Fabrication, ‘Optimisation,’ Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Testosterone Undecanoate Loaded Proniosome Capsule for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability
Main Article Content
Abstract
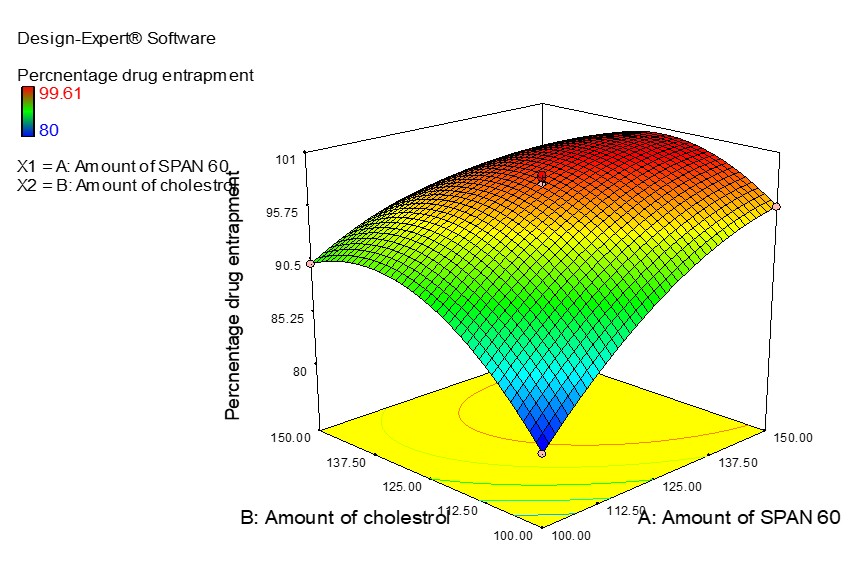
This study focuses on creating and evaluating proniosome capsules as a potential drug delivery method to increase the oral bioavailability of testosterone undecanoate. The three main stages of the study are proniosome capsule fabrication optimization, characterization, and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation. The most prominent response surface approach (CCD – Central Composite Design) was used in the fabrication-optimization phase to determine the appropriate ratios of the factors that have the greatest effects on the particle size, PDI, and percentage of drug entrapment of testosterone undecanoate proniosomes. Creating testosterone undecanoate-loaded proniosomal formulations was possible using various ratios of span 60 and cholesterol. The physical and chemical characteristics of proniosome capsules, such as size, shape, surface charge, and drug-release kinetics, such as percentage drug entrapment, Vesicle size (nm), and PDI, must be thoroughly analyzed. Animal models were used to determine how the proniosome capsules affect the bioavailability of testosterone undecanoate after oral administration. Factors like absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion are carefully evaluated to determine whether the capsules successfully enhance drug delivery. The reduced particle size, polydispersity index (PDI, 282.33 ± 1.52 nm and 0.181 ± 0.003), and the highest entrapment efficiency (98.12 ± 1.03%) made the optimized formulation the ideal formulation. The Higuchi model provided the most comprehensive justification for releasing the testosterone undecanoate from proniosome compositions. Up to six months of storage, no changes of any type, even those to the proniosomes' color, were seen. There was no drug leakage during the stability study, according to the percentage of drug entrapment data. Positive findings from the in vivo pharmacokinetic investigation also suggested that testosterone undecanoate proniosome formulations may last significantly longer than a pure drug in vivo.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Saxena, A.; Apurvi, P.; Aslam, R. A Review on Proniosomes: A Propitious Outlook to the Provesicular Drug Delivery System. Current drug delivery. 2023, 20(8), 1115-1126. 10.2174/1567201820666221019093921. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201820666221019093921
Mittal, S.; Chaudhary, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Kumar, A. Proniosomes: the effective and efficient drug-carrier system. Therapeutic delivery. 2020, 11 (2), 125-137. 10.4155/tde-2019-0065. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde-2019-0065
Sabale, V.; Charde, M.; Dumore, N.; Mahajan, U. Recent Developments in Proniosomal Transdermal Drug Delivery: An Overview. Current drug delivery. 2023, 20(6), 683-693. 10.2174/1567201819666220422153059. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201819666220422153059
Adki, K. M.; Kulkarni, Y. A. Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology and recent novel drug delivery systems of paeonol. Life sciences. 2020, 250, 117544. 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117544
