Study of Spent Coffee Grounds Using Cytological Technique on Root Tip of Allium cepa
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
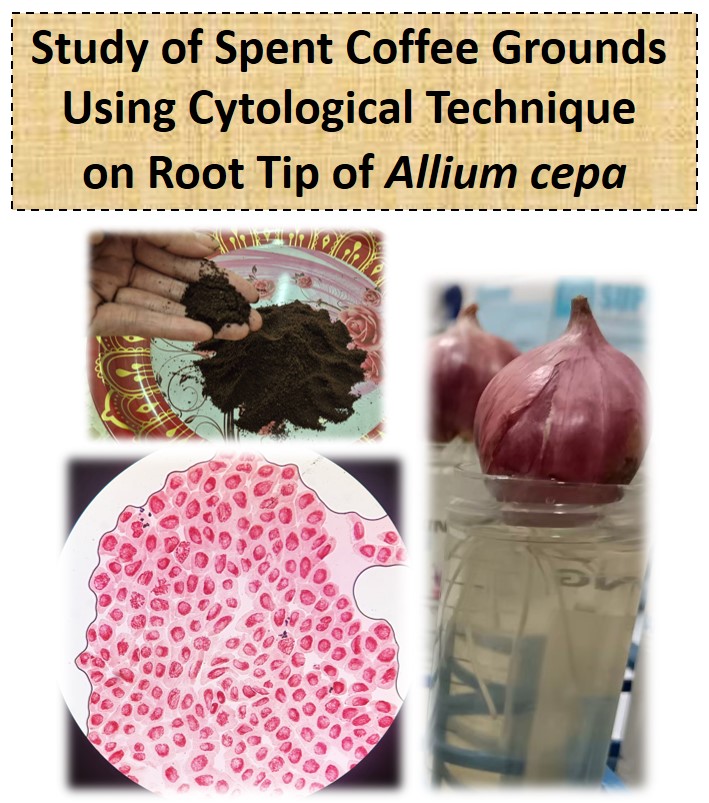
Coffee is a widely consumed beverage that has a major impact on economies, markets, and industries; however, the postproduction of coffee drinks results in wasted or spent coffee grounds (SCG). SCG is used as a plant growth medium; however, its suitable level of use is uncertain. This research determined the optimal amount of SCG for root development and its effect on the cells of Allium cepa. The SCG was mixed with sand (S) in different ratios (SCG:S = 40:60, 50:50, 60:40, 70:30, 80:20, 90:10) to evaluate their effects on root growth and cytotoxicity on cells. Root number and length were measured to assess growth, while the mitotic index (MI) and chromosomal abnormalities were analyzed to determine cytotoxic effects. The 40:60 SCG:S mixture produced the highest root growth compared to controls, whereas higher SCG ratios (70:30, 80:20, 90:10) reduced the MI. Various chromosomal abnormalities were observed, such as micronuclei, c-mitosis, fragmented chromosomes, chromosome bridges, sticky chromosomes, and laggard chromosomes. Therefore, the chemical compounds in SCG affected cytotoxicity on A. cepa roots. The most beneficial use of SCG for addition to plant growth media resulted from a precisely defined mixture to balance growth enhancement with potential cytotoxic risk.
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Clifford, MN; Williams, T.; Bridson, D. Chlorogenic acids and caffeine as possible taxonomic criteria in Coffea and Psilanthus. Phytochemistry. 1989, 28, 829–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(89)80124-4
Davis, A.P.; Govaerts, R.; Bridson, D.M.; Stoffelen, P. An annotated taxonomic conspectus of the genus Coffea (Rubiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 152, 465–512. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2006.00584.x
Esquivel, P.; Jiménez, V.M. Functional properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.05.028
de Melo Pereira, G.V.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.; Júnior, A.I.M.; do Prado, F.G.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; Karp, S.G.; Soccol, C.R. Chemical composition and health properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. 2020, 91, 65–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.10.002
Murthy, P.S.; Naidu, M.M. Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—A review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 2012, 66, 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.06.005
Mussatto, S.I.; Carneiro, L.M.; Silva, J.P.A.; Roberto, I.C.; Teixeira, J.A. A study on chemical constituents and sugars extraction from spent coffee grounds. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 83, 368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.07.063
Colantoni, A.; Paris, E.; Bianchini, L.; Ferri, S.; Marcantonio, V.; Carnevale, M.; Palma, A.; Civitarese, V.; Gallucci, F. Spent coffee ground characterization, pelletization test and emissions assessment in the combustion process. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, Article 5119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84772-y
Santos, C.; Fonseca, J.; Aires, A.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H. Effect of different rates of spent coffee grounds (SCG) on composting process, gaseous emissions and quality of end-product. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.020
dos Santos, É.M.; de Macedo, L.M.; Tundisi, L.L.; Ataide, J.A.; Camargo, G.A.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mazzola, P.G. Coffee by-products in topical formulations: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 111, 208–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.064
Ramalakshmi, K.; Rao, L.J.M.; Takano-Ishikawa, Y.; Goto, M. Bioactivities of low-grade green coffee and spent coffee in different in vitro model systems. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.063
Bravo, J.; Juániz, I.; Monente, C.; Caemmerer, B.; Kroh, L.W.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Evaluation of spent coffee obtained from the most common coffeemakers as a source of hydrophilic bioactive compounds. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12565–12573. https://doi.org /10.1021/jf3040594
Hechmi, S.; Guizani, M.; Kallel, A.; Zoghlami1, R.I.; Zrig, E.B.; Louati, Z.; Jedidi, N.; Trabelsi, I. Impact of raw and pre‑treated spent coffee grounds on soil properties and plant growth: a mini‑review. Clean Technol. Envi. 2023, 25, 2831–2843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02544-w
Hardgrove, S.J.; Livesley, S.J. Applying spent coffee grounds directly to urban agriculture soils greatly reduces plant growth. Urban For. Urban Gree. 2016, 18, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2016.02.015
Cruz, R.; Cardoso, M.M.; Fernandes, L.; Oliveira, M.; Mendes, E.; Baptista, P.; Morais, S.; Casal, S. Espresso coffee residues: a valuable source of unextracted compounds. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7777–7784. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf3018854
