Optimization Conditions for Ethanol Production from Spent Coffee Ground by Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Keywords:
Spent coffee ground, Ethanol, Lignocellulose, Saccharomyces cerevisiaeAbstract
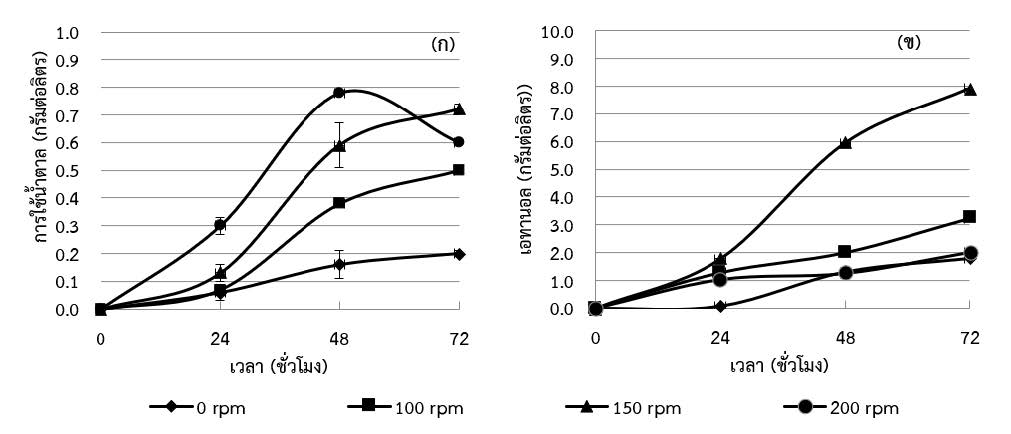
Spent coffee ground (SCG) is the solid residue obtained during the treatment of coffee powder with hot water or steam. SGC is the main waste generated during the instant coffee preparation. SCG are usually disposed as common garbage, without specific reuse strategies implemented so far. Therefore, the objectives of this research are study the pretreatment method of spent coffee ground and optimization for ethanol production. The composition of spent coffee ground consists of cellulose 41.78±4.66 % w/w, hemicellulose 28.02±3.38 % w/w, lignin 29.01±0.92 % w/w and ash 1.10±0.01 % w/w. The fiber was pretreated by heat-chemical and hydrolyzed by 13 unit cellulase enzyme. The results showed 1 % (v/v) H2SO4 for 30 min at 90 °C and hydrolyzed by cellulase was the most suitable method for pretreat which gave 3.564±0.234 g/L reducing sugar. After that the pretreated spent coffee ground was used as substrate for ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The optimum conditions; ammonium phosphate was nitrogen source, optimum temperature at 28 °C, and 150 rpm of shaking speed for 72 h that gave the highest ethanol production, substrate consumption rate and ethanol yield were 7.92±0.02 g/L, 0.01±0.001 g/L/h and 0.11±0.001 g/L/h, respectively. Therefore, spent coffee ground (SCG) can be utilized in the production of ethanol as an alternative energy source in the future.
References
กนกรัตน์ ใสสอาด, เบญจมาศ หนูแป้น และกิตติมา คงทน. (2560). การผลิตเอทานอลจากเส้นใยเปลือกผลจากโดย Saccharomyces cerevisiae. รายงานวิจัย สาขาวิชาชีววิทยา คณะวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสุราษฎร์ธานี.
นันทิกา คล้ายชม, เพ็ญจิตร ศรีนพคุณ และอนุสิษฐ์ ธนะพิมพ์เมธา. (2554). การผลิตน้ำตาลรีดิวซ์จากซังข้างฟางหวานโดยกระบวนการไฮโดรไลซิสด้วยกรด. วิศวกรรมสาร มก. 24(75):น. 91-102.
รพีพรรณ กองตูม. (2560). กากกาแฟ: มูลค่าเพิ่มและการใช้ประโยชน์. ในการประชุมวิชาการระดับชาติ ราชภัฏหมู่บ้านจอมบึงวิจัย ครั้งที่ 5 (น. 362). ราชบุรี.
วนิดา ปานอุทัย, นิคม แหลมสัก, สาโรจน์ ศิริศันสนียกุล, วิรัตน์ วาณิชย์ศรีรัตร และประมุข ภระกูลสุขสถิตย์. (2553). การผลิตเอทานอลจากไม้ยูคาลิปตัสโดยกระบวนการย่อยเป็นน้ำตาลและหมักพร้อมกัน. ในการประชุมทางวิชาการของมหาวิทยาลัยเกษตรศาสตร์ ครั้งที่ 48 (น. 392). กรุงเทพ: สาขาอุตสาหกรรมเกษตร.
สาวิตรี ลิ่มทอง. (2549). ยีสต์: ความหลากหลายทางเทคโนโลยีชีวภาพ. กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยเกษตรศาสตร์.
Arrizon, J. and Gschaedler. A. (2002). Increasing fermentation efficiency at high sugar concentrations by supplementing an additional source of nitrogen during the exponential phase of the tequila fermentation process. Canadian Journal Microbiology, 48(11), pp. 965-970.
Association of official analytical chemists. (1999). Official methods of analysis. The Association, D.C. Washington.
