Molecular Docking of Bioactive Compounds from Thai Medicinal Plants Against Xanthine Oxidase for Gout Treatment
Main Article Content
Abstract
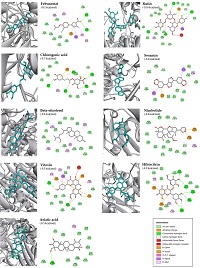
Xanthine oxidase (XO) is a crucial enzyme of the purine catabolism pathway, which catalyzes the reaction of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid. The high level of uric acid leads to gout, kidney disease, and several disorders. In this study, molecular docking was performed to investigate potential bioactive compounds from Thai medicinal plants that acted as XO inhibitors compared to commercial drugs. Among 30 bioactive compounds tested, 16 were classified as strong XO inhibitors. These compounds include asiatic acid, benzyl glucosinolate, beta-sitosterol, chlorogenic acid, curcumin, eupatorin, gamma-mangostin, hibiscitrin, lutein, nimbolide, piperine, quercetin, rosmarinic acid, rutin, sesamin, and vitexin. They exhibited binding affinity values ranging from -8.5 to -10.6 kcal/mol. Moreover, moderate XO inhibitors were identified with binding affinity of -6.2 to -8.0 kcal/mol, consisting of the 7 compounds of gallic acid, garcinia acid, gingerol, limonene, linalyl acetate, panduratin A, and scopoletin. As a result, Thai medicinal plants could serve as potential sources of bioactive compounds for further drug design for treating gout patients.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2020,16(7), 380-390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-020-0441-1
Neogi, T.; Jansen, T.L.; Dalbeth, N.; Fransen, J.; Schumacher, H.R.; Berendsen, D.; Brown, M.; Choi, H.; Edwards, N.L.; Janssens, H.J.; Lioté, F.; Naden, R.P.; Nuki, G.; Ogdie,A.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Saag, K.; Singh, J.A.; Sundy, J.S.; Tausche, A.K.; Vaquez-Mellado, J.; Yarows, S.A.; Taylor, W.J. Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015, 74(10), 1789-1798. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208237
Choi, H.K.; McCormick, N.; Yokose, C. Excess comorbidities in gout: the causal paradigm and pleiotropic approaches to care. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2022, 18(2), 97-111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-021-00725-9
Miric, D.J.; Kisic, B.M.; Filipovic-Danic, S.; Grbic, R.; Dragojevic, I.; Miric, M.B.; Puhalo-Sladoje, D. Xanthine oxidase activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with and without diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Journal of Diabetes Research. 2016, 4370490. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4370490
Santi, M.D.; Paulino Zunini, M.; Vera, B.; Bouzidi, C.; Dumontet, V.; Abin-Carriquiry, A.; Grougnet, R.; Ortega, M.G. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of natural and hemisynthetic flavonoids from Gardenia oudiepe (Rubiaceae) in vitro and molecular docking studies. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2018, 143, 577-582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.071
Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine oxidoreductase-derived reactive species: physiological and pathological effects. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2016, Article 3527579. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3527579
Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Kong, L.D.; Yang, C.; Cheng, C.H.; Zhang, X. Administration of procyanidins from grape seeds reduces serum uric acid levels and decreases hepatic xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase activities in oxonate-treated mice. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 2004, 94(5), 232-237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2004.pto940506.x
Sezai, A.; Soma, M.; Nakata, K.; Osaka, S.; Ishii, Y.; Yaoita, H.; Hata, H.; Shiono, M. Comparison of febuxostat and allopurinol for hyperuricemia in cardiac surgery patients with chronic kidney disease (NU-FLASH trial for CKD). Journal of Cardiology. 2015, 66(4), 298-303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2014.12.017
Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; Zhao, T.; Xie, Z.; Sun, J. The major cardiovascular events of febuxostat versus allopurinol in treating gout or asymptomatic hyperuricemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Palliative Medicine. 2021, 10(10), 10327-10337. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-21-1564 [
Mohamed Isa, S.S.P.; Ablat, A.; Mohamad, J. The antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Plumeria rubra flowers. Molecules. 2018, 23(2), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020400
Liang, H.; Deng, P.; Ma, Y.F.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.D.; Qi, Y.Z.; Pan, X.Y.; Huang, F.S.; Lv, S.Y.; Han, J.L.; Dai, W.D.; Chen, Z. Advances in experimental and clinical research of the gouty arthritis treatment with traditional Chinese medicine. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2021, Article 8698232. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8698232
Kumar, S.; Pagar, A.D.; Ahmad, F.; Dwibedi, V.; Wani, A.; Bharatam, P.V.; Chhibber, M.; Saxena, S.; Singh, I.P. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors from an endophytic fungus Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2019, 87, 851-856. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.12.008 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.12.008
Tran, L.T.T.; Le, T.N.; Ho, D.V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, V.P.T.; Pham, K.T.V.; Nguyen, T.K.; Tran, M.H. Virtual screening and in vitro evaluation to identify a potential xanthine oxidase inhibitor isolated from Vietnamese Uvaria cordata. Natural Product Communications. 2022, 17(2), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X221080339
Hendriani, R.; Nursamsiar, N.; Tjitraresmi, A. In vitro and in silico evaluation of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of quercetin contained in Sonchus arvensis leaf extract. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2017, 10(14), 50-53. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10s2.19486
Sicho, M.; Svozil, D. Molecular docking as a tool to virtually develop drugs. Chemicke Listy. 2017, 111(11), 754-759.
