decha, P.; Pravaree, P. The antiaging property of aqueous extract of Millingtonia hortensis flowers in aging neuron. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2023, IP: 110.170.138.204.
Tansuwanwong, S.; Hiroyuki, Y.; Kohzoh, I; Viniketkumnen, U. Induction of apoptosis in RKO colon cancer cell line by an aqueous extract of Millingtonia hortensis. Asian Pac. Cancer Prev. 2006, 7, 641-644.
Babitha, S.; Banji, D.; Banji, O.J.F. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of flower extract of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicty. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 307-312.
Jananie, R.K.; Prya, V.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Determination of bioactive components of Cynodon dactylon by GC-MS analysis. N. Y. sci. j. 2011, 4, 16-20.
Maneemegali, S.; Monika, P. Determination of activity of leaf and flower extracts of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. against primary and opportunistic pathogens. J. herb. med. toxicol. 2010, 4, 127-132.
Nagaraja, M.S.; Padmaa, M.P. Antioxidant activity of different extracts of stem bark of Millingtonia hortensis Linn. Pharmacologyonline. 2011, 2, 643-649.
Sivaraj, D.C.; Aswitha, V.; Srinidhi, M.; Saraswathi, K.; Arumugam, P. Antibacterial, antioxidant activities and GC-MS analysis of leaf extract of Millingtonia hortensis L. J. Pharm. Innov. 2019, 8, 513-521.