Trace Metal Contamination and Biomarker Responses in Fish from a Mining-Impacted River Basin in Cebu, Philippines
Main Article Content
Abstract
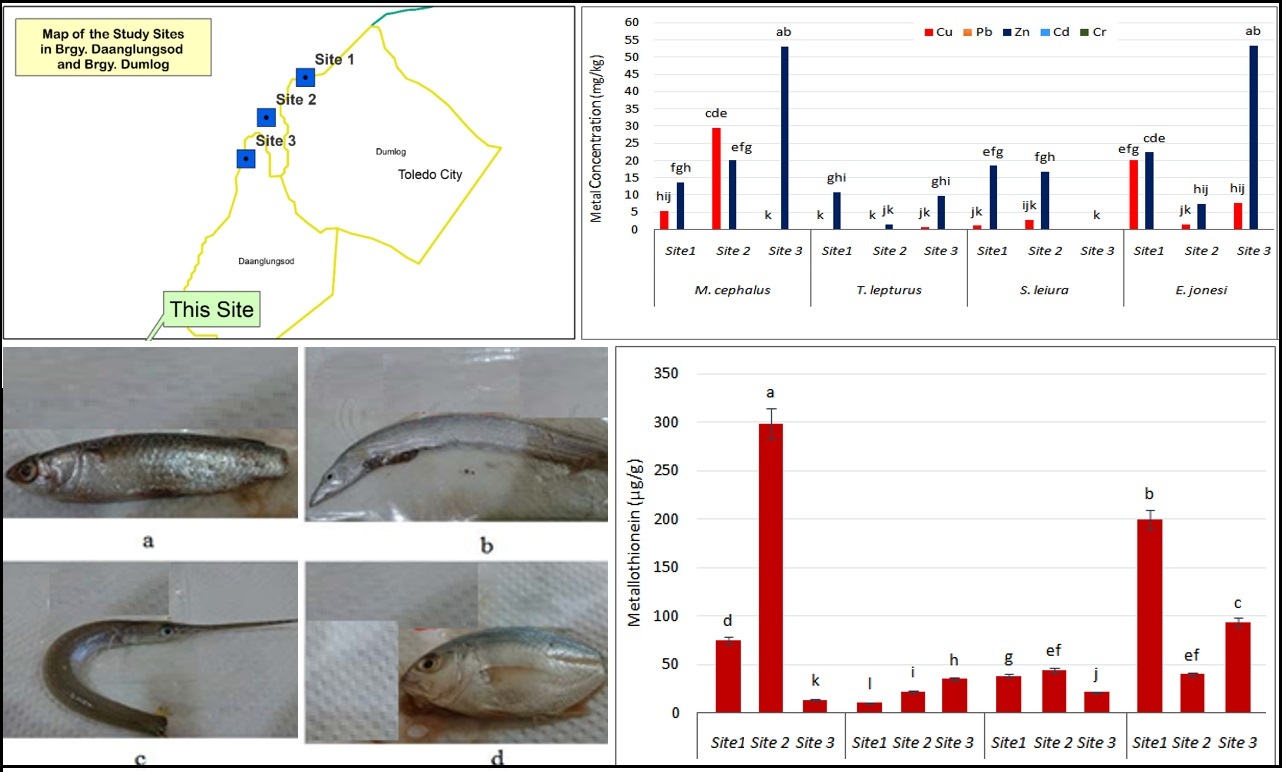
Mining activities in Toledo City, Cebu, have created extensive mined-out lands and left a legacy of metal contamination in surrounding aquatic systems. This study assessed trace metal concentrations and molecular biomarker responses in fish from the downstream section of the Sapangdaku River and adjacent Tañon Strait coastline. Pore water and sediments were analyzed for Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn using FAAS and ICP-MS, while biomarker assays measured metallothionein (MT) induction in liver tissues and genotoxicity through the assessment of micronuclei (MN) and nuclear abnormalities (NA) in erythrocytes. Results revealed that Cu was the dominant pollutant in pore water (mean 173 µg/L; peak 831 µg/L at Station 3), exceeding the U.S. EPA and Philippine DENR criteria by more than tenfold. Sediment indices (Igeo, CF, PLI) confirmed very high contamination from Cu, with Pb and Zn contributing moderately, while Cd and Cr remained near background levels. Fish analyses showed substantial bioaccumulation of Cu and Zn, particularly in benthic feeders (Mugil cephalus, Eubleekeria jonesi), which also exhibited the strongest biomarker responses. MT levels reached 299 µg/g in M. cephalus, while MN and NA frequencies were strongly correlated with Cu concentrations (R > 0.98, p < 0.05). NA were consistently more frequent than MN, suggesting their greater sensitivity as early markers of genotoxic stress. These results demonstrate that legacy mining continues to exert significant ecological stress on the Sapangdaku River system. The combined use of chemical analyses and biomarkers provides valuable baseline data, with MT, MN, and NA emerging as sensitive indicators of metal contamination and ecological risk.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Aggangan, N.; Pampolina, N.; Cadiz, N.; Raymundo, A. Assessment of Plant Diversity and Associated Mycorrhizal Fungi in the Mined-out Sites of Atlas Mines in Toledo City, Cebu for Bioremediation. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2015, 18(1), 71–86. https://doi.org/10.47125/jesam/2015_1/08