Limongi, T.; Susa, F.; Marini, M.; Allione, M.; Torre, B.; Pisano, R.; di Fabrizio, E. Lipid-Based Nanovesicular Drug Delivery Systems. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland). 2021, 11(12). 10.3390/nano11123391. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123391
Zhu, Y.; Cao, S.; Huo, M.; van Hest, J. C. M.; Che, H. Recent advances in permeable polymersomes: fabrication, responsiveness, and applications. Chemical science. 2023, 14(27), 7411-7437. 10.1039/d3sc01707a. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01707A
Abildgaard, J.; Petersen, J. H.; Bang, A. K.; Aksglaede, L.; Christiansen, P.; Juul, A.; Jørgensen, N. Long-term testosterone undecanoate treatment in the elderly testosterone deficient male: An observational cohort study. Andrology. 2022, 10(2), 322-332. 10.1111/andr.13124. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.13124
An, J.; Kong, H. Comparative application of testosterone undecanoate and/or testosterone propionate in induction of benign prostatic hyperplasia in Wistar rats. PloS one. 2022, 17(5), e0268695. 10.1371/journal.pone.0268695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268695
Chillarón, J. J.; Fernández-Miró, M.; Albareda, M.; Fontserè, S.; Colom, C.; Vila, L.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Flores Le-Roux, J. A. Testosterone undecanoate improves lipid profile in patients with type 1 diabetes and hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism. Endocrine journal. 2016, 63(9), 849-855. 10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0195. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0195
Nieschlag, E.; Nieschlag, S. Testosterone deficiency: a historical perspective. Asian journal of andrology. 2014, 16(2), 161-8. 10.4103/1008-682x.122358. https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682X.122358
Saenger, P.; Steiner, M. Oral testosterone undecanoate is an effective treatment for micropenis therapy. Pediatric investigation. 2021, 5(4), 323-324. 10.1002/ped4.12304. https://doi.org/10.1002/ped4.12304
Miller, J. A.; Nguyen, T. T.; Loeb, C.; Khera, M.; Yafi, F. A. Oral testosterone therapy: past, present, and future. Sexual medicine reviews. 2023, 11(2), 124-138. 10.1093/sxmrev/qead003. https://doi.org/10.1093/sxmrev/qead003
Swerdloff, R. S.; Dudley, R. E. A new oral testosterone undecanoate therapy comes of age for the treatment of hypogonadal men. Therapeutic advances in urology. 2020, 12, 1756287220937232. 10.1177/1756287220937232. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287220937232
Schlich, M.; Lai, F.; Maria Fadda, A.; Sinico, C.; Pini, E. Drug-Excipients Compatibility Studies in Proniosomal Formulation: A Case Study with Resveratrol. Journal of nanoscience and nanotechnology. 2021, 21(5), 2917-2921. 10.1166/jnn.2021.19056. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2021.19056
Pankaj, S.; Rini, T.; Dandagi, P. Formulation and Evaluation of Proniosome Based Drug Delivery System of the Antifungal Drug Clotrimazole. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology. 2013, 6, 1945-1951. 10.37285/ijpsn.2013.6.1.4. https://doi.org/10.37285/ijpsn.2013.6.1.4
Radha, G. V.; Rani, T. S.; Sarvani, B. A review on proniosomal drug delivery system for targeted drug action. Journal of basic and clinical pharmacy. 2013, 4(2), 42-8. 10.4103/0976-0105.113609. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-0105.113609
Sudhamani, T.; Ganesan, V.; Priyadarsini, N.; Radhakrishnan, M. In FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF IBUPROFEN LOADED MALTODEXTRIN BASED PRONIOSOME, 2010.