Kim, M-.S.; Min, H-.G.; Koo, N.; Park, J.; Lee, S-.H.; Bak, G-.I.; Kim, J-.G. The effectiveness of spent coffee grounds and its biochar on the amelioration of heavy metals-contaminated water and soil using chemical and biological assessments. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.07.001
Ribeiro, J.P.; Vicente, E.D.; Gomes, A.P.; Nunes, M.I.; Alves, C.; Tarelho, L.A. Effect of industrial and domestic ash from biomass combustion, and spent coffee grounds, on soil fertility and plant growth: experiments at field conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2017, 24, 15270–15277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9134-y
Nicuță, D.; Grosu, L.; Patriciu, O.-I.; Voicu, R.-E.; Alexa, I.-C. The Allium cepa model: a review of its application as a cytogenetic tool for evaluating the biosafety potential of plant extracts. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, Article 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040088
Kourmentza, C.; Economou, C.N.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Kornaros, M. Spent coffee grounds make much more than waste: exploring recent advances and future exploitation strategies for the valorization of an emerging food waste stream. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 980–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.088
Page, J.C.; Arruda, N.P.; Freitas, S.P. Crude ethanolic extract from spent coffee grounds: Volatile and functional properties. Waste Manage. 2017, 69, 463–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.043
González-Moreno, M.; García, G.B.; Marcelino, S.S.; Zaratiegui, U.J.; Robles, D.E.; Ezcurdia, P.; Seco, M.A. Feasibility of vermicomposting of spent coffee grounds and Silverskin from coffee industries: a laboratory study. Agronomy. 2020, 10, Article 1125. 10.3390/agronomy10081125
Caliskan, S.; Ozok, N.; Makineci, E. Utilization of spent coffee grounds as media for stone pine (Pinus pinea) seedling. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2020, 20, 2014–2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00271-5
Dafouz, R.; Caceres, N.; Rodriguez-Gil, J.L.; Mastroianni, N.; de Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D.; de Miguel, Á.G.; Valcarcel, Y. Does the presence of caffeine in the marine environment represent an environmental risk? A regional and global study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.155
Campos-Vega, R.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Vergara-Castañeda, H.A.; Oomah, B.D. Spent coffee grounds: A review on current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2015, 45, 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.04.012
Cervera-Mata, A.; Navarro-Alarcon, M.; Rufán-Henares, J.Á.; Pastoriza, S.; Montilla-Gómez, J.; Delgado, G. Phytotoxicity and chelating capacity of spent coffee grounds: two contrasting faces in its use as soil organic amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, Article 137247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137247
Kim, H.J.; Cho, S.; Jacobs, D.R.J.; Park, K. Instant coffee consumption may be associated with higher risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2014, 106, 145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.07.007
de Souza, L.Z.M.; Pinto, B.C.; Alves, A.B.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, A.V.; Feliciano, D.C.T.; da Silva, L.H.; Dias, T.T.M.; Yılmaz, M.; de Oliveira, M.A.; da Silva Bezerra, A.C.; Ferreira, O.E.; de Lima, R.P.; do Santos Pimenta, L.P.; Machado, A.R.T. Ecotoxicological effects of biochar obtained from spent coffee grounds. Materials Research. 2022, 25, Article e20220013. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2022-0013
Khan, I.S.; Ali, M.N.; Hamid, R.; Ganie, S.A. Genotoxic effect of two commonly used food dyes metanil yellow and carmoisine using Allium cepa L. as indicator. Toxicology Reports. 2020, 7, 370–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.02.009
Thanasoponkul, W.; Changbunjong, T.; Sukkurd, R.; Saiwichai, T. Spent coffee grounds and novaluron are toxic to Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Insects. 2023, 14, Article 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14060564
Wani, K.I.; Naeem, M.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; Kalaji, H.M.; Albaqami, M.; Aftab, T. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide (NO) signaling and reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis during abiotic stresses in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, Article 9656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179656
da Rosa, S.D.V.F.; de Oliveira Vilela, A.L.; Alves, M.V.P.; Cardoso, M.D.G.; Vieira, L.F.A.; Ferreira, A.M.O.; da Silva, L.M. Allelopathic activity of coffee extracts: implications for germination and initial growth in select weeds and polyploidy in Lactuca sativa L. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A . 2024, 88, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2024.2434952
Chandraker, S.K.; Singh, P.; Pandey, B. Clastogenic effect of soft drink on root tip of Allium cepa. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences. 2018, 3, 200–206. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326381584