Lo, J. M.; Sakamoto, H. Heavy metals distribution in the surface sediments from central west coast of Cebu, Philippines. J. Sedimentol. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 62(62), 31–41. https://doi.org/10.4096/jssj1995.62.31
Sanchez, J. M. P.; Picardal, M.; Libres, M. T.; Pineda, H. A.; Paloma, M. L. B.; Librinca, J. M.; Raymund, R.; Ramayla, S. P.; Armada, R. L.; Picardal, J. P. Characterization of a river at risk: the case of Sapangdaku River in Toledo City, Cebu, Philippines. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2020, 7(6), 559–574. https://doi.org/10.3934/environsci.2020035
Wiklund, J. A.; Hall, R. I.; Wolfe, B. B.; Edwards, T. W.; Farwell, A. J.; George Dixon, D. Use of pre-industrial floodplain lake sediments to establish baseline river metal concentrations downstream of Alberta oil sands: a new approach for detecting pollution of rivers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9(12), 124019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/9/12/124019
Mohiuddin, K. M.; Zakir, H. M.; Otomo, K.; Sharmin, S.; Shikazono, N. Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an urban river. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 7(1), 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03326113
van Leeuwen, C. J.; Dan, N. P.; Dieperink, C. The Challenges of Water Governance in Ho Chi Minh City. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 12(2), 345–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1664
Ramayla, S.; Picardal, M.; Sanchez, J. M.; Librinca, J.; Pineda, H.; Libres, M.; Paloma, M. L.; Caturza, R. R.; Picardal, J. Phytoplankton Diversity and Macroinvertebrate Assemblage as Pollution Indicators in Sapangdaku River, Toledo City, Cebu, Philippines. Int. J. Biosci. 2021, 18 (4), 38–46.