Cheriyan, P.; George, B. J.; Thomas, N.; Raj, P.; Samuel, J.; Carla, S. B. Formulation and characterization of maltodextrin based proniosomes of cephalosporins. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015, 62-74.
Hsieh, C. M.; Yang, T. L.; Putri, A. D.; Chen, C. T. Application of Design of Experiments in the Development of Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland). 2023, 16(2). 10.3390/ph16020283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020283
Rampado, R.; Peer, D. Design of experiments in the optimization of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2023, 358, 398-419. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.05.001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.05.001
Mukerjee, A.; Vishwanatha, J. K. Formulation, characterization and evaluation of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanospheres for cancer therapy. Anticancer research. 2009, 29(10), 3867-3875.
Maji, R.; Dey, N. S.; Satapathy, B. S.; Mukherjee, B.; Mondal, S. Preparation and characterization of Tamoxifen citrate loaded nanoparticles for breast cancer therapy. International journal of nanomedicine. 2014, 9, 3107. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S63535
Cetin, M.; Atila, A.; Kadioglu, Y. Formulation and in vitro characterization of Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® L100-PLGA nanoparticles containing diclofenac sodium. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11(3), 1250-6. 10.1208/s12249-010-9489-6. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9489-6
Jain, S. K.; Awasthi, A. M.; Jain, N. K.; Agrawal, G. P. Calcium silicate based microspheres of repaglinide for gastroretentive floating drug delivery: preparation and in vitro characterization. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2005, 107(2), 300-9. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.06.007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.06.007
Averineni, R. K.; Shavi, G. V.; Gurram, A. K.; Deshpande, P. B.; Arumugam, K.; Maliyakkal, N.; Meka, S. R. J. B. o. M. S. PLGA 50: 50 nanoparticles of paclitaxel: development, in vitro anti-tumor activity in BT-549 cells and in vivo evaluation. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35(3), 319-326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-012-0313-7
Dora, C. P.; Singh, S. K.; Kumar, S.; Datusalia, A. K.; Deep, A. Development and characterization of nanoparticles of glibenclamide by solvent displacement method. Acta pol pharm. 2010, 67(3), 283-290.
Rasul, A.; Imran Khan, M.; Ur Rehman, M.; Abbas, G.; Aslam, N.; Ahmad, S.; Abbas, K.; Akhtar Shah, P.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed Al Subari, A. M.; Shaheer, T.; Shah, S. In vitro Characterization and Release Studies of Combined Nonionic Surfactant-Based Vesicles for the Prolonged Delivery of an Immunosuppressant Model Drug. International journal of nanomedicine. 2020, 15, 7937-7949. 10.2147/ijn.S268846. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S268846
Kumar, A.; Gulati, M.; Singh, S. K.; Gowthamarajan, K.; Prashar, R.; Mankotia, D.; Gupta, J. P.; Banerjee, M.; Sinha, S.; Awasthi, A.; Corrie, L.; Kumar, R.; Patni, P.; Kumar, B.; Pandey, N. K.; Sadotra, M.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Wadhwa, S.; Khursheed, R. Effect of co-administration of probiotics with guar gum, pectin and eudragit S100 based colon targeted mini tablets containing 5-Fluorouracil for site specific release. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2020, 60, 102004. 10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102004
Liu, H.; Tu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dang, Z.; Wang, L.; Du, J.; Feng, J.; Hu, K. Improved Bioavailability and Antitumor Effect of Docetaxel by TPGS Modified Proniosomes: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Scientific reports. 2017, 7, 43372. 10.1038/srep43372. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43372
Nasr, M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of proniosomes containing celecoxib for oral administration. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11(1), 85-9. 10.1208/s12249-009-9364-5. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9364-5