Exploring the Efficacy of Bacillus oceanisediminis Ba9 from Asian Seabass Cage Sediment in Saline Wastewater Treatment
Main Article Content
Abstract
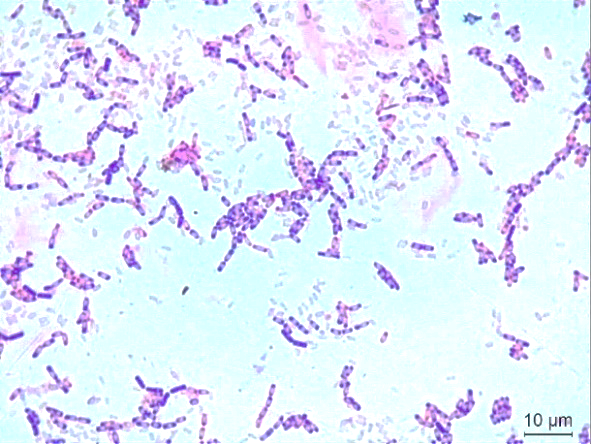
Preventing toxicity in aquaculture systems from ammonia and nitrite is important. This study isolated the salt-tolerant Bacillus sp. strain Ba9 from bottom sediment under an Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer) cage cultivating at Koh Yor, Songkhla, Thailand. Morphological characteristics showed that strain Ba9 was rod-shaped, endospore-forming, and Gram-positive. Strain Ba9 grew well at a salinity of 1.5 to 4.0% NaCl. The catalase test of the isolate was positive, while the oxidase test was negative. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing data and phylogenetic tree analysis, strain Ba9 was identified as B. oceanisediminis with 97% similarity (strain HQB337T). The result showed that the ammonium removal efficiency of Ba9 in a high ammonium medium was 64.24%. The nitrite and nitrate production were 0.10% and 0.08%, respectively. Consequently, sucrose had been the optimal carbon source for Ba9, which showed ammonium removal was 61.05%. Ammonium sulfate is the most suitable for ammonium oxidation, with 50.53% for the nitrogen source. The optimal C/N ratio of strain Ba9 was 8, with 71.15% ammonia removal. For wastewater improvement, strain Ba9 was inoculated into artificial wastewater for 14 days. The result showed that the ammonium removal efficiency of Ba9 was 96.87%. In addition, the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) removal efficiency of Ba9 was 90.86%. From this result, the salt-tolerant B. oceanisediminis Ba9 has a high potential as a microbial product for water quality management in marine aquaculture.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Gupta, A. B.; Gupta, S. K. Simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removal from high strength domestic wastewater in an aerobic RBC biofilm. Water Res. 2001; 35, 1714–1722.
Herrero, M.; Stuckey, D. C. Bioaugmentation and its application in wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2015; 140, 119–128.
Zhao, B.; Tian, M.; An, Q.; Ye, J.; Guo, J. S. Characteristics of a heterotrophic nitrogen removal bacterium and its potential application on treatment of ammonium-rich wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017; 226, 46–54.
Kim, T. S.; Kim, H. S.; Kwon, S.; Park, H. D. Nitrifying bacterial community structure of a full-scale integrated fixed-film activated sludge process as investigated by pyrosequencing. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011; 21, 293–298.
Zhao, B.; An, Q.; He, Y. L.; Guo, J. S. N2O and N2 production during heterotrophic nitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis strain NR. Bioresour. Technol. 2012; 116, 379–385.
Kim, Y. M.; Park, D.; Lee, D. S.; Park, J. M. Inhibitory effects of toxic compounds on nitrification process for cokes wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008; 152, 915–921.
Zheng, H. Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X. Y.; Ai, G. M.; Miao, L. L.; Liu, Z. P. Characterization of a marine origin aerobic nitrifying-denitrifying bacterium. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 33–37.
Zhao, B.; Cheng, D. Y.; Tan, P.; An, Q.; Guo, J. S. Characterization of an aerobic denitrifier Pseudomonas stutzeri strain XL-2 to achieve efficient nitrate removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018; 250, 564–573.
Li, Y.; Chapman, S. J.; Nicol, G. W.; Yao, H. Nitrification and nitrifiers in acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018; 116, 290–301.