Ballesteros, L.F., Teixeira, J.A. and Mussatto, S.I. (2014). Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Silverskin. Food Bioprocess Technology, 7, pp. 3493–3503.
Banat, I.M., Nigam, P., Singh, D., Marchant, R. and McHale, A.P. (1998). Review: Ethanol production at elevated temperatures and alcohol concentrations: Part I: Yeasts in general. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, pp. 809-821.
Battista, F., Barampouti, E.M., Mai, S., Bolzonella, D., Malamis, D., Moustakas, K. and Loizidou, M. (2020). Added-value molecules recovery and biofuels production from spent coffee grounds. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 131, 110007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110007
Bomfim, A.S.C., Oliveira, D.M., Walling, E., Babin, A., Hersant, G., Vaneeckhaute, C., Dumont, M.J. and Rodrigue, D. (2023). Spent Coffee Grounds Characterization and Reuse in Composting and Soil Amendment. Waste, 1, pp. 2-20. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1010002.
Boudrahem, F., Soualah, A. and Aissani-Benissad, F. (2011). Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from aqueous solutions using activated carbon developed from coffee residue activated with phosphoric acid and zinc chloride. Journal of Chemical & Engineeing Data, 56(5), pp. 1946-1955.
Chhandama, M.V.L., Satyan, K.B., Changmai, B., Vanlalveni, C. and Rokhum, S.L. (2021). Microalgae as a feedstock for the production of biodiesel: a review. Bioresource Technology Report, 15, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100771.
Jutakanoke, R., Leepipatpiboon, N., Tolieng, V., Kitpreechavanich, V., Srinorakutara, T. and Akaracharanya, A. (2012). Sugarcane leaves: Pretreatment and ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biomass and Bioenergy, 39, pp. 283-289.
Khenniche, L. and Benissad-Aissani, F. (2010). Adsorptive removal of phenol by coffee residue activated carbon and commercial activated carbon: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 55(11), pp. 4677-4686.
Kittiratmai, P. (2003). Improvement of ethanol fermentation efficiency by flocculent yeast and repeated fedbatch. (Masters thesis, Kasetsart University, Thailand.)
Kovalcik, A., Obruca, S. and Marova, I. (2018). Valorization of spent coffee grounds: A review. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 110, pp. 104–119.
Kwon, E.E., Yi, H., and Jeon, Y.J. (2013). Sequential co-production of biodiesel and bioethanol with spent coffee grounds. Bioresource Technology, 136, pp. 475–480.
Lucero, P., Penalver, E., Moreno, E. and Lagunas, R. (2000). Internal trehalose protects endocytosis from inhibition by ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 66(10), pp. 4456-4461.
Manivannan, A., Jayarani, P.H. and Narendhirakannan, R.T. (2012). Enhanced acid hydrolysis for bioethanol production from water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) using fermenting yeast Candida intermedia NRRL Y-981. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 71(1), pp. 51-56.
Mas, A., Torija, M.J., Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. and Troncoso A. (2014). Acetic acid bacteria and the production and quality of wine vinegar. The Science World Journal, 39, pp. 46-57.
Mussatto, S.I., Carneiro, L.M., Silva, J.P.A., Roberto, I.C. and Teixeira, J.A. (2011). A study on chemical constituents and sugars extraction from spent coffee grounds. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2), pp. 368-374.
Nuanpeng, S., Thanonkeo, S., Yamada, M. and Thanonkeo, P. (2016). Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice at high temperature using a newly isolated thermotolerant yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae DBKKU Y-53. Energies, 9, pp. 253.
Sun, Y. and Cheng, J. (2002). Hydrolysis of linocellulosic material for ethanol production: a review. Bioresource Technology, 83(1), pp. 1-11.
Torija, M.J., Beltran, G., Novo, M., Poblet, M., Guillamon, J.M., Mas, A. and Rozes, N. (2003). Effects of fermentation temperature nd Saccharomyces species on the cell fatty acid composition and presence of volatile compounds in wine. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 85, pp. 127-136.
Torija, M.J., Beltran, G., Novo, M., Poblet, M., Rozes, N., Mas, A. and Guillamoan J.M. (2003). Effect of organic acids and nitrogen source on alcoholic fermentation: Study of their buffering capacity. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(4), pp. 916-922.
Wong, Y.Y., Rawindran, H., Lim, J. W., Tiong, Z. W., Liew, C. S., Lam, M. K., Kiatkittipong, W., Abdelfattah, E. A., Oh, W. D. and Ho, Y. C. (2022). Attached microalgae converting spent coffee ground into lipid for biodiesel production and sequestering atmospheric CO2 simultaneously. Algal Research, 66, http://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2022.102780.
Zhang, J., Zhou, H., Liu, D. and Zhao, X. (2020). Chapter 2 – Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient enzymatic saccharification of cellulose. in book Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels (pp. 17-65). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-03529-2.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH JOURNAL NAKHON RATCHASIMA RAJABHAT UNIVERSITY

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิจัย วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครราชสีมา ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิจัย วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครราชสีมา ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิจัย วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครราชสีมา หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใด ๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากวารสารวิจัย วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครราชสีมา ก่อนเท่านั้น


