Study of Orbit Motion of Hydrogen and Deuterium Beam Ions Toward Neutral Beam Injection Experiment in Thailand Tokamak-1
Main Article Content
Abstract
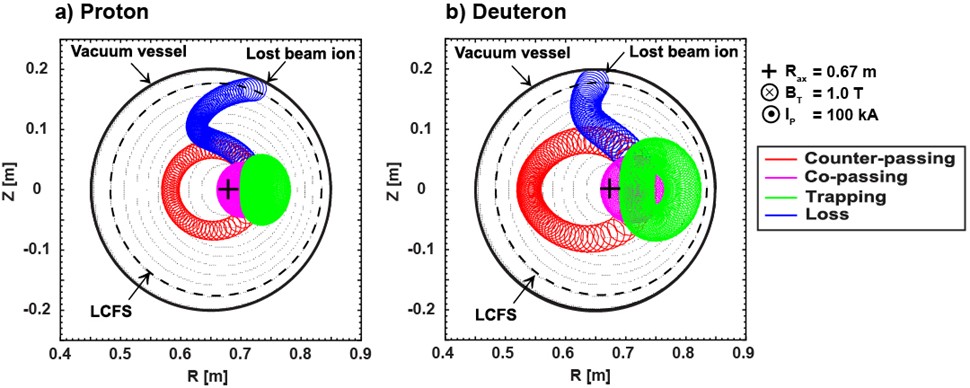
Thailand Tokamak-1 (TT-1) is a small tokamak under the operation of the Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology. In our future plans, TT-1 has the feasibility of being equipped with external heating systems to achieve high-performance plasma operation and conduct physics associated with fast ions generated by the external heating system. One of the potential external heating systems under consideration is a positive-ion-source-based neutral beam injection (NBI) heating system. The primary source of fast ions for the NBI can be either hydrogen or deuterium-doped hydrogen beams. This study examines how hydrogen and deuterium ions, namely protons and deuterons, respectively, move in orbits, using the Lorentz orbit (LORBIT) code to track their full gyromotion. The energy of the ions has been varied between 200 eV and 40 keV. Three trajectory motions have been characterized, i.e., counter-passing ion, co-passing ion, and trapped ion. The average Larmor radius, dependent on the ion energies, has been investigated. The Larmor radius significantly increases with increasing ion energy in the case of trapped ions, while in the case of counter- and co-passing ions, the Larmor radius exhibits a slight increase with increasing ion energy. Furthermore, the pitch angle range of the lost ion in the TT-1 has been investigated. The results demonstrate the feasibility of utilizing a deuterium-doped hydrogen beam in TT-1 to study fast ion physics. To avoid a large number of lost ions, it is possible to use a deuterium-doped hydrogen beam with an energy not exceeding approximately 10 keV in the TT-1.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Sergei Sharapov. Energetic Particles in Tokamak Plasmas. CRC Press. 2021.
Moseev, D.; Salewski, M.; Garcia-Munoz, M.; Geiger, B.; Nocente, M. Recent progress in fast-ion diagnostics for magnetically confined plasmas. Reviews of Modern Plasma Physics. 2018, 2(7), 1-68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-018-0019-4
Fasoli, A.; Gormenzano, C.; Berk, H. L.; Breizman, B.; Briguglio, S.; Darrow, D. S.; Gorelenkov, N.; Heidbrink, W.W.; Janu, A.; Konovalov, S.V.; Nazikian, R.; Noterdaeme, J.-M.; Sharapov, S.; Shinohara, K.; Testa, D.; Tobita, K.; Todo, Y.; Vlad, G.; Zonca, F. Chapter 5: Physics of energetic ions. 2007, 47(6), S264-S284. https://doi.org/10.1088/0029-5515/47/6/s05
Isobe, M.; Okamura, S.; Nagaoka, K.; Osakabe, M.; Toi, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Sasao, M.; Darrow, D.S. Fast-Ion-Diagnostics for CHS Experiment. Plasma and Fusion Research. 2007, 2, S1076. https://doi.org/10.1585/pfr.2.s1076
Isobe, M.; Sasao, M.; Okamura, S.; Osakabe, M.; Kubo. S.; Minami, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Takahashi, C.; CHS Group. Experimental Study of Fast Ion Confinement in CHS. J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES. 1998, 1. 366-369.