Zafar, H.; Iqbal, S.; Javaid, S.; Khan, K.M.; Choudhary, M.I. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory and molecular docking studies on pyrimidones. Medicinal Chemistry. 2018, 14(5), 524-535. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406413666171129224919
Pan, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.; Qi, R.; Chang, H.; Han, L.; Han, W. Molecular dockings and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the potency of different inhibitors against xanthine oxidase. ACS omega. 2021, 6(17), 11639-11649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00968
Hou, C.; Shi, C.; Ren, J. Xanthine oxidase targeted model setup and its application for antihyperuricemic compounds prediction by in silico methods. eFood. 2021, 2, 296-306. https://doi.org/10.53365/efood.k/147019
Choudhary, D.K.; Chaturvedi, N.; Singh, A.; Mishra, A. Investigation of hypoglycemic effects, oxidative stress potential and xanthine-oxidase activity of polyphenols (gallic acid, catechin) derived from faba bean on 3T3-L1 cell line: insights into molecular docking and simulation study. Toxicology Research. 2020, 9(3), 308-322. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxres/tfaa025
Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Nuansrithong, P.; Sirintharawech, N. Antioxidant activity and xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Thai medicinal plants used for tonic and longevity. Proceedings of 47th Kasetsart University Annual Conference: Science. (pp 94-102). The Thailand Research Fund, Bangkok, Thailand, 2009.
Taejarernwiriyakul, O.; Buasai, M.; Rattanatranurak, I.; Sriyod, P.; Chanluang, S. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of medical plants. Thai Pharmaceutical and Health Science Journal. 2011, 6(1), 1-6.
Seephonkai, P.; Mongkolsiri, N.; Thiabphet, W.; Traisathit, R.; Sedlak, S.; Wongpakam, K.; Dhammaraj, T.; Sangdee, A. Antioxidant, xanthine oxidase inhibitory and antibacterial activities of selected galactogogue Thai medicinal plant water and ethyl acetate extracts. Journal of Research in Pharmacy. 2021, 25(4), 519-530. https://doi.org/10.29228/jrp.42
Bernstein, F.C.; Koetzle, T.F.; Williams, G.J.; Meyer, E.F.; Brice, J.M.D.; Rodgers, J.R.; Kennard, O.; Shimanouchi, T.; Tasumi, M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1977, 112(3), 535-542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(77)80200-3
Okamoto, K.; Eger, B.T.; Nishino, T.; Kondo, S.; Pai, E. F.; Nishino, T. An extremely potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidoreductase. Crystal structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex and mechanism of inhibition. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003, 278(3), 1848-1855. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208307200
Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: improved protein-ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Research. 2022, 50(W1), W159-W164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac394
Biovia, D.S. Discovery Studio Visualizer. 2021, San Diego.
Thangathirupathi, A.; Ali, N.; Natarajan, P.; Kumar, R.D. Molecular docking studies of andrographolide with xanthine oxidase. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2013, 6, 295-297.
Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ruan, S.; Ao, J.; Liao, S.-G. Insights into the inhibitory mechanism of viniferifuran on xanthine oxidase by multiple spectroscopic techniques and molecular docking. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7730. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227730
Jiwajinda, S.; Santisopasri, V.; Murakami, A.; Kim, O.K.; Kim, H.W.; Ohigashi, H. Suppressive effects of edible Thai plants on superoxide and nitric oxide generation. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2002, 3(3), 215-223.
Peamaroon, N.; Moonrungsee, N.; Boonmee, A.; Suwancharoen, S.; Kasemsuk, T.; Jakmunee, J. Phytochemical and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Carissa carandas L. Fruit Extract. RMUTP Research Journal. 2020, 13(2), 106-118.
Niu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tu, C.; Li, N.; Gao, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L. Hypouricemic actions of the pericarp of mangosteen in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Natural Products. 2023, 86(1), 24-33. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00531
Malik, N.; Dhiman, P.; Khatkar, A. In silico design and synthesis of targeted rutin derivatives as xanthine oxidase inhibitors. BMC Chemistry. 2019, 13, 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0585-8
Pathomweepisut, N.; Thetsana, P.; Tengumnuay, P. Effect of quercetin supplementation on serum uric acid in obese male patients. Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences. 2022, 29(1), 15-25.
