การสกัดและการกำหนดคุณลักษณะของไฟเบอร์-เซลลูโลสที่แยกได้จากใบปาล์มน้ำมันเพื่อใช้ในวัสดุการพิมพ์ 3 มิติและ 4 มิติ
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
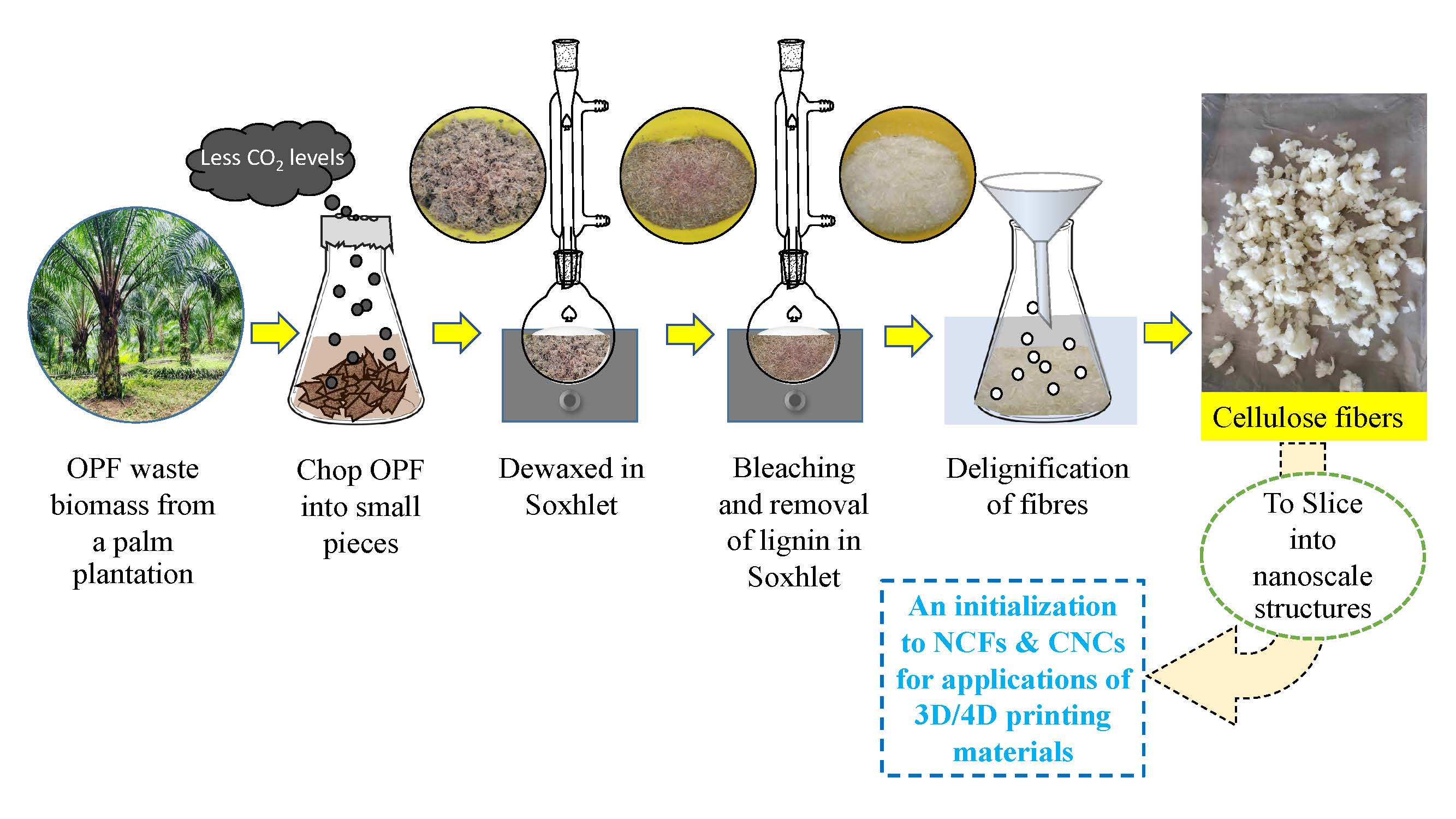
หนึ่งในชีวมวลปาล์มน้ำมันหลักที่ได้จากขยะทางการเกษตรคือใบปาล์มน้ำมัน (OPF) สามารถแปลงเป็นเส้นใยเซลลูโลสได้ เซลลูโลสสามารถสกัดได้จากวัสดุธรรมชาติซึ่งเป็นมิตรต่อสิ่งแวดล้อมอย่างยั่งยืน วัตถุประสงค์ของงานนี้คือการสกัดเส้นใยเซลลูโลสจากชีวมวล OPF OPF ถูกแบ่งออกเป็นส่วนใบและแกนทางปาล์ม โดยใช้วิธีการสกัดทางเคมีที่ง่ายและต้นทุนต่ำเพื่อประเมินประสิทธิภาพและผลผลิตของเส้นใยเซลลูโลส จากการศึกษาพบว่าเส้นใยเซลลูโลสที่สกัดได้จากส่วนแกนทางปาล์มและส่วนใบมีประสิทธิภาพเพียงพอที่จะใช้เป็นขั้นตอนเริ่มต้นในกระบวนการสกัดก่อนจะเข้าสู่ขั้นตอนการหั่นให้มีขนาดระดับนาโน อัตราการสกัดแสดงให้เห็นว่าอาจสกัดได้ 14.13% และ 19.52% ของส่วนใบและแกนทางปาล์ม 100 กรัมตามลำดับ ภาพ SEM แสดงให้เห็นการกระจายตัวเพียงพอของเส้นใยเซลลูโลส ผลลัพธ์ของ GCMS เผยให้เห็นปริมาณก๊าซคาร์บอนไดออกไซด์ในตัวอย่างส่วนใบปาล์มสูงกว่าตัวอย่างแกนทางปาล์มเล็กน้อยหลังจากแช่ตัวอย่างในน้ำเป็นเวลาห้าวัน อย่างไรก็ตาม มีการผลิตก๊าซคาร์บอนไดออกไซด์น้อยมากในทั้งสองตัวอย่าง ดังนั้น OPF จึงสามารถใช้เริ่มต้นสกัดเส้นใยเซลลูโลสได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพผ่านขั้นตอนของเรา และใช้เป็นวัสดุเริ่มต้นสำหรับการผลิตวัสดุนาโนเซลลูโลสในขั้นตอนต่อไป
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Roslan, A. M.; Zahari, M. A. K.; Hassan, M. A.; Shirai, Y. Investigation of Oil Palm Frond Properties for Use as Biomaterials and Biofuels. Trop. Agr. Develop. 2014, 58(1), 26–29. https://doi.org/10.11248/jsta.58.26
Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Yao, Q.; Ji, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Q. 3D printing with cellulose materials. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4275–4301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1888-y
Mehanny, S.; Magd, E. E. A-E.; Ibrahim, M.; Farag, M.; Gil-San-Millan, R.; Navarro, J.; Habbak, A. E. H. E.; El Kashif, E. Extraction and Characterization of Nanocellulose from three types of Palm Residues, JMR&T 2021, 10, 526-537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.027
Finny, A.S.; Popoola, O.; Andreescu, S. 3D-Printable Nanocellulose-Based Functional Materials: Fundamentals and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092358
Pal, A. K.; Mohanty, A. K.; Misra, M. Additive Manufacturing Technology of Polymeric Materials for Customized Products: Recent Developments and Future Prospective. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 36398 – 36438. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04060J