HT-6M TEAM. Engineering Aspects of The HT-6M Tokamak. Fusion Technology. 1986, 9(3), 476–480. https://doi.org/10.13182/fst86-a24733
Paenthong, W.; Wisitsorasak, A.; Sangaroon, S.; Promping, J.; Ogawa, K.; Isobe, M. Fast-ion orbit analysis in Thailand Tokamak-1. Fusion Engineering and Design. 2022, 183, 113254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2022.113254
Sangaroon, S.; Ogawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Wisitsorasak, A.; Paenthong, W.; Promping, J.; Poolyarat, N.; Tamman, A.; Ploykrachang, K.; Dangtip, S.; Onjun, T. Feasibility study of neutral beam injection in Thailand Tokamak-1. Fusion Engineering and Design. 2023, 188, 113419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2023.113419
Mitsutaka, I.; Dan, F.; Mamiko, S. Lorentz alpha orbit calculation in search of position suitable for escaping alpha particle diagnostics in ITER. J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES. 2009, 43(4). https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:43003775
Ogawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Nishitani, T.; Murakami, S.; Seki, R.; Nuga, H; Pu, N.; Osakabe, M.; LHD Experiment Group. Study of first orbit losses of 1 MeV tritons using the Lorentz orbit code in the LHD. Plasma Science & Technology. 2019, 21(2), 025102. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-6272/aaeba8
Ogawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Nuga, H.; Seki, R.; Ohdachi, S.; Osakabe, M. Evaluation of Alpha Particle Emission Rate Due to the p-11B Fusion Reaction in the Large Helical Device. Fusion Science and Technology. 2022, 78(3), 175–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/15361055.2021.1973294
Ogawa, K.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, R.; Li, K.; Isobe, M.; Hu, L. 1 MeV Triton Orbit Analysis in EAST Plasmas. Plasma and Fusion Research. 2020, 15, 2402022. https://doi.org/10.1585/pfr.15.2402022
Jun Young Kim; Rhee, T.; Kim, J.-H.; Yoon, S. W.; Park, B. H.; Isobe, M.; Ogawa, K.; Ko, W. H. Prompt loss of beam ions in KSTAR plasmas. AIP Advances. 2016, 6, 105013. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4966588
Ogawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Seki, R.; Nuga, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sangaroon, S.; Shimizu, A.; Okamura, S.; Takahashi, H.; Oishi, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Murase, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Tanoue, H.; Osakabe, M.; Liu, H. F.; Xu, Y. Feasibility study of fast ion loss diagnostics for CFQS by beam ion loss calculation on vacuum vessel. Journal of Instrumentation. 2021, 16(9), C09029. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/16/09/c09029
Ogawa, K.; Bozhenkov, S. A.; Äkäslompolo, S.; Killer, C.; Grulke, O.; Nicolai, D.; Satheeswaran, G.; Isobe, M.; Osakabe, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Wolf, R. C. Energy-and-pitch-angle-resolved escaping beam ion measurements by Faraday-cup-based fast-ion loss detector in Wendelstein 7-X. Journal of Instrumentation. 2019, 14(9), C09021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/14/09/c09021
Ogawa, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sangaroon, S.; Isobe, M.; Liu, Y. Predictive analysis for triton burnup ratio in HL-2A and HL-2M plasmas. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion. 2021, 63(4), 045013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6587/abe054
Dudson, B. (n.d.). Welcome to FreeGS’s documentation! — FreeGS 0.2.0 documentation. Freegs.readthedocs.io. Retrieved September 25, 2023, from https://freegs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
The MathWorks, Inc. (n.d.). Envelope Extraction - MATLAB & Simulink. www.mathworks.com. Retrieved September 25, 2023, from https://www.mathworks.com/help/signal/ug/envelope-extraction-using-the-analytic-signal.html