Pan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; He, X. Effects of COD/TN ratio on nitrogen removal efficiency, microbial community for high saline wastewater treatment based on heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020; 301, 122726.
Duan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S. Heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria in wastewater biological nitrogen removal systems: A review. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2021; 52, 1–37.
Thurlow, C. M.; Williams, M. A.; Carrias, A.; Ran, C.; Newman, M.; Tweedie, J.; Allison, E.; Jescovitch, L. N.; Wilson, A. E.; Terhune, J. S.; Liles, M. R. Bacillus velezensis AP193 exerts probiotic effects in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and reduces aquaculture pond eutrophication. Aquaculture 2019; 503, 347–356.
Lalloo, R.; Ramchuran, S.; Ramduth, D.; Görgens, J.; Gardiner, N. Isolation and selection of Bacillus spp. As potential biological agents for enhancement of water quality in culture of ornamental fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007; 103, 1471–1479.
Song, Z. F.; An, J.; Fu, G. H.; Yang, X. L. Isolation and characterization of an aerobic denitrifying Bacillus sp. YX-6 from shrimp culture ponds. Aquaculture 2011; 319, 188–193.
Nimrat, S.; Suksawat, S.; Boonthai, T.; Vuthiphandchai, V. Potential Bacillus probiotics enhance bacterial numbers, water quality and growth during early development of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Vet. Microbiol. 2012; 159, 443–450.
Xie, F.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for remediation of aquaculture water. SpringerPlus 2013; 2, 119.
Zokaeifar, H.; Babaei, N.; Saad, C. R.; Kamarudin, M. S.; Sijam, K.; Balcazar, J. L. Administration of Bacillus subtilis strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, growth performance, immune response, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2014; 36, 68–74.
Hura, M. U. D.; Zafar, T.; Borana, K.; Prasad, J. R.; Iqbal, J. Effect of commercial probiotic Bacillus megaterium on water quality in composite culture of major carps. Int. J. Curr. Agric. Sci. 2018; 8, 268–273.
Cha, J. H.; Rahimnejad, S.; Yang, S. Y.; Kim, K. W.; Lee, K. J. Evaluations of Bacillus spp. as dietary additives on growth performance, innate immunity and disease resistance of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against Streptococcus iniae and as water additives. Aquaculture 2013; 402–403, 50–57.
Das, A.; Nakhro, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Kamilya, D. Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus amyloliquifaciens FPTB16 on systemic and cutaneous mucosal immune responses and disease resistance of catla (Catla catla). Fish Shellfish Immun. 2013; 35, 1547–1553.
Saputra, F.; Shiu, Y. L.; Chen, Y. C.; Puspitasari, A. W.; Danata, R. H.; Liu, C. H.; Hu, S. Y. Dietary supplementation with xylanase-expressing B. amyloliquefaciens R8 improves growth performance and enhances immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immun. 2016; 58, 397–405.
Fei, H.; Lin, G. D.; Zheng, C. C.; Huang, M. M.; Qian, S. C.; Wu, Z. J.; Sun, C.; Shi, Z. G.; Li, J. Y.; Han, B. N. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Yarrowia lipolytica lipase 2 on immunology and growth performance of hybrid sturgeon. Fish Shellfish Immun., 2018; 82, 250–257.
Zhang, F.; Xie, F.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Song, Z.; Cui, H. Nitrogen removal performance of novel isolated Bacillus sp. capable of simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2022; 194, 3196–3211.
Reddy, K. V.; Reddy, A. V. K.; Babu, B. S.; Lakshmi, T. V. Applications of Bacillus sp. in aquaculture wastewater treatment. Int. J. S. Res. Sci. Tech. 2018; 4, 1806–1812.
Divya, M. Isolation, Characterization and biodegradation potential of bacterial strains of seafood processing plant effluent for bioremediation. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2015; 1, 530–537.
Zhou, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chu, W. Isolation of marine Bacillus sp. with antagonistic and organic-substances-degrading activities and its potential application as a fish probiotic. Mar. Drugs 2018; 16, 196.