Fitria, L.; Widyananda, M.H.; Sakti, S.P. Analysis of allopurinol, cucurbitacin b, morindine, and piperine as xanthine oxidase inhibitor by molecular docking. Journal of Smart Bioprospecting and Technology. 2019, 1(1), 6-11. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jsmartech.2019.001.01.2
Shaik, A.H.; Shaik, S.R.; Shaik, A.S.; Daoud, A.; Salim, M.; Kodidhela, L.D. Analysis of maslinic acid and gallic acid compounds as xanthine oxidase inhibitors in isoprenaline administered myocardial necrotic rats. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 2021, 28(4), 2575-2580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.062
Kikuchi, H.; Fujisaki, H.; Furuta, T.; Okamoto, K.; Leimkühler, S.; Nishino, T. Different inhibitory potency of febuxostat towards mammalian and bacterial xanthine oxidoreductases: insight from molecular dynamics. Scientific Reports. 2012, 2, 331. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00331
Yamamoto, T.; Moriwaki, Y.; Suda, M.; Nasako, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Hiroishi, K.; Nakano, T.; Hada, T.; Higashino, K. Effect of BOF-4272 on the oxidation of allopurinol and pyrazinamide in vivo. Is xanthine dehydrogenase or aldehyde oxidase more important in oxidizing both allopurinol and pyrazinamide?. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1993, 46(12), 2277-2284. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(93)90618-7
Berglund, L.; Rasmussen, J.T.; Andersen, M.D.; Rasmussen, M.S.; Petersen, T.E. Purification of the bovine xanthine oxidoreductase from milk fat globule membranes and cloning of complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Journal of Dairy Science. 1996, 79(2), 198-204. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(96)76351-8 https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(96)76351-8
Habtemariam, S.; Varghese, G.K. Extractability of rutin in herbal tea preparations of Moringa stenopetala leaves. Beverages. 2015, 1(3), 169-182. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1030169
Buathong, R.; Duangsrisai, S. Plant ingredients in Thai food: a well-rounded diet for natural bioactive associated with medicinal properties. PeerJ. 2023, 11, e14568. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14568
Chriscensia, E.; Arham, A.A.; Wibowo, E.C.; Gracius, L.; Nathanael, J.; Hartrianti, P. Eupatorin from Orthosiphon aristatus: A Review of The Botanical Origin, Pharmacological Effects and Isolation Methods. Current Biocative Compounds. 2023, 19(8), e310323215364. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573407219666230331122318
Alotaibi, H.N.; Anderson, A.K.; Sidhu, J.S. Influence of lutein content of marigold flowers on functional properties of baked pan bread. Annals of Agricultural Sciences. 2021, 66(2), 162-168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2021.12.002
Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, W.T.; Zhou, P. Content determination of benzyl glucosinolate and anti-cancer activity of its hydrolysis product in Carica papaya L. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine. 2012, 5(3), 231-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60030-3
Yorsin, S.; Sriwiriyajan, S.; Chongsa, W. Vasorelaxing effect of Garcinia cowa leaf extract in rat thoracic aorta and its underlying mechanisms. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. 2022, 13(3), 219-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.12.001
Da-Costa-Rocha, I.; Bonnlaender, B.; Sievers, H.; Pischel, I.; Heinrich, M. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. - a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Food chemistry. 2014, 165, 424-443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.002
Mackeen, M.M.; Ali, A.M.; Lajis, N.H.; Kawazu, K.; Kikuzaki, H.; Nakatani, N. Antifungal garcinia acid esters from the fruits of Garcinia atroviridis. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung. C, Journal of biosciences. 2002, 57(3-4), 291-295. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2002-3-416
Siriamornpun, S.; Sriket, C; Sriket, P. Phytochemicals of Thai local edible herbs. International Food Research Journal. 2014, 21(3), 1009-1016.
Muangthai, P; Nookaew, P. Monitoring on some organic acids in fresh and processed rural plant leaves in Thailand. Asian Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences. 2015, 4(1), 82-89.
Paederia Foetida Linn: Phytochemistry, pharmacological and traditional uses. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 2013, 4(12), 4525-4530. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.4(12).4525-30
Tangjitjareonkun, J.; Yahayo, W.; Supabphol, R. Application of Orthosiphon stamineus for diuretic effect. Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences. 2017, 24(1), 67-78.
Azmi, S.M.N.; Jamal, P.; Amid, A. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity from potential Malaysian medicinal plant as remedies for gout. International Food Research Journal. 2012, 19(1), 159-165.