Predicting Dew Point Temperatures: A Machine Learning Approach with SHAP Explanations
Main Article Content
Abstract
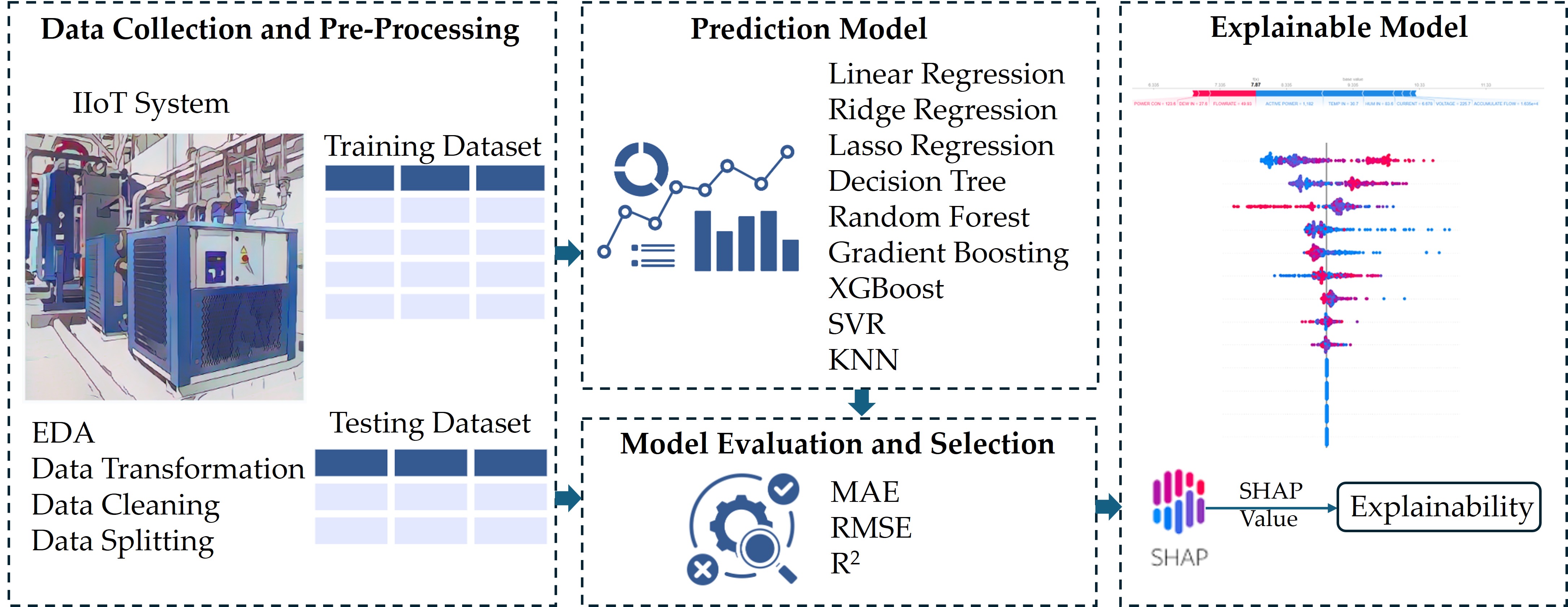
In industrial production, controlling the dew point temperature is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and product quality. This research aims to apply machine learning models to predict dew point temperatures and enhance model interpretability using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) to explain feature contributions. The data was collected from an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) system, and models evaluated include Linear Regression, Ridge Regression, Lasso Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost, Support Vector Regression (SVR), and k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN). The results indicated that the Random Forest model performed best, with the highest R² (0.94) and the lowest RMSE (0.82). Other well-performing models include Gradient Boosting, with an R² of 0.93 and an RMSE of 0.86, and XGBoost, with an R² of 0.93 and an RMSE of 0.87. For model interpretability, the real-time power consumption of the system ("ACTIVE POWER"), supply air temperature ("TEMP IN"), and supply air humidity ("HUM IN") were identified as important factors influencing the predictions. The SHAP analysis provided local and global insights into feature importance, enabling more informed decision-making in dew point control. These findings demonstrate the potential of integrating machine learning and explainable AI in industrial applications to advance operational strategies and safety measures.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Xu, H.; Yu, W.; Griffith, D.; Golmie, N. A Survey on Industrial Internet of Things: A Cyber-Physical Systems Perspective. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 78238-78259. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884906.
Tange, K.; Donno, M. D.; Fafoutis, X.; Dragoni, N. A Systematic Survey of Industrial Internet of Things Security: Requirements and Fog Computing Opportunities. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2020, 22(4), 2489-2520. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2020.3011208.
Yan, J.; Huang, J. Modeling Method Of Dew-Point Temperature Prediction In Industrial Workshop Based On Machine Learning. In 2021 IEEE 5th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), 22-24 Oct. 2021, 2021, 3160-3165. https://doi.org/10.1109/EI252483.2021.9713267.
The International Organization for Standardization. ISO 8573-1:2010(en) Compressed air — Part 1: Contaminants and purity classes. https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:8573:-1:ed-3:v1:en (accessed 8 December 2024).
Baghban, A.; Bahadori, M.; Rozyn, J.; Lee, M.; Abbas, A.; Bahadori, A.; Rahimali, A. Estimation of air dew point temperature using computational intelligence schemes. Applied Thermal Engineering 2016, 93, 1043-1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.10.056.