Purivirojkul, W.; Maketon, M.; Areechon, N. Probiotic properties of Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus subtilis in Black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon Fabricius) culture. Kasetsart Journal Natural Science 2005; 39, 262–273.
Chankaew, S.; O-Thong, S.; Sangnoi, Y. Halomonas sp. SKNB4, a proficient ammonium oxidizing bacterium. Proceedings of the 3rd National Meeting on Biodiversity Management in Thailand, June 15-17, 2016; Publisher Nan province, Thailand. 2016; 187–192.
Chankaew, S.; O-Thong, S.; Sangnoi, Y. Nitrogen removal efficiency of salt-tolerant heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria. Chiang Mai. J. Sci. 2018; 45, 11–20.
Sangnoi, Y.; Chankaew, S.; O-Thong, S. Indigenous Halomonas spp., the potential nitrifying bacteria for saline ammonium wastewater treatment. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017; 20(1), 52–58.
Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021; 38, 3022–3027.
Strickland, J. D. H.; Parsons, T. R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed.; The Alger Press Ltd.: Fishery Research Board, Canada, 1972; 49–131.
Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, F.; Peng, J.; Peng, Y.; Wu, J. Nitrogen removal characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria, Alcaligenes faecalis strain WT14. J. Environ. Manage. 2021; 282, 111961.
Yang, X. P.; Wang, S. M.; Zhang, D. W.; Zhou, L. X. Isolation and nitrogen removal characteristics of an aerobic heterotrophic nitrifying–denitrifying bacterium, Bacillus subtilis A1. Bioresour. Technol. 2011; 102, 854–862.
Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Isolation and characterization of heterotrophic nitrifying strain W1. Chinese. J. Chem. Eng. 2012; 20, 995–1002.
APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, Part 3, Determination of Metals, 17th ed, American Public Health Association Inc.: Washington DC, 1989.
Xiao, J.; Zhu, C.; Sun, D.; Guo, P.; Tian, Y. Removal of ammonium-N from ammonium-rich sewage using an immobilized Bacillus subtilis AYC bioreactor system. J. Environ. Sci. 2011; 23, 1279–1285.
Joo, H. S.; Hirai, M.; Shoda, M. Piggery wastewater treatment using Alcaligenes faecalis strain No. 4 with heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification. Water Res. 2006; 40, 3029–3036.
Zeng, J.; Liao, S.; Qiu, M.; Chen, M.; Ye, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, A. Effects of carbon sources on the removal of ammonium, nitrite and nitrate nitrogen by the red yeast Sporidiobolus pararoseus Y1. Bioresour. Technol. 2020; 312, 123593.
Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.; Song, F.; Xin, Y.; Qu, L.; Ding, K. Bacillus oceanisediminis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2010; 60, 2924–2929.
Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Characterization of a salt-tolerant bacterium Bacillus sp. from a membrane bioreactor for saline wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2014; 26, 1369–1374.
Pal, D.; Kumar, R. M.; Kaur, N.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, G.; Singh, N. K.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Mayilraj, S. Bacillus maritimus sp. nov., a novel member of the genus Bacillus isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2017; 67, 60–66.
Fan, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, W.; Meng, S.; Song, C.; Qu, J.; Xu, P. Exploration of three heterotrophic nitrifying strains from a tilapia pond for their characteristics of inorganic nitrogen use and application in aquaculture water. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015; 119, 303–309.
Zhang, Q. L.; Liu, Y.; Ai, G. M.; Miao, L. L.; Zheng, H. Y.; Liu, Z. P. The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification bacterium, Bacillus methylotrophicus strain L7. Bioresour. Technol. 2012; 108, 35–44.
Khin. T.; Annachhatre, A. P. Nitrogen removal in a fluidized bed bioreactor by using mixed culture under oxygen limited conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2004; 50, 313–320.
Kim, J. K.; Park, K. J.; Cho, K. S.; Nam, S. W.; Park, T. J.; Bajpai, R. Aerobic nitrification–denitrification by heterotrophic Bacillus strains. Bioresour. Technol. 2005; 96, 1897–1906.
Huang, F.; Pan, L.; Lv, N.; Tang, X. Characterization of novel Bacillus strain N31 from mariculture water capable of halophilic heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017; 124, 564–571.