Azcue, J. M.; Rosa, F.; Mudroch, A. Distribution of Major and Trace Elements in Sediments and Pore Water of Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22(2), 389–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0380-1330(96)70964-4
Kalnejais, L. H.; Martin, W. R.; Bothner, M. H. Porewater dynamics of silver, lead and copper in coastal sediments and implications for benthic metal fluxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 178–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.011
Sterckeman, T.; Douay, F.; Proix, N.; Fourrier, H. Vertical distribution of Cd, Pb and Zn in soils near smelters in the North of France. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107(3), 377–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(99)00165-7
Louriño-Cabana, B.; Lesven, L.; Charriau, A.; Billon, G.; Ouddane, B.; Boughriet, A. Potential risks of metal toxicity in contaminated sediments of Deûle river in Northern France. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186 (2-3), 2129–2137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.124
Liu, W. X.; Coveney, R. M.; Chen, J. L. Environmental quality assessment on a river system polluted by mining activities. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18(5), 749–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-2927(02)00155-5
Zhu, X.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Li, S.; Rong, N. Distributions, fluxes, and toxicities of heavy metals in sediment pore water from tributaries of the Ziya River system, northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 23(6), 5516–5526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5709-7
Islam, M. S.; Ahmed, M. K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah -Al- Mamun, M.; Islam, M. K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016
Bacolod, E. T.; Uno, S.; Tanaka, H.; Koyama, J. Micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities induction in erythrocytes of marbled flounder, Pleuronectes yokohamae, exposed to dietary nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Kankyou Dokusei Gakkaishi/Kankyō Dokusei Gakkaishi 2013, 16(2), 79–89. https://doi.org/10.11403/jset.16.79
Al-Sabti, K.; Metcalfe, C. D. Fish micronuclei for assessing genotoxicity in water. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1995, 343(2-3), 121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(95)90078-0
Fenech, M.; Chang, W. P.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Holland, N.; Bonassi, S.; Zeiger, E. HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2003, 534(1-2), 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5718(02)00249-8
Linde, A. R.; Garcia‐Vazquez, E. A simple assay to quantify metallothionein helps to learn about bioindicators and environmental health. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006, 34(5), 360–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmb.2006.494034052653
Pulatsü, S.; Topçu, A. Review of 15 Years of Research on Sediment Heavy Metal Contents and Sediment Nutrient Release in Inland Aquatic Ecosystems, Turkey. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 07(02), 85–100. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.72007
Geolin, K. R. C.; Villegas, L. M. G.; Alburo, R. P. Metallothionein Response of Aninikad, Canarium Labiatum (Roding, 1798) to Heavy Metal Concentrations in Balamban Coastline, Cebu. J. Agric. Technol. Manag. 2021, 24(1), 1–12.
Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wen, X.; Tang, H. The application of preliminary sediment quality criteria to metal contamination in the Le An River. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 105(3), 355–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(99)00041-x
Özşeker, K. Investigation of Sediment Pore Water Heavy Metal (Cu and Pb) Geochimistry in Deriner Dam Lake, Artvin, Turkey. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Eğirdir Su Ürünleri Fakültesi Dergisi 2019. https://doi.org/10.22392/egirdir.438914
Wulan, D. R.; Marganingrum, D.; Yoneda, M. Distribution, source identification, and assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface and pore waters of Cipeles River, West Java, Indonesia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27(31), 39123–39134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09823-9
Duman, F.; Kar, M. Temporal Variation of Metals in Water, Sediment and Tissues of the European Chup (Squalius cephalus L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89(2), 428–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0679-7
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Human Health Toxicity Values in Superfund Risk Assessments. 2015. https://www.epa.gov/risk/human-health-toxicity-values-superfund-risk-assessments (accessed 2025-09-27).
Mehdizadeh, Y.; Karbassi, A. R.; Nasrabadi, T.; Sarang, A. Behavior, toxicity and diffusive flux of metals in a sediment core and pore-water from Anzali wetland. Acta Geochim. 2022, 42(2), 309–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-022-00578-3
Gavriil, A. M.; Angelidis, M. O. Metal diagenesis in a shallow semi-enclosed marine system in the Aegean Sea, Greece. Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 2006, 70(3), 487–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2006.06.029
Müller, B.; Berg, M.; Yao, Z. P.; Zhang, X. F.; Wang, D.; Pfluger, A. How polluted is the Yangtze river? Water quality downstream from the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402(2), 232–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.04.049
Alburo, R. P.; Villegas, L. M. G. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Water and Sediment of Lahug River, Cebu, Philippines. ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Rep. 2025, 28(3), e257492. https://doi.org/10.55164/ajstr.v28i3.257492
Villacarlos, C. J. A.; Villegas, L. M. G.; Alburo, R. P. Metallothionein induction in bivalves exposed to heavy metals in sediment of the Balamban Coast, Cebu, Philippines. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2025, 14(2). https://doi.org/10.22034/ijab.v13i2.2425
Kalay, M.; Canli, M. Elimination of Essential (Cu, Zn) and Non-Essential (Cd, Pb) Metals from Tissues of a Freshwater Fish Tilapia zilli. TÜBİTAK Academic Journals 2022. https://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/zoology/vol24/iss4/11
Cañete, R. C.; Villegas, L. M. G.; Castañares, J. M. Seasonal Bioaccumulation of Copper in Guppy, Poecilia reticulata (Peters) with Characterization of the Hydrophobic Fraction of Its Octanol - Water Emulsion. KIMIKA 2014, 25(1), 27–37. https://doi.org/10.26534/kimika.v25i1.27-37
World Health Organization. Report on integrated risk assessment prepared for the WHO/UNEP/ILO International Programme on Chemical Safety. 2001. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-IPCS-IRA-01-12 (accessed 2021-11-9).
