Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Smilax ovalifolia Roxb. and Chemical Compositions
Main Article Content
Abstract
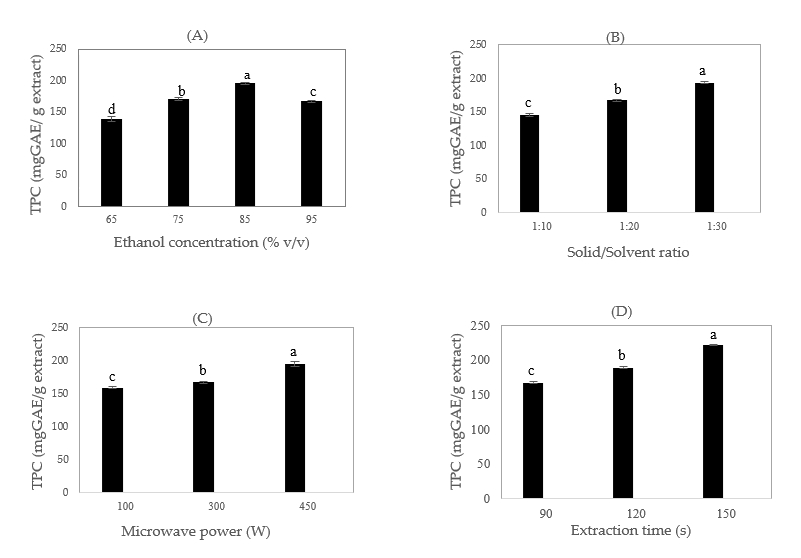
Smilax ovalifolia Roxb. is a medicinal herb in southern Thailand. However, there are not many studies on active compounds from this plant. This study aimed to optimize extraction conditions for total phenolic content (TPC) from S. ovalifolia root using microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) and to determine the phytochemical compositions and antioxidant activity of the extract. The result showed that the optimal conditions of phenolic compounds extraction include ethanol concentration of 85% v/v, a solid-to-solvent ratio of 1:30 (g/mL), microwave power of 450 W, and extraction time of 150 s. The phenolic-rich extract exhibited strong antioxidant activity with IC50 of 6.31 ± 0.05 mg/mL. LC-MS was used to fingerprint analysis of the extract. The result revealed the presence of 18 bioactive compounds. The main components of S. ovalifolia root extract were some flavonoids, including catechin, epicatechin, procyanidin B2, and quercetin.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Mandal, V.; Mohan, Y.; Hemalatha, S. Microwave-assisted extraction-an innovative and promising extraction tool for medicinal plant research. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 2007; 1, 7-18.
Lovric’, V.; Putnik, P.; Kovacevic, D.R.; Jukic, M.; Dragovic-Uzelac, V. Effect of microwave-assisted extraction on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of blackthorn flowers. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 2017, 55, 243-250. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.55.02.17.4687.
Dahmoune, F.; Boulekbache, L.; Mossi, K.; Aoun, O.; Spigno, G.; Madani, K. Optimization of microwave-assisted of polyphenols from Myrtus communis L. leaves. Food Chemistry, 2015, 166, 585-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.013.
Nguyen, N.H.K.; Duong, H.N.; Long, H.; Nhi, T.T.; Phat, D.T. Effect of microwave extraction conditions on polyphenol content and antioxidant activity of pomelo extract (Citrus maxima (Burm.)Merr.). IOP Conf. Series.: Materials Science Engineering, 2020, 991, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.013.
Lasunon, P.; Phonkerd, N.; Tettawong, P.; Sengkhamparn, N. Effect of microwave extraction on bioactive compounds from industrial tomato waste and its antioxidant activity. Food Research, 2021, 5(2), 468-474. https://doi.org/10.26656/fr.2017.5(2).516.
Pansumrit, P.; Pathomwichaiwat, T.; Kladwong, P.; Tiyaworanant, S.; Nguanchoo, V.; Bongcheewin, B. An ethnobotanical study of the genus Smilax in Thailand and its botanical authentication for Hua-khao-yen crude drugs. Pharmaceutical Sciences Asia, 2022, 49(3), 230-241. https://doi.org/10.29090/psa.2022.03.21.220.
Shah, R.K. A review on ethnobotanical uses of Smilax ovalifolia. International Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2015, 3, 16-19.
Murali, A.; Ashok, P.; Madhavan, V. In vitro antoxidant activity and HPTLC studies on the roots and rhizomes of Smilax zeylanica L. (Smilacaceae). International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2011, 3(1), 192-195.
Shao, B.; Guo, H.; Cui, Y.; Ye, M., Han, J.; Guo, D. Steroidal saponins from Smilax china and their anti-inflammatory activities. Phytochemistry, 2007, 68, 623-630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.10.026.
Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Jia, A.; Ding, Q. Cytotoxic polyphenols against breast tumor cell in Smilax china L. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2010; 130(3), 460-464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.032
Smitinand, T.; Larsen, X. Smilax ovalifolia Roxb. e-Flora of Thailand, 1975, 2, 215. https://botany.dnp.go.th/eflora/floraspecies.html?tdcode=00383.
Tran N.Y.T.; Le T.D.; Dao P.T.; Bach G.L.; Huynh, P.X.; Tran, Q.N. Evaluation of different extraction methods on the polyphenols yield, flavonoids yield, and antioxidant activity of the pomelo flavedo extract from Da Xanh (Citrus maxima [burm] merr.) variety. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 42, e97021. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.97021.
Zaki, N.A.M.; Hashib, S.A.; Ibrahim, U.K.; Bakhtiar, P.A.N.A. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Pandanus amaryllifolia by soaking and microwave-assisted extraction. IOP Conf. Series.: Materials Science Engineering, 2020, 778, 012155. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/778/1/012155.
Romah, F.U.; Rahmawati, A.; Rizkiana, M.F.; Susanti, A. Optimization of extraction of bioactive. compound from pegagan leaves using ethanol solvent with microwave-assisted extraction method (MAE). Journal of Biobased Chemicals, 2022, 2, 43-55. https://doi.org/10.19184/jobc.v2i1.119
Singh, R.; Singh, P.; Pandey, V.K.; Dash, K.K.; Ashish, Mukarram, S.A.; Harsányi, E.; Kovács, B. Microwave-assisted phytochemical extraction from walnut hull and process optimization using box-behnken design (BBD). Processes, 2023, 11, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041243.
Tsai, P.J.; Delva, L.; Yu, T.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Dufosse, L. Effect of sucrose on the anthocyanin and antioxidant capacity of mulberry extract during high temperature heating. Food Research International, 2005, 38, 1059-1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2005.03.017
Antony, A.; Farid, M. Effect of temperatures on polyphenols during extraction. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(2017), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042107
Rostagno, M.A.; Prado, J.M. Natural product extraction: principals and applications. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2013.
Kark, P. (2019). Biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 2019, 10(4), 1567-1574. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(4).
Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant flavonoids: chemical characteristics and biological activity. Molecules, 2021, 26(17), 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175377
Paneru, D.P.; Rajbhandari, M. (2020). Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of Smilax ovalifolia Roxb. Ex D. Don. Napal Journal of Science and Technology, 2020, 19(1), 89-96. https://doi.org/10.3126/njst.v19il.29787.
Divya, V.V. Kumar, K.V.; Perumal, A.; Stelin Wersly, A.M. (2023). Amelioration of inflammation by Smilax ovalifolia Roxb. European Chemical Bullitin, 2023, 12(6), 46-57.