Guvendiren, M.; Molde, J.; Soares, R. M.D.; Kohn, J. Designing Biomaterials for 3D Printing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2(10), 1679-1693. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00121
Ahmed, A.; Arya, S.; Gupta, V.; Furukawa, H.; Khosla, A. 4D Printing: Fundamentals, Materials, Applications and Challenges. Polymer 2021, 228, 123926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123926
Kumar, S. B.; Jeevamalar, J.; Ramu, P.; Suresh, G.; Senthilnathan, K. Evaluation in 4D printing – A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 45, Part 2. 1433-1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.335
Alsaadi, M.; Hinchy, E.P.; McCarthy, C.T.; Moritz, V.F.; Zhuo, S.; Fuenmayor, E.; Devine, D.M. Liquid-Based 4D Printing of Shape Memory Nanocomposites: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7010035
Dizon, J.R.C.; Gache, C.C.L.; Cascolan, H.M.S.; Cancino, L.T.; Advincula, R.C. Post-Processing of 3D-Printed Polymers. Technologies 2021, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030061
Petousis, M.; Vidakis, N.; Mountakis, N.; Papadakis, V.; Kanellopoulou, S.; Gaganatsiou, A.; Stefanoudakis, N.; Kechagias, J. Multifunctional Material Extrusion 3D-Printed Antibacterial Polylactic Acid (PLA) with Binary Inclusions: The Effect of Cuprous Oxide and Cellulose Nanofibers. Fibers 2022, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib10060052
Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Ridzuan, R.; Kamarudin, H.; Khairul, A. Chemical Composition, Morphological Characteristics, and Cell Wall Structure of Malaysian Oil Palm Fibers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng 2008, 47, 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550701866840
Rosli, W.D.W.; Zainuddin, Z.; Law, K.N.; Asro, R. Pulp from Oil Palm Fronds by Chemical Processes. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2007, 25, 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2006.07.005
Chen, H.; 4 - Lignocellulose biorefinery conversion engineering. In Lignocellulose Biorefinery Engineering, Chen, H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Amsterdam. 2015, pp. 87-124.
Romruen O.; Karbowiak T.; Tongdeesoontorn W.; Shiekh K.A., Rawdkuen S. Extraction and Characterization of Cellulose from Agricultural By-Products of Chiang Rai Province, Thailand. Polymers 2022, 14(9), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091830
Izani, M.A.N.; Paridah, M.T.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Mohd Nor, M.Y.; H’ng, P.S. Effects of fiber treatment on morphology, tensile and thermogravimetric analysis of oil palm empty fruit bunches fibers. Compos. Part B 2013, 45, 1251–1257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.07.027