Food and Agriculture Organization. Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food additives. Geneva, World Health Organization. Report Series 922, 2000. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/trs/WHO_TRS_922.pdf (accessed 2022-01-12).
European Union. Commission Regulation as regards heavy metals, Directive, 2001/22/EC, No: 466, 2001. https://www.ecolex.org/details/legislation/commission-regulation-ec-no-4662001-setting-maximum-levels-for-certain-contaminants-in-foodstuffs-lex-faoc034471/ (accessed 2020-10-18).
Federal Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines and standards for environmental pollution control in Nigeria. 2003. https://leap.unep.org/en/countries/ng/national-legislation/interim-guidelines-and-standards-environmental-pollution-control (accessed 2020-10-18).
Dhanakumar, S.; Solaraj, G.; Mohanraj, R. Heavy metal partitioning in sediments and bioaccumulation in commercial fish species of three major reservoirs of river Cauvery delta region, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.032
Rajkowska, M.; Protasowicki, M. Distribution of metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu) in fish tissues in two lakes of different trophy in Northwestern Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185(4), 3493–3502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2805-8
Yap, C. K.; Edward, F. B.; Emila, R. A. A.; Ainey, F. I.; Ismail, A.; Tan, S. G.; Sharizat, Y. Determination of contamination and bioavailabilities of heavy metals (Cu, Cd, Zn, Pb and Ni) in the Serdang urban lake by using guppy fish Poecilia reticulata. Trends Appl. Sci. Res. 2008, 3, 69–75. https://doi.org/10.3923/tasr.2008.69.75
Carrasco, K. R.; Tilbury, K. L.; Myers, M. S. Assessment of the Piscine Micronucleus Test as an in situ Biological indicator of Chemical Contaminant Effects. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47 (11), 2123–2136. https://doi.org/10.1139/f90-237
Al-Sabti, K.; Metcalfe, C. D. Fish micronuclei for assessing genotoxicity in water. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1995, 343 (2-3), 121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(95)90078-0. [42] da Silva Souza, T.; Fontanetti, C. S. Micronucleus test and observation of nuclear alterations in erythrocytes of Nile tilapia exposed to waters affected by refinery effluent. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2006, 605(1-2), 87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.02.010
Pandey, A. K.; Nagpure, N. S.; Trivedi, S. P. Evaluation of genotoxicity of profenofos to freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch) using the micronucleus assay. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13(39), 3985–3988. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajb2014.14095
Stankevičiūtė, M.; Butrimavičienė, L.; Valskienė, R.; Greiciūnaitė, J.; Baršienė, J.; Vosylienė, M. Z.; Svecevičius, G. Analysis of nuclear abnormalities in erythrocytes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) treated with Cu and Zn and after 4-, 8-, and 12-day depuration (post-treatment recovery). Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 797, 26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.01.003
Ferrante, M.; Pappalardo, A. M.; Ferrito, V.; Pulvirenti, V.; Fruciano, C.; Grasso, A.; Sciacca, S.; Tigano, C.; Copat, C. Bioaccumulation of metals and biomarkers of environmental stress in Parablennius sanguinolentus (Pallas, 1814) sampled along the Italian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122(1-2), 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.060
Mazon, A. F.; Cerqueira, C. C. C.; Fernandes, M. N. Gill Cellular Changes Induced by Copper Exposure in the South American Tropical Freshwater Fish Prochilodus scrofa. Environ. Res. 2002, 88(1), 52–63. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.2001.4315.