Mane, A.; Lekurwale, N.; Maidamwar, P.; Khobragade, P.; Dongre, S. Artificial Intelligence Based Heatwave Intensity Prediction Model. In 2023 International Conference on IoT, Communication and Automation Technology (ICICAT), 23-24 June 2023, 2023, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICAT57735.2023.10263728.
Mi, J. X.; Li, A. D.; Zhou, L. F. Review Study of Interpretation Methods for Future Interpretable Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191969-191985. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3032756.
Ersöz, B.; Ş, S.; Bülbül, H. İ. A Short Review on Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Renewable Energy and Resources. In 2022 11th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Application (ICRERA), 18-21 Sept. 2022, 2022, 247-252. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRERA55966.2022.9922870.
Cambria, E.; Malandri, L.; Mercorio, F.; Mezzanzanica, M.; Nobani, N. A survey on XAI and natural language explanations. Information Processing & Management 2023, 60(1), 103111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2022.103111.
Alenezi, R.; Ludwig, S. A. Explainability of Cybersecurity Threats Data Using SHAP. In 2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), 5-7 Dec. 2021, 2021, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI50451.2021.9659888.
İ, K.; Okay, F. Y.; Ö, M.; Özdemir, S. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) for Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10(16), 14764-14779. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3287678.
Machlev, R.; Heistrene, L.; Perl, M.; Levy, K. Y.; Belikov, J.; Mannor, S.; Levron, Y. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques for energy and power systems: Review, challenges and opportunities. Energy and AI 2022, 9, 100169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyai.2022.100169.
Hamilton, R. I.; Papadopoulos, P. N. Using SHAP Values and Machine Learning to Understand Trends in the Transient Stability Limit. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2024, 39(1), 1384-1397. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2023.3248941.
Javeed, D.; Gao, T.; Kumar, P.; Jolfaei, A. An Explainable and Resilient Intrusion Detection System for Industry 5.0. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2024, 70(1), 1342-1350. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2023.3283704.
Kumar, R.; Javeed, D.; Aljuhani, A.; Jolfaei, A.; Kumar, P.; Islam, A. K. M. N. Blockchain-Based Authentication and Explainable AI for Securing Consumer IoT Applications. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2024, 70(1), 1145-1154. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2023.3320157.
Sahlaoui, H.; Alaoui, E. A. A.; Nayyar, A.; Agoujil, S.; Jaber, M. M. Predicting and Interpreting Student Performance Using Ensemble Models and Shapley Additive Explanations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 152688-152703. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3124270.
Guryanov, A. Efficient Computation of SHAP Values for Piecewise-Linear Decision Trees. In 2021 International Conference on Information Technology and Nanotechnology (ITNT), 20-24 Sept. 2021, 2021, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITNT52450.2021.9649051.
Golizadeh Akhlaghi, Y.; Aslansefat, K.; Zhao, X.; Sadati, S.; Badiei, A.; Xiao, X.; Shittu, S.; Fan, Y.; Ma, X. Hourly performance forecast of a dew point cooler using explainable Artificial Intelligence and evolutionary optimisations by 2050. Applied Energy 2021, 281, 116062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116062.
Wani, N. A.; Bedi, J.; Kumar, R.; Khan, M. A.; Rida, I. Synergizing Fusion Modelling for Accurate Cardiac Prediction Through Explainable Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2024, 1-1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2024.3419814.
Doulani, K.; Rajput, A.; Hazra, A.; Adhikari, M.; Singh, A. K. Explainable AI for Communicable Disease Prediction and Sustainable Living: Implications for Consumer Electronics. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2024, 70 (1), 2460-2467. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2023.3325155.
Lu, J.; Jin, R.; Song, E.; Alrashoud, M.; Al-Mutib, K. N.; Al-Rakhami, M. S. An Explainable System for Diagnosis and Prognosis of COVID-19. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8(21), 15839-15846. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3037915.
Leonita, L.; Jeby, N. H.; Sevien; Ohyver, M. Predicting Cancer Death Rate and Determining the Major Cause of Cancer using Ridge Regression. Procedia Computer Science 2023, 227, 599-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.10.563.
Xiao, Y.; Huo, Y.; Cai, J.; Gong, Y.; Liang, W.; Kołodziej, J. ERF-XGB: An Edge-IoT-Based Explainable Model for Predictive Maintenance. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2024, 70 (1), 4016-4025. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2024.3371440.
Dombry, C.; Duchamps, J.-J. Infinitesimal gradient boosting. Stochastic Processes and their Applications 2024, 170, 104310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spa.2024.104310.
Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Gu, K. A support vector regression (SVR)-based method for dynamic load identification using heterogeneous responses under interval uncertainties. Applied Soft Computing 2021, 110, 107599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107599.
Sumayli, A. Development of advanced machine learning models for optimization of methyl ester biofuel production from papaya oil: Gaussian process regression (GPR), multilayer perceptron (MLP), and K-nearest neighbor (KNN) regression models. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2023, 16(7), 104833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104833.
Shawi, R. E.; Bahman, M.; Sakr, S. To tune or not to tune? An approach for recommending important hyperparameters for classification and clustering algorithms. Future Generation Computer Systems 2025, 163, 107524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2024.107524.
Tao, Y.; Yan, H.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Application of SVR optimized by Modified Simulated Annealing (MSA-SVR) air conditioning load prediction model. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2019, 15, 247-251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2018.04.003.